Part 20 - I used to do it this way… Now how do I do it? Administering Exchange 2003 vs. Exchange 2007
To return to part 1 click here
Transport
Outbound SMTP connections to other messaging servers
In Exchange 2003, the routing group represented a communication boundary between Exchange servers that were part of the same organization. All Exchange servers that were in the same routing group were able to communicate directly with each other.
To create connections to the Internet you created a SMTP connector.
In Exchange 2007, Send Connectors control outbound SMTP traffic to remote domains. By default, a Send Connector is available to the entire organization. However, a Send Connector can be scoped so that it is available only to other Hub Transport servers in its local Active Directory site. For more information see Send Connectors.
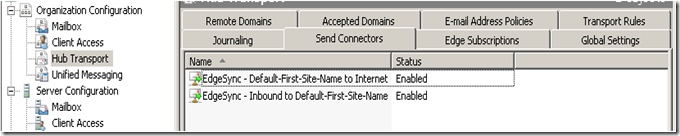
When the Edge Subscription is created you will see the following:
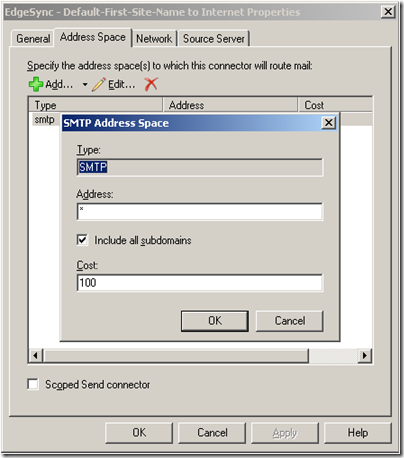
As you can see, with the EdgeSync set up the properties allow all mail to flow out the new Send Connector.
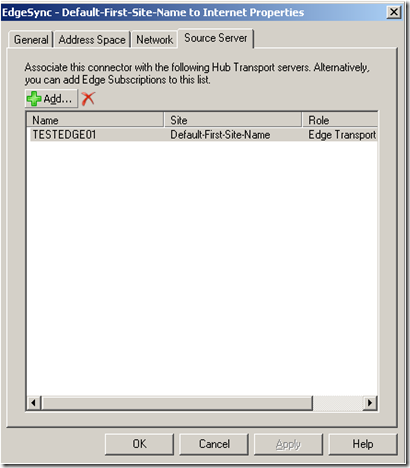
And the source sever is the Edge server.
Journaling
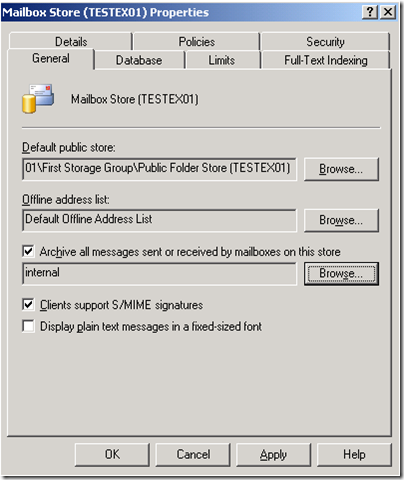
In Exchange 2003, you configured journaling on the mailbox store that contained the mailboxes that you wanted to journal.
In Exchange 2007, if you have an Exchange Enterprise Client Access License for the mailboxes you want to journal then you can use journal rules that are configured organization wide on Hub Transport servers. The journal rules enable you to specify per-recipient journaling. For more information see: Managing Journal Rules.
The following types of journaling are available in Exchange 2007:
Standard journaling - Standard journaling enables the Journaling agent in Exchange 2007 to journal all messages sent to and from recipients and senders that are located on a specific mailbox database on a computer running the Mailbox server role. Standard journaling is also called per-mailbox database journaling.
Premium journaling - Premium journaling enables the Journaling agent in Exchange 2007 to use rules that you can configure to match the specific needs of your organization. You can create journal rules for a single mailbox recipient or for entire groups within your organization. Premium journaling is also called per-recipient journaling.
Important: You must have an Exchange Enterprise Client Access License (CAL) to use premium journaling.
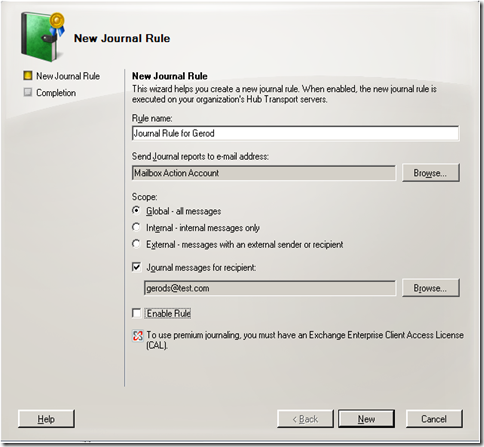
Lets look through how the wizard for per-recipient journaling:
Here I have set up a journaling rule for my mailbox only.
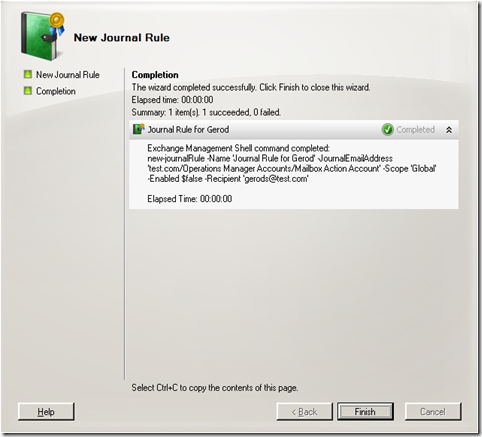
And here you can see the the cmdlet used is New-JournalRule.
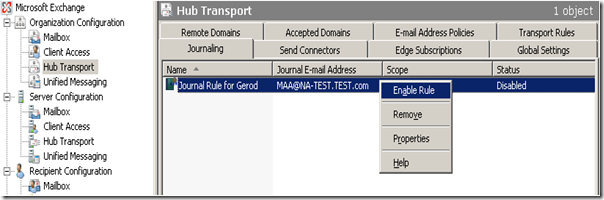
I didn’t create this rule with it enabled, so to enable it you can right-click on it in the GUI.
Next: Part 21 – Transport: POP3, IMAP4, and Transport Layer Security (TLS)
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
To return to part 1 click here Transport Disclaimer messages In Exchange 2003, you needed to create a