Explore Microsoft Defender Cloud Apps
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps (formerly Microsoft Cloud App Security) natively integrates with leading Microsoft solutions. It identifies and combats cyberthreats across all your Microsoft and third-party cloud services. It does so by providing:
- Rich visibility
- Control over data travel
- Sophisticated analytics
- Simple deployment
- Centralized management
- Innovative automation capabilities
The Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps framework provides the following threat intelligence protection:
- Discover and control the use of Shadow IT. Identifies the cloud apps and the IaaS and PaaS services used by organizations. Investigates usage patterns and assesses the risk levels and business readiness of more than 25,000 SaaS apps against more than 80 risks. In turn, organizations can manage them to ensure security and compliance.
- Protect your sensitive information anywhere in the cloud. Understands, classifies, and protects the exposure of sensitive information at rest. Uses out-of-the-box policies and automated processes to apply controls in real time across all the cloud apps in an organization.
- Protect against cyberthreats and anomalies. Analyzes high-risk usage and remediates issues automatically to limit the risk to organizations. Detects unusual behavior across cloud apps to identify:
- Ransomware
- Compromised users
- Rogue applications
- Assess the compliance of your cloud apps. Assesses whether an organization's cloud apps meet relevant compliance requirements. These requirements include regulatory compliance and industry standards. This feature prevents data leaks to noncompliant apps. It also limits access to regulated data.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps is a critical component of the Microsoft Cloud Security stack. It's a comprehensive solution that helps organizations take full advantage of the promise of cloud applications. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps keeps organizations in control through comprehensive visibility, auditing, and granular controls over your sensitive data.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps has tools that help uncover shadow IT and assess risk. At the same time, these tools enable organizations to enforce policies and investigate activities. It helps them control access in real time and stop threats so they can more safely move to the cloud.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps architecture
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps integrates visibility with an organization's cloud by:
- Using Cloud Discovery to map and identify an organization's cloud environment and the cloud apps it uses.
- Sanctioning and unsanctioning apps in the organization's cloud.
- Using easy-to-deploy app connectors that take advantage of provider APIs, for visibility and governance of apps that an organization can connect to.
- Using Conditional Access App Control protection to get real-time visibility and control over access and activities within an organization's cloud apps.
- Helping an organization have continuous control by setting, and then continually fine-tuning, policies.
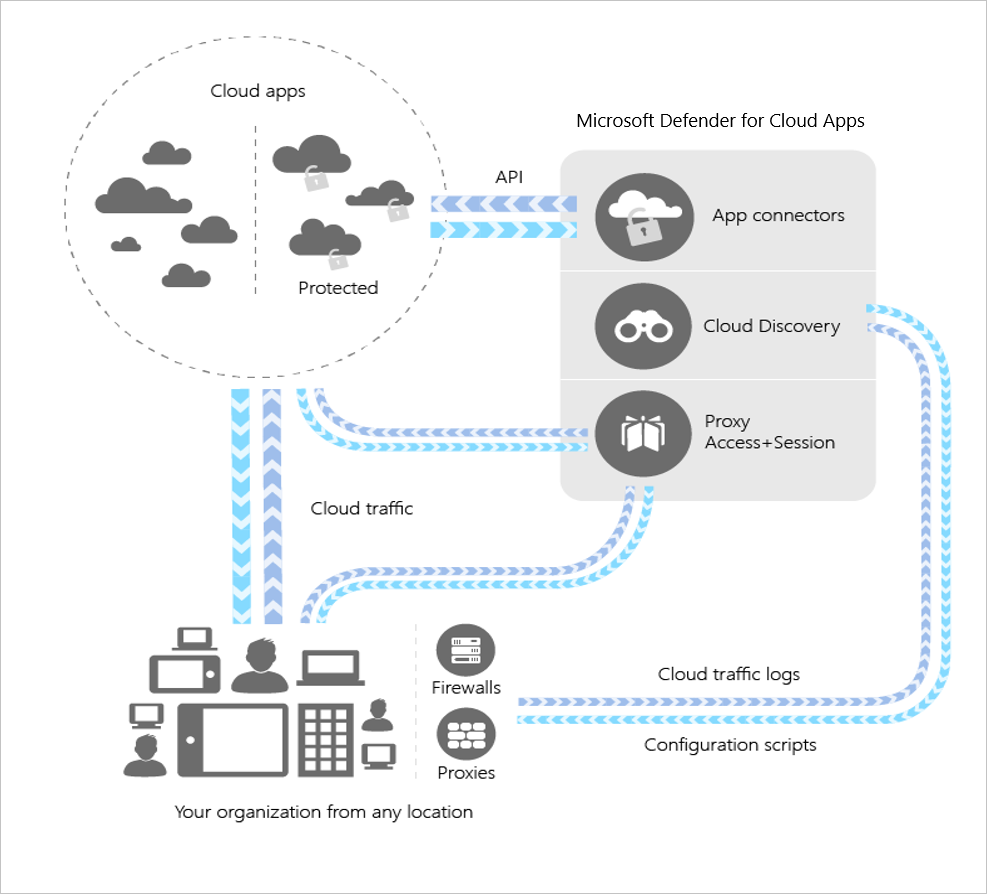
Cloud Discovery
Cloud Discovery uses an organization's traffic logs to dynamically discover and analyze the cloud apps that it's using. To create a snapshot report of an organization's cloud use, an organization can manually upload log files from its firewalls or proxies for analysis. To set up continuous reports, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps log collectors can periodically forward logs.
Additional reading. For more information, see Set up Cloud Discovery.
Sanctioning and unsanctioning an app
An organization can use Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to sanction or unsanction its apps by using the Cloud app catalog. Microsoft has an extensive and continuously growing catalog of over 25,000 cloud apps. Microsoft ranked and scored the apps based on industry standards. An organization can use the Cloud app catalog to rate the risk for its cloud apps based on regulatory certifications, industry standards, and best practices. It can then customize the scores and weights of various parameters to its needs. Based on these scores, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps lets an organization know how risky an app is. Scoring is based on over 80 risk factors that can affect an organization's environment.
App connectors
App connectors are an integral part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps. They facilitate the integration between the Cloud App Security service and cloud applications. This design enables Microsoft to collect and analyze relevant security and usage data from those applications. These connectors establish a connection between the Cloud App Security service and the cloud application's APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). Doing so enables the service to gain insights into the application's activities, configurations, and security events.
By connecting an app using app connectors, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps gains visibility and control over the cloud application's activities. It can monitor user behavior, detect potential security risks or anomalies, and apply security policies to protect against threats like data leaks, unauthorized access, or suspicious activity. The service's machine learning algorithms process and analyze the collected data. Doing so enables the service to identify patterns, generate security alerts, and provide actionable insights for organizations to improve their cloud security posture.
To connect an app and extend protection, the app administrator authorizes Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to access the app. Then, Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps queries the app for activity logs, and it scans data, accounts, and cloud content. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps can enforce policies, detects threats, and provides governance actions for resolving issues.
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps uses the APIs provided by the cloud provider. Each app has its own framework and API limitations. Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps works with app providers on optimizing the use of APIs to ensure the best performance. Considering the various limitations that apps impose on APIs (such as throttling, API limits, and dynamic time-shifting API windows), the Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps engines utilize the allowed capacity. Some operations, like scanning all files in the tenant, require many APIs, so they run over a longer period. Expect some policies to run for several hours or several days.
Conditional Access App Control protection
Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps Conditional Access App Control uses reverse proxy architecture. Organizations typically deploy the reverse proxy server in the same network segment as the application server. The proxy server routes incoming traffic to the appropriate backend server based on the requested URL. For Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps, organizations configure the reverse proxy server to redirect traffic to the Microsoft Defender proxy server for inspection and policy enforcement before forwarding it to the application server.
Once the traffic reaches the Microsoft Defender proxy server, it inspects the traffic for any malicious activity or policy violations based on the organization's security policies. If the Microsoft Defender proxy server deems the traffic safe, it forwards it to the application server. If the traffic is malicious or violates the security policies, Microsoft Defender proxy server either blocks it or redirects it to a quarantine area for further analysis.
This architecture allows Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps to provide real-time protection against various types of attacks. For example, cross-site scripting, SQL injection, and other web application vulnerabilities. Because the Microsoft Defender proxy server intercepts and inspects traffic at the network layer, the proxy can detect and block malicious traffic before it reaches the application server. This design provides an extra layer of defense against cyber threats.
The reverse proxy architecture used by Conditional Access App Control gives organizations real-time visibility and control over access to and activities performed within their cloud environments. With Conditional Access App Control, organizations can:
- Avoid data leaks by blocking downloads before they happen.
- Set rules that protect data downloaded from the cloud by encrypting it.
- Gain visibility into unprotected endpoints so that organizations can monitor activity on unmanaged devices.
- Control access from noncorporate networks and risky IP addresses.
Policy control
Organizations can use policies to define their users' behavior in the cloud. Policies detect risky behavior, violations, or suspicious data points and activities in an organization's cloud environment. If needed, an organization can use policies to integrate remediation processes to achieve complete risk mitigation. Types of policies correlate to the different types of information they might want to gather about their cloud environment and the types of remediation actions they can take.
Knowledge check
Choose the best response for the following question.