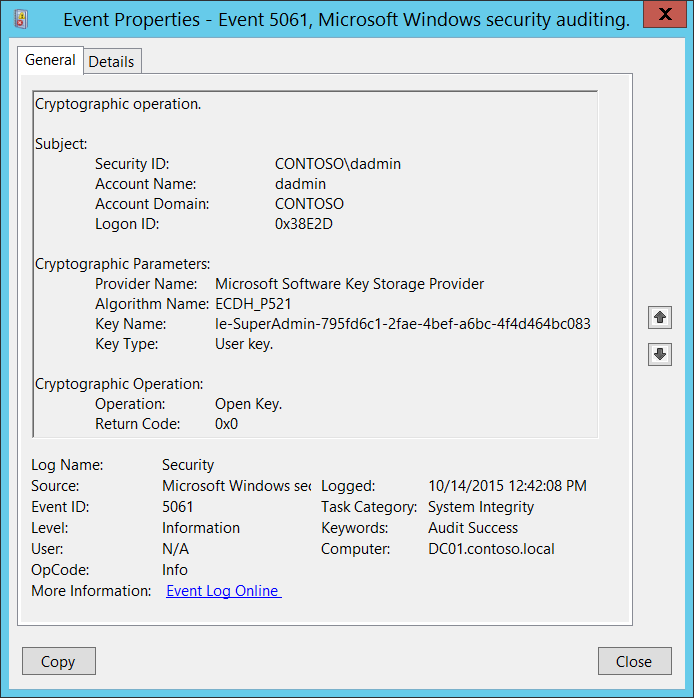
5061(S, F): Cryptographic operation.
Subcategory: Audit System Integrity
Event Description:
This event generates when a cryptographic operation (open key, create key, create key, and so on) was performed using a Key Storage Provider (KSP). This event generates only if one of the following KSPs was used:
Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider
Note For recommendations, see Security Monitoring Recommendations for this event.
Event XML:
- <Event xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/win/2004/08/events/event">
- <System>
<Provider Name="Microsoft-Windows-Security-Auditing" Guid="{54849625-5478-4994-A5BA-3E3B0328C30D}" />
<EventID>5061</EventID>
<Version>0</Version>
<Level>0</Level>
<Task>12290</Task>
<Opcode>0</Opcode>
<Keywords>0x8020000000000000</Keywords>
<TimeCreated SystemTime="2015-10-14T19:42:08.104008000Z" />
<EventRecordID>1048444</EventRecordID>
<Correlation />
<Execution ProcessID="520" ThreadID="3496" />
<Channel>Security</Channel>
<Computer>DC01.contoso.local</Computer>
<Security />
</System>
- <EventData>
<Data Name="SubjectUserSid">S-1-5-21-3457937927-2839227994-823803824-1104</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectUserName">dadmin</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectDomainName">CONTOSO</Data>
<Data Name="SubjectLogonId">0x38e2d</Data>
<Data Name="ProviderName">Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider</Data>
<Data Name="AlgorithmName">ECDH\_P521</Data>
<Data Name="KeyName">le-SuperAdmin-795fd6c1-2fae-4bef-a6bc-4f4d464bc083</Data>
<Data Name="KeyType">%%2500</Data>
<Data Name="Operation">%%2480</Data>
<Data Name="ReturnCode">0x0</Data>
</EventData>
</Event>
Required Server Roles: None.
Minimum OS Version: Windows Server 2008, Windows Vista.
Event Versions: 0.
Field Descriptions:
Subject:
- Security ID [Type = SID]: SID of account that requested specific cryptographic operation. Event Viewer automatically tries to resolve SIDs and show the account name. If the SID can't be resolved, you'll see the source data in the event.
Note A security identifier (SID) is a unique value of variable length used to identify a trustee (security principal). Each account has a unique SID that is issued by an authority, such as an Active Directory domain controller, and stored in a security database. Each time a user logs on, the system retrieves the SID for that user from the database and places it in the access token for that user. The system uses the SID in the access token to identify the user in all subsequent interactions with Windows security. When a SID has been used as the unique identifier for a user or group, it cannot ever be used again to identify another user or group. For more information about SIDs, see Security identifiers.
Account Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the account that requested specific cryptographic operation.
Account Domain [Type = UnicodeString]: subject’s domain or computer name. Formats vary, and include the following ones:
Domain NETBIOS name example: CONTOSO
Lowercase full domain name: contoso.local
Uppercase full domain name: CONTOSO.LOCAL
For some well-known security principals, such as LOCAL SERVICE or ANONYMOUS LOGON, the value of this field is “NT AUTHORITY”.
For local user accounts, this field will contain the name of the computer or device that this account belongs to, for example: “Win81”.
Logon ID [Type = HexInt64]: hexadecimal value that can help you correlate this event with recent events that might contain the same Logon ID, for example, “4624: An account was successfully logged on.”
Cryptographic Parameters:
Provider Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of KSP through which the operation was performed. Can have one of the following values:
Microsoft Software Key Storage Provider
Microsoft Smart Card Key Storage Provider
Algorithm Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of cryptographic algorithm through which the key was used or accessed. For “Read persisted key from file” operation, this algorithm has “UNKNOWN” value. Can also have one of the following values:
RSA – algorithm created by Ron Rivest, Adi Shamir, and Leonard Adleman.
DSA – Digital Signature Algorithm.
DH – Diffie-Hellman.
ECDH_P521 – Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman algorithm with 512-bit key length.
ECDH_P384 – Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman algorithm with 384-bit key length.
ECDH_P256 – Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman algorithm with 256-bit key length.
ECDSA_P256 – Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm with 256-bit key length.
ECDSA_P384 – Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm with 384-bit key length.
ECDSA_P521 – Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm with 521-bit key length.
Key Name [Type = UnicodeString]: the name of the key (key container) with which operation was performed. For example, to get the list of Key Names for certificates for logged in user you can use “certutil -store -user my” command and check Key Container parameter in the output. Here's an output example:
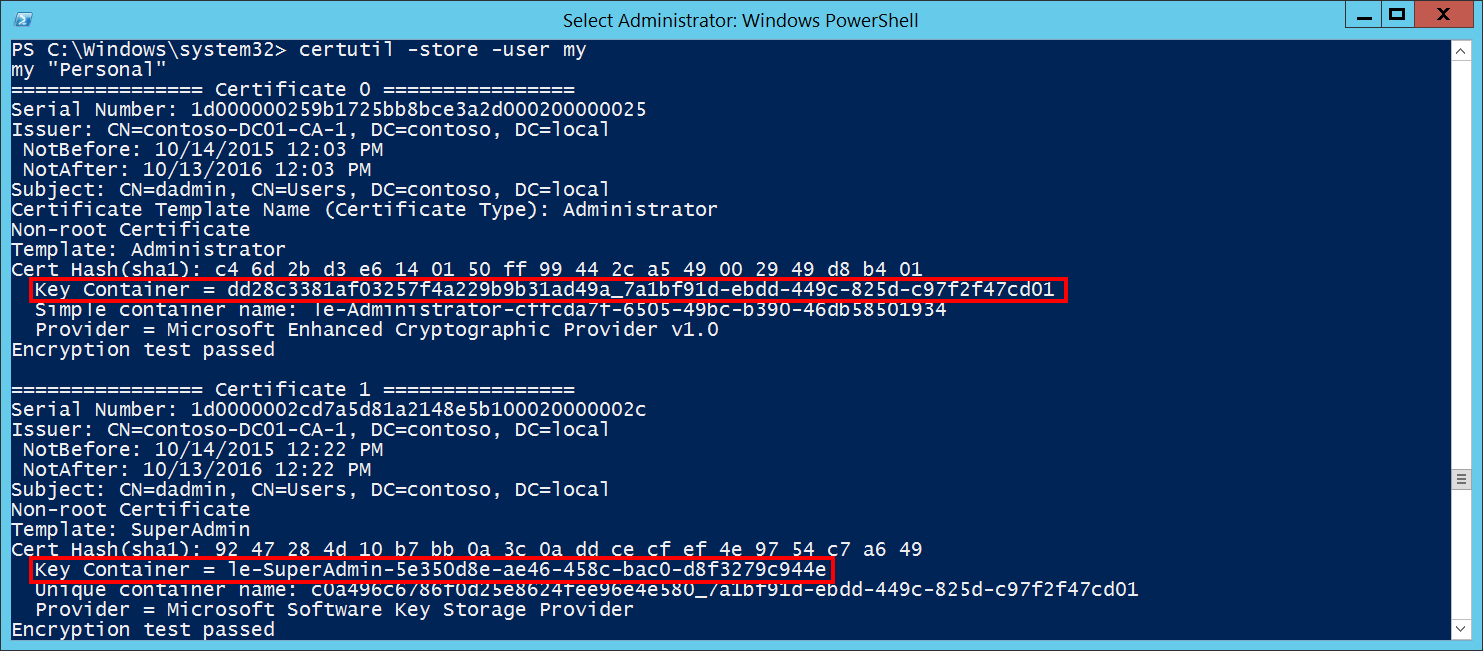
Key Type [Type = UnicodeString]: can have one of the following values:
“User key.” – user’s cryptographic key.
“Machine key.” – machine’s cryptographic key.
Cryptographic Operation:
Operation [Type = UnicodeString]: performed operation. Possible values:
Open Key. – open existing cryptographic key.
Create Key. – create new cryptographic key.
Delete Key. – delete existing cryptographic key.
Sign hash. – cryptographic signing operation.
Secret agreement.
Key Derivation. – key derivation operation.
Encrypt. – encryption operation.
Decrypt. – decryption operation.
Return Code [Type = HexInt32]: has “0x0” value for Success events. For failure events, provides a hexadecimal error code number.
Security Monitoring Recommendations
For 5061(S, F): Cryptographic operation.
- Typically this event is required for detailed monitoring of KSP-related actions with cryptographic keys. If you need to monitor actions related to specific cryptographic keys (“Key Name”) or a specific “Operation”, such as “Delete Key”, create monitoring rules and use this event as an information source.
Important For this event, also see Appendix A: Security monitoring recommendations for many audit events.