Jak utworzyć predyktor wiersza polecenia
PSReadLine 2.1.0 wprowadził koncepcję inteligentnego narzędzia do prognozowania wiersza poleceń poprzez zaimplementowanie funkcji Predictive IntelliSense. Funkcja PSReadLine 2.2.2 została rozszerzona o tę funkcję, dodając model wtyczki, który umożliwia tworzenie własnych predyktorów wiersza polecenia.
Predykcyjna funkcja IntelliSense poprawia funkcję uzupełniania poleceń, podając sugestie w trakcie wpisywania w wierszu polecenia. Sugestia przewidywania jest wyświetlana jako kolorowy tekst po kursorze. Dzięki temu można odnajdywać, edytować i wykonywać pełne polecenia na podstawie pasujących przewidywań z historii poleceń lub dodatkowych wtyczek specyficznych dla domeny.
Wymagania systemowe
Aby utworzyć i użyć predyktora wtyczki, należy użyć następujących wersji oprogramowania:
- Program PowerShell 7.2 (lub nowszy) — udostępnia interfejsy API niezbędne do utworzenia predyktora poleceń
- PSReadLine 2.2.2 (lub nowszy) — umożliwia skonfigurowanie programu PSReadLine do korzystania z wtyczki
Omówienie predyktora
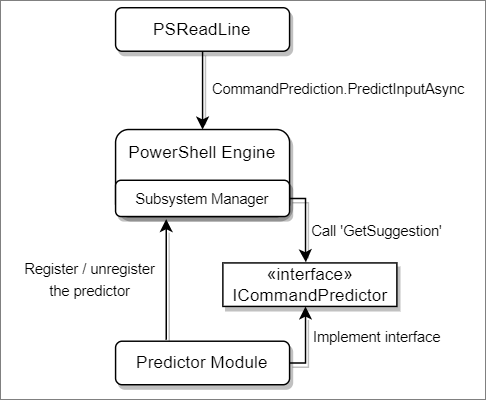
Predyktor to moduł binarny programu PowerShell. Moduł musi zaimplementować interfejs System.Management.Automation.Subsystem.Prediction.ICommandPredictor. Ten interfejs deklaruje metody używane do wykonywania zapytań dotyczących wyników przewidywania i przekazywania opinii.
Moduł predyktora musi zarejestrować podsystem CommandPredictor w SubsystemManager programu PowerShell przy ładowaniu i wyrejestrować się przy rozładowywaniu.
Na poniższym diagramie przedstawiono architekturę predyktora w programie PowerShell.
Tworzenie kodu
Aby utworzyć predyktor, musisz mieć zainstalowany zestaw .NET 6 SDK dla danej platformy. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat zestawu SDK, odwiedź stronę Pobierz .NET 6.0.
Utwórz nowy projekt modułu programu PowerShell, wykonując następujące kroki:
Użyj narzędzia wiersza polecenia
dotnet, aby utworzyć projekt starter classlib.dotnet new classlib --name SamplePredictorEdytuj
SamplePredictor.csproj, aby zawierał następujące informacje:<Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk"> <PropertyGroup> <TargetFramework>net6.0</TargetFramework> </PropertyGroup> <ItemGroup> <PackageReference Include="Microsoft.PowerShell.SDK" Version="7.2.0" /> </ItemGroup> </Project>Usuń domyślny plik
Class1.csutworzony przezdotneti skopiuj następujący kod do plikuSamplePredictorClass.csw folderze projektu.using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Threading; using System.Management.Automation; using System.Management.Automation.Subsystem; using System.Management.Automation.Subsystem.Prediction; namespace PowerShell.Sample { public class SamplePredictor : ICommandPredictor { private readonly Guid _guid; internal SamplePredictor(string guid) { _guid = new Guid(guid); } /// <summary> /// Gets the unique identifier for a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public Guid Id => _guid; /// <summary> /// Gets the name of a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public string Name => "SamplePredictor"; /// <summary> /// Gets the description of a subsystem implementation. /// </summary> public string Description => "A sample predictor"; /// <summary> /// Get the predictive suggestions. It indicates the start of a suggestion rendering session. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="context">The <see cref="PredictionContext"/> object to be used for prediction.</param> /// <param name="cancellationToken">The cancellation token to cancel the prediction.</param> /// <returns>An instance of <see cref="SuggestionPackage"/>.</returns> public SuggestionPackage GetSuggestion(PredictionClient client, PredictionContext context, CancellationToken cancellationToken) { string input = context.InputAst.Extent.Text; if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(input)) { return default; } return new SuggestionPackage(new List<PredictiveSuggestion>{ new PredictiveSuggestion(string.Concat(input, " HELLO WORLD")) }); } #region "interface methods for processing feedback" /// <summary> /// Gets a value indicating whether the predictor accepts a specific kind of feedback. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="feedback">A specific type of feedback.</param> /// <returns>True or false, to indicate whether the specific feedback is accepted.</returns> public bool CanAcceptFeedback(PredictionClient client, PredictorFeedbackKind feedback) => false; /// <summary> /// One or more suggestions provided by the predictor were displayed to the user. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="session">The mini-session where the displayed suggestions came from.</param> /// <param name="countOrIndex"> /// When the value is greater than 0, it's the number of displayed suggestions from the list /// returned in <paramref name="session"/>, starting from the index 0. When the value is /// less than or equal to 0, it means a single suggestion from the list got displayed, and /// the index is the absolute value. /// </param> public void OnSuggestionDisplayed(PredictionClient client, uint session, int countOrIndex) { } /// <summary> /// The suggestion provided by the predictor was accepted. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="session">Represents the mini-session where the accepted suggestion came from.</param> /// <param name="acceptedSuggestion">The accepted suggestion text.</param> public void OnSuggestionAccepted(PredictionClient client, uint session, string acceptedSuggestion) { } /// <summary> /// A command line was accepted to execute. /// The predictor can start processing early as needed with the latest history. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="history">History command lines provided as references for prediction.</param> public void OnCommandLineAccepted(PredictionClient client, IReadOnlyList<string> history) { } /// <summary> /// A command line was done execution. /// </summary> /// <param name="client">Represents the client that initiates the call.</param> /// <param name="commandLine">The last accepted command line.</param> /// <param name="success">Shows whether the execution was successful.</param> public void OnCommandLineExecuted(PredictionClient client, string commandLine, bool success) { } #endregion; } /// <summary> /// Register the predictor on module loading and unregister it on module un-loading. /// </summary> public class Init : IModuleAssemblyInitializer, IModuleAssemblyCleanup { private const string Identifier = "843b51d0-55c8-4c1a-8116-f0728d419306"; /// <summary> /// Gets called when assembly is loaded. /// </summary> public void OnImport() { var predictor = new SamplePredictor(Identifier); SubsystemManager.RegisterSubsystem(SubsystemKind.CommandPredictor, predictor); } /// <summary> /// Gets called when the binary module is unloaded. /// </summary> public void OnRemove(PSModuleInfo psModuleInfo) { SubsystemManager.UnregisterSubsystem(SubsystemKind.CommandPredictor, new Guid(Identifier)); } } }Poniższy przykładowy kod zwraca ciąg "HELLO WORLD" dla wyniku przewidywania dla wszystkich danych wejściowych użytkownika. Ponieważ przykładowy predyktor nie przetwarza żadnych opinii, kod nie implementuje metod opinii z interfejsu. Zmień kod przewidywania i opinii, aby zaspokoić potrzeby twojego predyktora.
Notatka
Widok listy PSReadLine nie obsługuje sugestii wielowierszowych. Każda sugestia powinna być jedną linią. Jeśli kod zawiera sugestię wielowierszową, należy podzielić wiersze na oddzielne sugestie lub połączyć wiersze średnikami (
;).Uruchom
dotnet build, aby utworzyć zestaw. Skompilowany zestaw można znaleźć w lokalizacjibin/Debug/net6.0folderu projektu.Notatka
Aby zapewnić responsywne doświadczenie użytkownika, interfejs ICommandPredictor ma czas odpowiedzi ograniczony do 20 ms dla predyktorów. Kod predyktora musi zwracać wyniki w mniej niż 20 ms, aby zostały wyświetlone.
Korzystanie z wtyczki predyktora
Aby wypróbować nowy predyktor, otwórz nową sesję programu PowerShell 7.2 i uruchom następujące polecenia:
Set-PSReadLineOption -PredictionSource HistoryAndPlugin
Import-Module .\bin\Debug\net6.0\SamplePredictor.dll
Podczas gdy zestaw zostanie załadowany w sesji, zobaczysz, jak tekst "HELLO WORLD" pojawia się, gdy wpisujesz w terminalu. Możesz nacisnąć F2, aby przełączać się między widokiem Inline a widokiem List.
Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat opcji PSReadLine, zobacz Set-PSReadLineOption.
Listę zainstalowanych predyktorów można uzyskać przy użyciu następującego polecenia:
Get-PSSubsystem -Kind CommandPredictor
Kind SubsystemType IsRegistered Implementations
---- ------------- ------------ ---------------
CommandPredictor ICommandPredictor True {SamplePredictor}
Notatka
Get-PSSubsystem to eksperymentalne polecenie cmdlet wprowadzone w programie PowerShell 7.1 Aby użyć tego polecenia cmdlet, musisz włączyć funkcję eksperymentalną PSSubsystemPluginModel. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Korzystanie z funkcji eksperymentalnych.
