Configure federation between Google Workspace and Microsoft Entra ID
This article describes the steps required to configure Google Workspace as an identity provider (IdP) for Microsoft Entra ID.
Once configured, users can sign in to Microsoft Entra ID with their Google Workspace credentials.
Prerequisites
To configure Google Workspace as an IdP for Microsoft Entra ID, the following prerequisites must be met:
- A Microsoft Entra tenant, with one or multiple custom DNS domains (that is, domains that aren't in the format *.onmicrosoft.com)
- If the federated domain hasn't yet been added to Microsoft Entra ID, you must have access to the DNS domain to create a DNS record. This is required to verify the ownership of the DNS namespace
- Learn how to Add your custom domain name using the Microsoft Entra admin center
- Access to the Microsoft Entra admin center as at least a External Identity Provider Administrator
- Access to Google Workspace with an account with super admin privileges
To test federation, the following prerequisites must be met:
- A Google Workspace environment, with users already created
Important
Users require an email address defined in Google Workspace, which is used to match the users in Microsoft Entra ID. For more information about identity matching, see Identity matching in Microsoft Entra ID.
- Individual Microsoft Entra accounts already created: each Google Workspace user requires a matching account defined in Microsoft Entra ID. These accounts are commonly created through automated solutions, for example:
- School Data Sync (SDS)
- Microsoft Entra Connect Sync for environment with on-premises AD DS
- PowerShell scripts that call the Microsoft Graph API
- Provisioning tools offered by the IdP - Google Workspace offers autoprovisioning
Configure Google Workspace as an IdP for Microsoft Entra ID
Sign in to the Google Workspace Admin Console with an account with super admin privileges
Select Apps > Web and mobile apps
Select Add app > Search for apps and search for microsoft
In the search results page, hover over the Microsoft Office 365 - Web (SAML) app and select Select
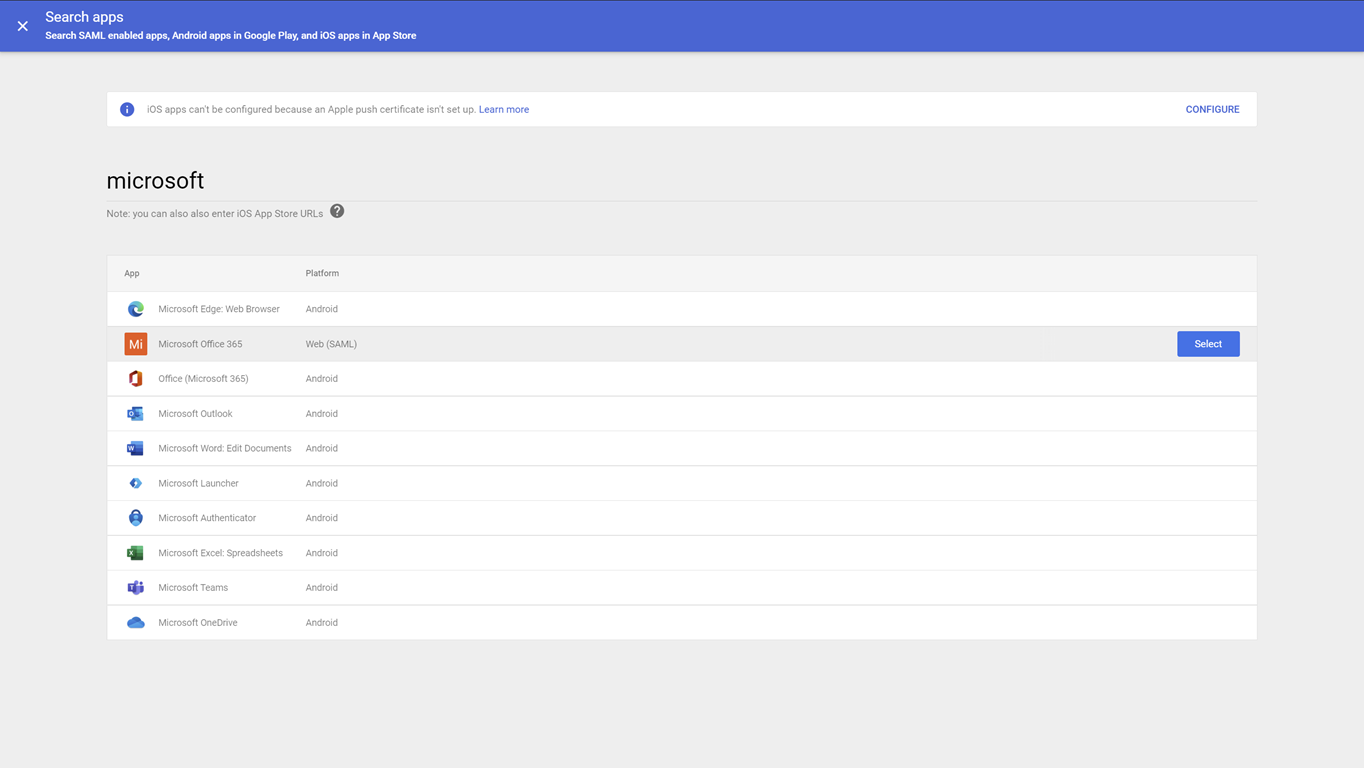
On the Google Identity Provider details page, select Download Metadata and take note of the location where the IdP metadata - GoogleIDPMetadata.xml - file is saved, as it's used to set up Microsoft Entra ID later
On the Service provider detail's page:
- Select the option Signed response
- Verify that the Name ID format is set to PERSISTENT
- Depending on how the Microsoft Entra users have been provisioned in Microsoft Entra ID, you might need to adjust the Name ID mapping
If using Google autoprovisioning, select Basic Information > Primary email - Select Continue
On the Attribute mapping page, map the Google attributes to the Microsoft Entra attributes
Google Directory attributes Microsoft Entra attributes Basic Information: Primary Email App attributes: IDPEmail Important
You must ensure that your Microsoft Entra user account's email matches that in your Google Workspace.
Select Finish
Now that the app is configured, you must enable it for the users in Google Workspace:
- Sign in to the Google Workspace Admin Console with an account with super admin privileges
- Select Apps > Web and mobile apps
- Select Microsoft Office 365
- Select User access
- Select ON for everyone > Save
Configure Microsoft Entra ID as a Service Provider (SP) for Google Workspace
The configuration of Microsoft Entra ID consists of changing the authentication method for the custom DNS domains. This configuration can be done using PowerShell.
Using the IdP metadata XML file downloaded from Google Workspace, modify the $DomainName variable of the following script to match your environment, and then run it in a PowerShell session. When prompted to authenticate to Microsoft Entra ID, sign in as at least a External Identity Provider Administrator
Set-ExecutionPolicy -ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser -Force
Install-Module Microsoft.Graph -Scope CurrentUser
Import-Module Microsoft.Graph
$domainId = "<your domain name>"
$xml = [Xml](Get-Content GoogleIDPMetadata.xml)
$cert = -join $xml.EntityDescriptor.IDPSSODescriptor.KeyDescriptor.KeyInfo.X509Data.X509Certificate.Split()
$issuerUri = $xml.EntityDescriptor.entityID
$signinUri = $xml.EntityDescriptor.IDPSSODescriptor.SingleSignOnService | ? { $_.Binding.Contains('Redirect') } | % { $_.Location }
$signoutUri = "https://accounts.google.com/logout"
$displayName = "Google Workspace Identity"
Connect-MGGraph -Scopes "Domain.ReadWrite.All", "Directory.AccessAsUser.All"
$domainAuthParams = @{
DomainId = $domainId
IssuerUri = $issuerUri
DisplayName = $displayName
ActiveSignInUri = $signinUri
PassiveSignInUri = $signinUri
SignOutUri = $signoutUri
SigningCertificate = $cert
PreferredAuthenticationProtocol = "saml"
federatedIdpMfaBehavior = "acceptIfMfaDoneByFederatedIdp"
}
New-MgDomainFederationConfiguration @domainAuthParams
To verify that the configuration is correct, you can use the following PowerShell command:
Get-MgDomainFederationConfiguration -DomainId $domainId |fl
ActiveSignInUri : https://accounts.google.com/o/saml2/idp?idpid=<GUID>
DisplayName : Google Workspace Identity
FederatedIdpMfaBehavior : acceptIfMfaDoneByFederatedIdp
Id : 3f600dce-ab37-4798-9341-ffd34b147f70
IsSignedAuthenticationRequestRequired :
IssuerUri : https://accounts.google.com/o/saml2?idpid=<GUID>
MetadataExchangeUri :
NextSigningCertificate :
PassiveSignInUri : https://accounts.google.com/o/saml2/idp?idpid=<GUID>
PreferredAuthenticationProtocol : saml
PromptLoginBehavior :
SignOutUri : https://accounts.google.com/logout
SigningCertificate : <BASE64 encoded certificate>
AdditionalProperties : {}
Verify federated authentication between Google Workspace and Microsoft Entra ID
From a private browser session, navigate to https://portal.azure.com and sign in with a Google Workspace account:
As username, use the email as defined in Google Workspace
The user is redirected to Google Workspace to sign in
After Google Workspace authentication, the user is redirected back to Microsoft Entra ID and signed in
