Operacje kwantyfikatora (Visual Basic)
Operacje kwantyfikatora zwracają wartość wskazującą Boolean , czy niektóre lub wszystkie elementy w sekwencji spełniają warunek.
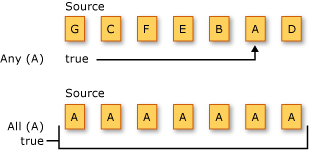
Poniższa ilustracja przedstawia dwie różne operacje kwantyfikatora na dwóch różnych sekwencjach źródłowych. Pierwsza operacja pyta, czy którykolwiek z elementów jest znakiem "A". Druga operacja pyta, czy wszystkie elementy są znakiem "A". Obie metody zwracają true w tym przykładzie.
Standardowe metody operatorów zapytań, które wykonują operacje kwantyfikatora, są wymienione w poniższej sekcji.
Metody
| Nazwa metody | opis | Składnia wyrażeń zapytań języka Visual Basic | Więcej informacji |
|---|---|---|---|
| wszystkie | Określa, czy wszystkie elementy w sekwencji spełniają warunek. | Aggregate … In … Into All(…) |
Enumerable.All Queryable.All |
| Dowolne | Określa, czy dowolne elementy w sekwencji spełniają warunek. | Aggregate … In … Into Any() |
Enumerable.Any Queryable.Any |
| Contains | Określa, czy sekwencja zawiera określony element. | Nie dotyczy. | Enumerable.Contains Queryable.Contains |
Przykłady składni wyrażeń zapytania
Te przykłady używają klauzuli Aggregate w Visual Basic w ramach warunku filtrowania w zapytaniu LINQ.
W poniższym przykładzie użyto klauzuli Aggregate i All metody rozszerzenia, aby wrócić z kolekcji tych osób, których zwierzęta domowe są starsze niż określony wiek.
Class Person
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Pets As Pet()
End Class
Class Pet
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Age As Integer
End Class
Sub All()
Dim barley As New Pet With {.Name = "Barley", .Age = 4}
Dim boots As New Pet With {.Name = "Boots", .Age = 1}
Dim whiskers As New Pet With {.Name = "Whiskers", .Age = 6}
Dim bluemoon As New Pet With {.Name = "Blue Moon", .Age = 9}
Dim daisy As New Pet With {.Name = "Daisy", .Age = 3}
Dim charlotte As New Person With {.Name = "Charlotte", .Pets = New Pet() {barley, boots}}
Dim arlene As New Person With {.Name = "Arlene", .Pets = New Pet() {whiskers}}
Dim rui As New Person With {.Name = "Rui", .Pets = New Pet() {bluemoon, daisy}}
' Create the list of Person objects that will be queried.
Dim people As New System.Collections.Generic.List(Of Person)(New Person() {charlotte, arlene, rui})
Dim query = From pers In people
Where (Aggregate pt In pers.Pets Into All(pt.Age > 2))
Select pers.Name
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each name As String In query
sb.AppendLine(name)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' Arlene
' Rui
End Sub
W następnym przykładzie użyto klauzuli Aggregate i Any metody rozszerzenia, aby wrócić z kolekcji tych osób, które mają co najmniej jedno zwierzę, które jest starsze niż określony wiek.
Class Person
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Pets As Pet()
End Class
Class Pet
Public Property Name As String
Public Property Age As Integer
End Class
Sub Any()
Dim barley As New Pet With {.Name = "Barley", .Age = 4}
Dim boots As New Pet With {.Name = "Boots", .Age = 1}
Dim whiskers As New Pet With {.Name = "Whiskers", .Age = 6}
Dim bluemoon As New Pet With {.Name = "Blue Moon", .Age = 9}
Dim daisy As New Pet With {.Name = "Daisy", .Age = 3}
Dim charlotte As New Person With {.Name = "Charlotte", .Pets = New Pet() {barley, boots}}
Dim arlene As New Person With {.Name = "Arlene", .Pets = New Pet() {whiskers}}
Dim rui As New Person With {.Name = "Rui", .Pets = New Pet() {bluemoon, daisy}}
' Create the list of Person objects that will be queried.
Dim people As New System.Collections.Generic.List(Of Person)(New Person() {charlotte, arlene, rui})
Dim query = From pers In people
Where (Aggregate pt In pers.Pets Into Any(pt.Age > 7))
Select pers.Name
Dim sb As New System.Text.StringBuilder()
For Each name As String In query
sb.AppendLine(name)
Next
' Display the results.
MsgBox(sb.ToString())
' This code produces the following output:
' Rui
End Sub
