Zgodność ANSI w środowisku Databricks Runtime
Dotyczy:![]() Databricks Runtime
Databricks Runtime
W tym artykule opisano zgodność ANSI w środowisku Databricks Runtime. W przypadku trybu ANSI w usłudze Databricks SQL zobacz ANSI_MODE.
Usługa Spark SQL oferuje dwie opcje obsługi zgodności ze standardem ANSI SQL: spark.sql.ansi.enabled i spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy.
Gdy spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest ustawiony na true, Spark SQL używa dialektu zgodnego z ANSI zamiast dialektu zgodnego z Hive. Na przykład platforma Spark zgłosi wyjątek w czasie wykonywania zamiast zwracać wyniki o wartości null, jeśli dane wejściowe do operatora/funkcji SQL są nieprawidłowe. Niektóre funkcje dialektu ANSI mogą nie pochodzić bezpośrednio ze standardu ANSI SQL, ale ich zachowania są zgodne ze stylem ANSI SQL.
Ponadto usługa Spark SQL ma niezależną opcję kontrolowania niejawnych zachowań rzutowania podczas przechowywania wierszy w tabeli. Zasady działania castingów są zdefiniowane jako reguły przypisywania w standardzie.
Gdy spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy jest ustawione na ANSI, Spark SQL przestrzega reguł przypisywania ANSI. Jest to oddzielna konfiguracja, ponieważ jej wartość domyślna to ANSI, a konfiguracja spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest domyślnie wyłączona.
Poniższa tabela zawiera podsumowanie zachowania:
| Nazwa właściwości | Wartość domyślna | Znaczenie |
|---|---|---|
spark.sql.ansi.enabled |
fałsz | Jeśli to prawda, platforma Spark próbuje dostosować się do specyfikacji ANSI SQL:
|
spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy |
ANSI | Podczas przechowywania wartości w kolumnie o innym typie danych platforma Spark wykonuje konwersję typu. Istnieją trzy zasady dotyczące reguł konwersji typów: ANSI, legacy i strict.
|
W poniższych podsekcjach przedstawiono zmiany zachowania operacji arytmetycznych, konwersji typów i analizowania SQL po włączeniu trybu ANSI. W przypadku konwersji typów w usłudze Spark SQL są trzy rodzaje i ten artykuł przedstawi je kolejno: rzutowanie, przypisywanie do magazynu oraz koercja typu.
Operacje arytmetyczne
W usłudze Spark SQL operacje arytmetyczne wykonywane na typach liczbowych (z wyjątkiem liczby dziesiętnej) nie są domyślnie sprawdzane pod kątem przepełnienia.
Oznacza to, że w przypadku, gdy operacja powoduje przepełnienie, wynik jest taki sam w przypadku odpowiedniej operacji w programie Java lub Scala (na przykład jeśli suma 2 liczb całkowitych jest wyższa niż maksymalna wartość, którą można przedstawić, wynik jest liczbą ujemną). Z drugiej strony usługa Spark SQL zwraca wartość null dla przepełnienia dziesiętnego.
Gdy spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest ustawiony na true i dochodzi do przepełnienia w operacjach arytmetycznych na liczbach i przedziałach, wyjątek arytmetyczny zostaje zgłoszony w czasie wykonywania.
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true`
> SELECT 2147483647 + 1;
error: integer overflow
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=false`
> SELECT 2147483647 + 1;
-2147483648
Rzutowanie
Gdy spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest ustawiona wartość true, jawne rzutowanie przez CAST składnię zgłasza wyjątek środowiska uruchomieniowego dla nielegalnych wzorców rzutowania zdefiniowanych w standardzie, takich jak rzutowania z ciągu na liczbę całkowitą.
Klauzula trybu ANSI Spark jest zgodna z regułami składni w sekcji 6.13 zatytułowanej „specyfikacja rzutowania” w standardzie ISO/IEC 9075-2:2011 Information technology — Database languages — SQL — Part 2: Foundation (SQL/Foundation), z wyjątkiem tego, że szczególnie umożliwia następujące proste konwersje typów, które są niedozwolone zgodnie ze standardem ANSI:
- NumericType <=> Typ logiczny
- StringType <=> BinaryType
Prawidłowe kombinacje typu danych źródłowych i docelowych w wyrażeniu CAST są podane w poniższej tabeli.
"Y" wskazuje, że kombinacja jest składniowo prawidłowa bez ograniczeń i "N" wskazuje, że kombinacja jest nieprawidłowa.
| SourceTarget | Liczbowe | String | Data | Sygnatura czasowa | Interwał | Typ logiczny | Plik binarny | Tablica | Mapa | Struktur |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Liczbowe | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| String | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N |
| Data | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Sygnatura czasowa | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N |
| Interwał | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N |
| boolean | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N |
| Plik binarny | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N |
| Tablica | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N |
| Mapa | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N |
| Struktura | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y |
-- Examples of explicit casting
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true`
> SELECT CAST('a' AS INT);
ERROR: [CAST_INVALID_INPUT] The value 'a' of the type "STRING" cannot be cast to "INT" because it is malformed.
> SELECT CAST(2147483648L AS INT);
ERROR: [CAST_OVERFLOW] The value 2147483648L of the type "BIGINT" cannot be cast to "INT" due to an overflow.
> SELECT CAST(DATE'2020-01-01' AS INT)
ERROR: [DATATYPE_MISMATCH.CAST_WITH_FUNC_SUGGESTION] Cannot resolve "CAST(DATE '2020-01-01' AS INT)" due to data type mismatch: cannot cast "DATE" to "INT".
-- `spark.sql.ansi.enabled=false` (This is a default behavior)
> SELECT cast('a' AS INT);
null
> SELECT CAST(2147483648L AS INT);
-2147483648
> SELECT CAST(DATE'2020-01-01' AS INT);
null
Przypisanie sklepu
spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy Ustawienie ma wartość domyślną ANSI. Dzięki temu ustawieniu, gdy typy danych wartości źródłowych nie są zgodne z typami kolumn docelowych, usługa Spark SQL automatycznie dodaje klauzule ANSI CAST do instrukcji INSERT.
Podczas wstawiania tabeli w ramach tych zasad platforma Spark sprawdza i odrzuca nieprawidłowe rzutowania, zgłaszając wyjątek w celu zapewnienia jakości danych. Oznacza to, że jeśli próba wstawiania nie powiedzie się z powodu niezgodności typu, nie spowoduje to częściowego zapisania danych w tabeli.
Przykłady:
-- spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy=ANSI
> CREATE TABLE test(i INT);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES (2147483648L);
ERROR: [CAST_OVERFLOW_IN_TABLE_INSERT] Fail to insert a value of "BIGINT" type into the "INT" type column `i` due to an overflow.
> INSERT INTO test VALUES ('a');
ERROR: [CAST_INVALID_INPUT ERROR] The value 'a' of the type "STRING" cannot be cast to "INT" because it is malformed
W tych przykładach pokazano, że usługa Spark SQL uniemożliwia wstawianie niezgodnych danych, zapewniając integralność danych.
Gdy spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy jest ustawiony na LEGACY, usługa Spark SQL przywraca zachowanie znane do wersji Spark 2.x. W tym trybie zamiast używać funkcji ANSI CAST, stosuje starsze operacje CAST. W ramach tych zasad nieprawidłowe rzutowania podczas wstawiania tabeli powodują wstawienie wartości NULL lub niepoprawnych wartości zamiast zgłaszania wyjątku.
Przykłady:
-- spark.sql.storeAssignmentPolicy=LEGACY
> CREATE TABLE test(i INT);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES (2147483648L);
> INSERT INTO test VALUES ('a');
> SELECT * FROM test;
-- Results
-- -2147483648 (incorrect value due to overflow)
-- null (cannot cast 'a' to INT)
Wymuszanie typu
Typ Podwyższanie poziomu i pierwszeństwo
Gdy spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest ustawiona wartość true, usługa Spark SQL używa kilku reguł, które określają sposób rozwiązywania konfliktów między typami danych.
Sednem rozwiązywania tego konfliktu jest lista pierwszeństwa typów, która określa, czy wartości danego typu danych mogą być promowane do innego typu danych niejawnie.
| Typ danych | lista pierwszeństwa (od najwęższej do najszerszej) |
|---|---|
| Byte | Byte - Short -> Int - Long ->> Decimal -> Float* -> Double> |
| Krótkie | Krótki - Int -> Długi -> Dziesiętny-> Zmiennoprzecinkowy* -> Podwójny |
| Int | Int - Long ->> Decimal -> Float* -> Double |
| Długi | Długi — dziesiętny —>> zmiennoprzecinkowy* —> podwójny |
| Dziesiętne | Liczba dziesiętna —> liczba zmiennoprzecinkowa* —> podwójna |
| float | Zmiennoprzecinkowy —> podwójny |
| Podwójny | Podwójna precyzja |
| Data | Data —> sygnatura czasowa |
| Sygnatura czasowa | Sygnatura czasowa |
| String | Sznurek |
| Plik binarny | Plik binarny |
| Typ logiczny | Boolean |
| Interwał | Interwał |
| Mapa | Mapa** |
| Tablica | Tablica** |
| Strukt | Struct** |
- Dla najmniej wspólnego typu zmienna zmiennoprzecinkowa (float) jest pomijana, aby uniknąć utraty precyzji.
** W przypadku typu złożonego reguła pierwszeństwa jest cyklicznie stosowana do jej elementów składowych.
Specjalne zasady mają zastosowanie do typu Łańcuch i nieokreślonego NULL. Wartość NULL można awansować do dowolnego innego typu, a ciąg może zostać podwyższony do dowolnego prostego typu danych.
Jest to graficzne przedstawienie listy pierwszeństwa jako drzewa kierowanego: 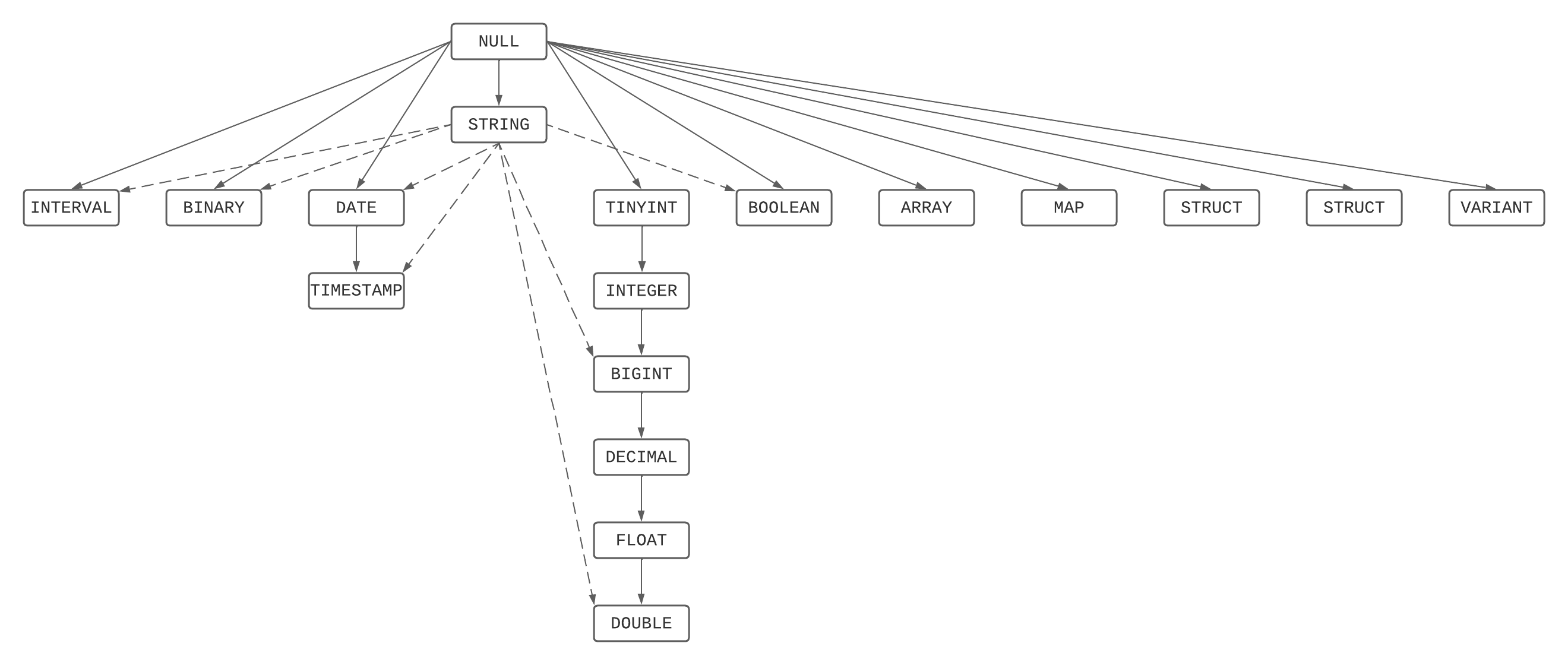
Rozwiązywanie najmniej wspólnego typu
Najmniej typowym typem z zestawu typów jest najwęższy typ osiągalny z listy pierwszeństwa przez wszystkie elementy zestawu typów.
Najmniej typowe rozpoznawanie typów jest używane do:
- Zdecyduj, czy można wywołać funkcję oczekującą parametru typu przy użyciu argumentu węższego typu.
- Utwórz typ argumentu dla funkcji, które oczekują współużytkowanego typu argumentu dla wielu parametrów, takich jak łączenie, najmniej lub największe.
- Wyprowadź typy operandów dla operatorów, takich jak operacje arytmetyczne lub porównania.
- Utwórz typ wyniku dla wyrażeń, takich jak wyrażenie przypadku.
- Wyodrębnij typy elementów, kluczy lub wartości dla konstruktorów tablic i map.
Specjalne reguły są stosowane, jeśli najmniej typowy typ jest rozpoznawany jako FLOAT. W przypadku wartości typu zmiennoprzecinkowego, jeśli którykolwiek z typów to INT, BIGINT lub DECIMAL najmniej typowy typ jest wypychany do wartości DOUBLE, aby uniknąć potencjalnej utraty cyfr.
-- The coalesce function accepts any set of argument types as long as they share a least common type.
-- The result type is the least common type of the arguments.
> SET spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true;
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1Y, 1L, NULL));
BIGINT
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1, DATE'2020-01-01'));
Error: Incompatible types [INT, DATE]
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(ARRAY(1Y), ARRAY(1L)));
ARRAY<BIGINT>
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1, 1F));
DOUBLE
> SELECT typeof(coalesce(1L, 1F));
DOUBLE
> SELECT (typeof(coalesce(1BD, 1F)));
DOUBLE
-- The substring function expects arguments of type INT for the start and length parameters.
> SELECT substring('hello', 1Y, 2);
he
> SELECT substring('hello', '1', 2);
he
> SELECT substring('hello', 1L, 2);
Error: Argument 2 requires an INT type.
> SELECT substring('hello', str, 2) FROM VALUES(CAST('1' AS STRING)) AS T(str);
Error: Argument 2 requires an INT type.
Funkcje SQL
Zachowanie niektórych funkcji SQL może być inne w trybie ANSI (spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true).
-
size: Ta funkcja zwraca wartość null dla danych wejściowych o wartości null w trybie ANSI. -
element_at:- Ta funkcja zgłasza wyjątek w przypadku używania indeksów
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionnieprawidłowych. - Ta funkcja zgłasza
NoSuchElementException, jeśli klucz nie istnieje w mapie.
- Ta funkcja zgłasza wyjątek w przypadku używania indeksów
-
elt: Ta funkcja zgłaszaArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionw przypadku używania nieprawidłowych indeksów. -
make_date: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli data wyniku jest nieprawidłowa. -
make_timestamp: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli sygnatura czasowa wyniku jest nieprawidłowa. -
make_interval: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli interwał wyników jest nieprawidłowy. -
next_day: Ta funkcja wyrzucaIllegalArgumentExceptionjeśli dane wejściowe nie są prawidłowym dniem tygodnia. -
parse_url: Ta funkcja zgłasza,IllegalArgumentExceptionjeśli ciąg wejściowy nie jest prawidłowym adresem URL. -
to_date: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego lub ciąg wzorca jest nieprawidłowy. -
to_timestamp: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego lub ciąg wzorca jest nieprawidłowy. -
to_unix_timestamp: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego lub ciąg wzorca jest nieprawidłowy. -
unix_timestamp: Ta funkcja kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego lub ciąg wzorca jest nieprawidłowy.
Operatory SQL
Zachowanie niektórych operatorów SQL może być inne w trybie ANSI (spark.sql.ansi.enabled=true).
-
array_col[index]: ten operator zgłasza wyjątek w przypadku używania nieprawidłowychArrayIndexOutOfBoundsExceptionindeksów. -
map_col[key]: Ten operator zgłaszaNoSuchElementException, jeśli klucz nie istnieje w mapie. -
CAST(string_col AS TIMESTAMP): Ten operator kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego. -
CAST(string_col AS DATE): Ten operator kończy się niepowodzeniem z wyjątkiem, jeśli nie można przeanalizować ciągu wejściowego.
Przydatne funkcje dla trybu ANSI
Gdy tryb ANSI jest włączony, zgłasza wyjątki dla nieprawidłowych operacji. Następujące funkcje SQL umożliwiają pomijanie takich wyjątków.
-
try_cast: identyczny zCAST, z tą różnicą, że zwracaNULLwynik zamiast zgłaszać wyjątek w przypadku błędu czasu wykonywania. -
try_add: identyczny z operatorem+add , z tą różnicą, że zwracaNULLwynik zamiast zgłaszać wyjątek w przepełnieniu wartości całkowitej. -
try_divide: jest identyczny z operatorem dzielenia/, z tą różnicą, że zwraca wynikNULLzamiast zgłaszać wyjątek podczas dzielenia przez 0.
Słowa kluczowe SQL
Jeśli spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest prawdziwy, usługa Spark SQL będzie używać parsera trybu ANSI.
W tym trybie usługa Spark SQL ma dwa rodzaje słów kluczowych:
- Zastrzeżone słowa kluczowe: słowa kluczowe zarezerwowane i nie mogą być używane jako identyfikatory dla tabeli, widoku, kolumny, funkcji, aliasu itp.
- Słowa kluczowe inne niż zastrzeżone: słowa kluczowe, które mają specjalne znaczenie tylko w określonych kontekstach i mogą być używane jako identyfikatory w innych kontekstach. Na przykład
EXPLAIN SELECT ...jest poleceniem, ale EXPLAIN można użyć jako identyfikatorów w innych miejscach.
Gdy tryb ANSI jest wyłączony, usługa Spark SQL ma dwa rodzaje słów kluczowych:
- Słowa kluczowe niezastrzeżone: mają tę samą definicję jak w trybie ANSI włączonym.
- Słowa kluczowe ściśle niezastrzeżone: ścisła wersja niezastrzeżonych słów kluczowych, których nie można używać jako aliasu tabeli.
Domyślnie spark.sql.ansi.enabled jest fałsz.
Poniżej znajduje się lista wszystkich słów kluczowych w usłudze Spark SQL.
| Słowo kluczowe | Tryb ANSI usługi Spark SQL | Tryb domyślny Spark SQL | SQL-2016 |
|---|---|---|---|
| DODAJ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| PO | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ALL | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ZMIENIANIE | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ZAWSZE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ANALIZA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ORAZ | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ANTY | niezarezerwowany | ścisłe-niezarezerwowane | niezarezerwowany |
| DOWOLNE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ARCHIWUM | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| TABLICA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| AS | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ASC | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| AT | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| AUTORYZACJA | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| POMIĘDZY | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| OBIE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| WIADRO | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| WIADRA | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| PRZEZ | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| PAMIĘĆ PODRĘCZNA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| KASKADA | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Przypadek | zastrzeżony | niewydzielony | zastrzeżony |
| obsada | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ZMIANA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| SPRAWDZIĆ | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| JASNY | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| KLASTER | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżony |
| zgrupowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| CODEGEN | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| COLLATE | zastrzeżony | niewykorzystany | zastrzeżony |
| KOLEKCJA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| COLUMN | zastrzeżony | niewykorzystany | zastrzeżony |
| COLUMNS | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| KOMENTARZ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| ZOBOWIĄZAĆ SIĘ | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| KOMPAKTOWY | niezarezerwowany | niewykorzystany | niezarezerwowany |
| KOMPAKTOWANIE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| WYSTĄPIENIA OBLICZENIOWE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| ZŁĄCZYĆ | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| CONSTRAINT | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| KOSZT | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| UTWÓRZ | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| KRZYŻ | zastrzeżony | ściśle niemiany | zastrzeżony |
| SZEŚCIAN | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| AKTUALNY | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| AKTUALNA_DATA | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| CURRENT_TIME | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| CURRENT_TIMESTAMP | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| BIEŻĄCY_UŻYTKOWNIK | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| DANE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| BAZA DANYCH | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone |
| BAZY DANYCH | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| DZIEŃ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| WŁAŚCIWOŚCI DB | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| zdefiniowany | niezarezerwowany | niewykorzystany | niezastrzeżony |
| USUŃ | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ODDZIELONY | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| DESC | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| OPISAĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| DFS | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowane | niezarezerwowany |
| KATALOGI | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| KATALOG | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżony |
| ODMIENNY | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ROZDZIELAĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone | niezarezerwowany |
| DIV | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | nie jest słowem kluczowym |
| Upuścić | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ELSE | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| KONIEC | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| UCIECZKA | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| UCIEKŁ | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| Z WYJĄTKIEM | zastrzeżony | strict-non-reserved | zastrzeżony |
| WYMIENIAĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ISTNIEJE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| EXPLAIN | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| EKSPORT | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niewyrezerwowane |
| Rozszerzony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżony |
| ZEWNĘTRZNY | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| EKSTRAKT | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| FAŁSZ | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| PRZYNOSIĆ | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| POLA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| FILTRUJ | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| FORMAT PLIKU | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| PIERWSZY | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| FN | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| NASTĘPUJĄCY | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżony |
| FOR | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ZAGRANICZNY | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| FORMAT | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowane |
| SFORMATOWANY | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | nienarezerwowany |
| FROM | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| PEŁNE | zastrzeżony | strict-non-reserved | zastrzeżony |
| FUNKCJA | niezastrzeżony | niewydzielone | zastrzeżony |
| FUNKCJE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| GENEROWANE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| GLOBALNE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| GRANT | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| DOTACJE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| GRUPA | zastrzeżony | niewykorzystany | zastrzeżony |
| GRUPOWANIE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| HAVING | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| GODZINA | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżone |
| JEŚLI | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | nie jest słowem kluczowym |
| IGNORE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| IMPORT | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| IN | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| INDEKS | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| INDEKSY | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| WEWNĘTRZNY | zastrzeżony | ścisły brak rezerwacji | zastrzeżony |
| INPATH | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| INPUTFORMAT | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niewykorzystany |
| INSERT | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| PRZECIĘCIE | zastrzeżony | ścisłe-niezarezerwowane | zastrzeżony |
| INTERWAŁ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| INTO | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| IS | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| POZYCJE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| JOIN | zastrzeżony | ściśle-niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| JSON | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| KLUCZ | niewykorzystany | niezarezerwowany | bez rezerwacji |
| KLUCZE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| Ostatni | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| BOCZNY | zastrzeżony | ścisłe-nierezerwowane | zastrzeżony |
| LENIWY | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| Wiodący | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowane | zastrzeżony |
| LEWO | zastrzeżony | ścisły-niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| LIKE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ILIKE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| LIMIT | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| LINIE | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| LIST | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| ŁADUNEK | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| Lokalny | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| LOKALIZACJA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| ZAMEK | niezastrzeżone | niezarezerwowane | niezarezerwowany |
| ZAMKI | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony |
| LOGICZNY | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| Makro | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| MAPA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| DOPASOWANE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| POŁĄCZYĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Minuta | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| MINUS | niezarezerwowany | ściśle niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| MIESIĄC | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| MSCK | nienazarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| NAMESPACE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| PRZESTRZENIE NAZW | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| NATURALNY | zastrzeżony | ścisłe-bez-rezerwacji | zastrzeżony |
| NIE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| NIE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| NULL | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| NULL | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| OF | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ON | zastrzeżony | ściśle-nie-zarezerwowane | zastrzeżony |
| TYLKO | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| OPCJA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony |
| OPCJE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone |
| LUB | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ZAMÓWIENIE | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| Na zewnątrz | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ZEWNĘTRZNE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| FORMAT WYJŚCIOWY | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | nierezerwowane |
| KONIEC | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| Zachodzenie | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| NAKŁADKA | niezarezerwowane | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| ZASTĄPIĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| PARTITION | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| PODZIELONA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| PARTYCJE | niezarezerwowane | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| PROCENT | nie zarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| PIVOT | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| UMIESZCZENIE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| POZYCJA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| POPRZEDZAJĄCY | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| PODSTAWOWE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| DYREKTORZY | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| WŁAŚCIWOŚCI | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Czystka | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| QUALIFY | zastrzeżony | nienastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ZAPYTANIE | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| ZAKRES | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ODBIORCA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| RECIPIENTS | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| RECORDREADER | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| PISARZ REKORDÓW | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ODZYSKAĆ | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ZMNIEJSZYĆ | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| BIBLIOGRAFIA | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| REFRESH | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| REGEXP | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | nie jest słowem kluczowym |
| REMOVE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Zmień nazwę | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| NAPRAWA | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| REPLACE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| RESET | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| SZACUNEK | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| OGRANICZAĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| REVOKE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| Prawo | zastrzeżony | ściśle-niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| RLIKE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| ROLA | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ROLE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Cofanie zmian | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ZESTAWIENIE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ROW | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| WIERSZE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| SCHEMA | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowane | niezastrzeżony |
| SCHEMATY | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | nie jest słowem kluczowym |
| SEKUNDA | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| SELECT | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| PÓŁ | niezarezerwowany | ściśle nierezerwowalne | niezarezerwowany |
| ODDZIELONE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| SERDE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| SERDEPROPERTIES | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| UŻYTKOWNIK_SESJI | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| SET | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| ZESTAWY | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| UDOSTĘPNIJ | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| SHARES | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| POKAŻ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| PRZEKRZYWIONY | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| TROCHĘ | zastrzeżony | nierezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| SORTUJ | niezastrzeżony | nierezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| SORTOWANE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ROZPOCZNIJ | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| STATYSTYKA | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| PRZECHOWYWANE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| Stratyfikować | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Struktura | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| SUBSTR | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| podciąg | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| SYNC | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| TABLE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| TABLES | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| TABLESAMPLE | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| TBLPROPERTIES | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| TEMP | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | nie jest słowem kluczowym |
| TYMCZASOWY | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| ZAKOŃCZONE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| Następnie | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| CZAS | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| TO | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| DOTYK | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowane |
| ŚLEDZENIE | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| TRANSAKCJA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| TRANSAKCJI | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| PRZEKSZTAŁCENIE | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| TRIM | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone | niezarezerwowany |
| PRAWDA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| OBCIĄĆ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| TRY_CAST | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony |
| TYP | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżone | niezastrzeżone |
| Odarchiwizuj | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| BEZGRANICZNY | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony |
| UNCACHE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowane |
| Unia | zastrzeżony | ścisły-niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| NIEPOWTARZALNY | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| NIEZNANY | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| ODBLOKOWAĆ | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| UNSET | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| UPDATE | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| UŻYJ | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| UŻYTKOWNIK | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| Używanie | zastrzeżony | surowy-niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| VALUES | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| WIDOK | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | niezarezerwowany |
| VIEWS | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |
| Kiedy… | zastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany | zastrzeżony |
| WHERE | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| WINDOW | niezastrzeżony | nienależący do rezerwacji | zastrzeżony |
| Z | zastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | zastrzeżony |
| YEAR | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżony | niezastrzeżone |
| STREFA | niezarezerwowany | niezastrzeżony | niezarezerwowany |