Smart chatbots are relegating the FAQs page to history
Whether you call them conversational agents, dialog systems, or chatbots, AI-powered bots that can hold human-like conversations are seeping into our everyday lives.
Chatbots work well in a structured environment with a predetermined dataset. Answering simple questions, for example, would be a task a chatbot could excel at. Which is why chatbots are now replacing the Frequently Asked Questions page on websites.
Here’s what you need to know about how these chatbots work and why you might never see a traditional FAQ page again:
Why Q&A?
Chatbots can be either retrieval-based or generative, which means they can either retrieve data from a predetermined dataset or generate new responses from scratch. These bots can also be open or closed domain, depending on whether the user can take the conversation anywhere and still expect a reply or whether a user needs to stick to a narrow set of inputs. The length of the responses also plays a key role in the structure of these bots.
While retrieval-based open domain chatbots would require an unrealistic number of inputs, generative open domain models would be on par with Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). At the moment, chatbots are exceedingly good at retrieving short responses based on a closed domain. This means chatbots are now ready to answer specific questions within a narrow field.
This makes them perfect for responding to questions visitors and customers might have on a certain subject. Asking a question such as, “When does the next train leave?” or “Where is the closest Indian restaurant?” is likely to yield better results than an open-ended question like “Describe Indian food,” or “How comfortable is a train journey?”
Precision is key and chatbots are good at offering precise answers to predetermined questions. Q&As, are thus the natural format for chatbots.
Q&As are naturally rule-based and chatbots can adapt to them quickly. Not only does this require minimum coding, but the datasets needed to train the machine are usually already at hand. Questions and answers are often found on websites in the form of FAQ sections. This data can be used to create a chatbot that answers any questions a user (usually a customer or site visitor) may have.
Q&As are ideal for chatbots because they can be utilized in a simple If-This-Then-That control flow code. Microsoft’s QnAMaker makes it easier to create and train an FAQ chatbot without the need for complex coding.
Creating an FAQ bot with QnAMaker and the BotFramework Microsoft's QnAMaker is a Cognitive Service tool that provides a graphical user interface to create and manipulate the FAQ knowledge base. This means there is no need for a developer to create and manage a chatbot created on the platform.
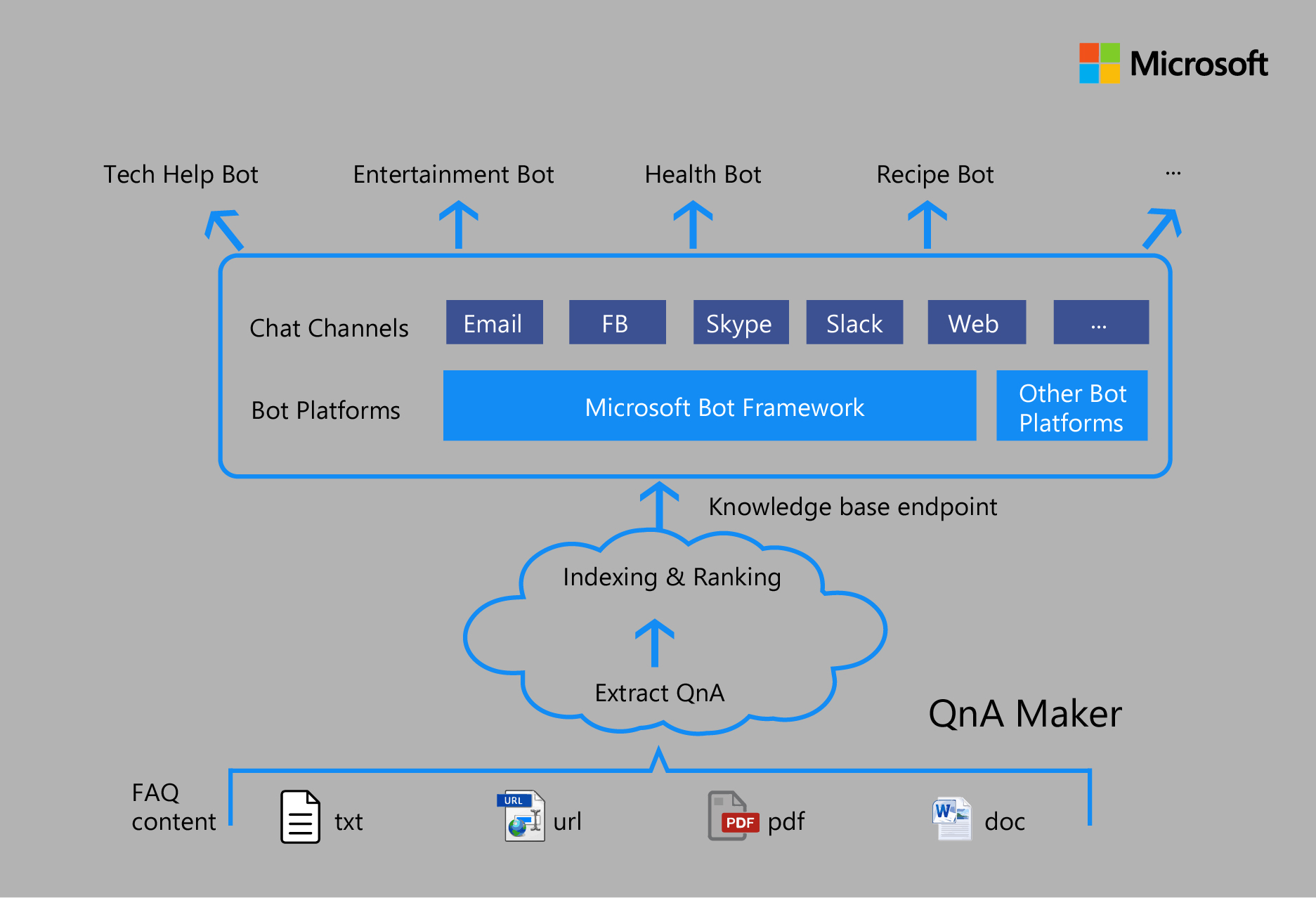
Working with the QnAMaker requires no special coding skills. The design is focused on creating a knowledge base or repository of FAQ data. Creating a new knowledge base is simply a matter of uploading files or inserting the URL for the site’s existing FAQ page. Microsoft QnA Maker also has a framework for updating the phrases or the content of certain questions or answers.
Training and maintaining the QnA bot is also easy. Users need to chat with the bot to see if the algorithm responds to every question as intended. Edits can be made within the platform even after the knowledge base has been published.
The knowledge base is the fundamental brain underlying the QnA bot. It can be shared with other users, who can edit/publish/delete the base and create changes. Changes from all users can later be merged.
This format is convenient especially for teams collaborating remotely on the same bot. A combination of industry-leading natural language processing (NLP) and cutting-edge machine learning built into the platform allows it to distill data and generate helpful answers correlated with appropriate questions.
Once the knowledge base has been sufficiently trained, you can publish the service as an HTTP endpoint, which can then be used in a Bot or any other application.
For advanced users, the service also supports features like Active Learning, managing alterations, training, etc.
Final Thoughts
Chatbots have advanced tremendously over the past few years. Quick, anytime and natural language information retrieval remains one of the most promising areas for Bots. Hence, FAQ Bots where the user can find the right answer through a conversation instead of looking through a dense FAQ page are a great use case.
Microsoft’s QnAMaker offers a simple and easy to use tool for creating chatbots that can effortlessly handle questions and submit appropriate replies. Advances in this interface could redefine the customer support interface of websites.