Szybki start: dołączanie do połączenia z pokojem
Wymagania wstępne
- Konto platformy Azure z aktywną subskrypcją. Utwórz konto bezpłatnie.
- Aktywny zasób usług komunikacyjnych i parametry połączenia. Utwórz zasób usług komunikacyjnych.
- Co najmniej dwie tożsamości użytkowników komunikacji. Tworzenie tokenów dostępu lub szybkie tworzenie tożsamości na potrzeby testowania i zarządzanie nimi.
- Utworzony pokój i uczestnik dodał do niego. Tworzenie pomieszczeń i zarządzanie nimi
Uzyskiwanie tokenu dostępu użytkownika
Jeśli już utworzono użytkowników i dodaliśmy ich jako uczestników w pokoju po sekcji "Konfigurowanie uczestników pokoju" na tej stronie, możesz bezpośrednio użyć tych użytkowników do dołączenia do pokoju.
W przeciwnym razie należy utworzyć token dostępu użytkownika dla każdego uczestnika połączenia. Dowiedz się, jak tworzyć tokeny dostępu użytkowników i zarządzać nimi. Możesz również użyć interfejsu wiersza polecenia platformy Azure i uruchomić poniższe polecenie za pomocą parametry połączenia, aby utworzyć użytkownika i token dostępu. Po utworzeniu użytkowników należy dodać je do pokoju jako uczestnicy, zanim będą mogli dołączyć do pokoju.
az communication identity token issue --scope voip --connection-string "yourConnectionString"
Aby uzyskać szczegółowe informacje, zobacz Tworzenie tokenów dostępu za pomocą interfejsu wiersza polecenia platformy Azure i zarządzanie nimi.
Uwaga
Dostęp do pokoi można uzyskać przy użyciu biblioteki interfejsu użytkownika usług Azure Communication Services. Biblioteka interfejsu użytkownika umożliwia deweloperom dodawanie klienta wywołania, który jest włączony w aplikacji Rooms z tylko kilkoma wierszami kodu.
Dołącz do połączenia z pokojem
Aby wykonać czynności opisane w tym przewodniku Szybki start, możesz pobrać przewodnik Szybki start dotyczący połączenia z pokojem w witrynie GitHub.
Wymagania wstępne
- Musisz mieć Node.js 18. Aby go zainstalować, możesz użyć instalatora msi.
Konfigurowanie
Tworzenie nowej aplikacji Node.js
Otwórz terminal lub okno polecenia utwórz nowy katalog dla aplikacji i przejdź do niego.
mkdir calling-rooms-quickstart && cd calling-rooms-quickstart
Uruchom polecenie npm init -y , aby utworzyć plik package.json z ustawieniami domyślnymi.
npm init -y
Instalowanie pakietu
npm install Użyj polecenia , aby zainstalować zestaw SDK wywołujący usługi Azure Communication Services dla języka JavaScript.
Ważne
W tym przewodniku Szybki start jest używana wersja 1.14.1zestawu SDK wywołującego usługi Azure Communication Services. Możliwość dołączania do połączenia pokoju i wyświetlania ról uczestników wywołań jest dostępna w zestawie SDK wywoływania języka JavaScript dla przeglądarek internetowych w wersji 1.13.1 lub nowszej.
npm install @azure/communication-common --save
npm install @azure/communication-calling@1.14.1 --save
Konfigurowanie struktury aplikacji
Ten przewodnik Szybki start używa pakietu webpack do tworzenia pakietów zawartości aplikacji. Uruchom następujące polecenie, aby zainstalować webpackpakiety i webpack-cliwebpack-dev-server npm i wyświetlić je jako zależności programistyczne w pliku package.json:
npm install copy-webpack-plugin@^11.0.0 webpack@^5.88.2 webpack-cli@^5.1.4 webpack-dev-server@^4.15.1 --save-dev
Oto kod:
index.html Utwórz plik w katalogu głównym projektu. Ten plik służy do konfigurowania podstawowego układu, który umożliwia użytkownikowi dołączanie do wywołania pomieszczeń.
<!-- index.html-->
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Azure Communication Services - Rooms Call Sample</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="styles.css"/>
</head>
<body>
<h4>Azure Communication Services - Rooms Call Sample</h4>
<input id="user-access-token"
type="text"
placeholder="User access token"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 500px;"/>
<button id="initialize-call-agent" type="button">Initialize Call Agent</button>
<br>
<br>
<input id="acs-room-id"
type="text"
placeholder="Enter Room Id"
style="margin-bottom:1em; width: 500px; display: block;"/>
<button id="join-room-call-button" type="button" disabled="true">Join Room Call</button>
<button id="hangup-call-button" type="button" disabled="true">Hang up Call</button>
<button id="start-video-button" type="button" disabled="true">Start Video</button>
<button id="stop-video-button" type="button" disabled="true">Stop Video</button>
<br>
<br>
<div id="connectedLabel" style="color: #13bb13;" hidden>Room Call is connected!</div>
<br>
<div id="remoteVideosGallery" style="width: 40%;" hidden>Remote participants' video streams:</div>
<br>
<div id="localVideoContainer" style="width: 30%;" hidden>Local video stream:</div>
<!-- points to the bundle generated from client.js -->
<script src="./main.js"></script>
</body>
</html>
Utwórz plik w katalogu głównym projektu o nazwie index.js , aby zawierał logikę aplikacji na potrzeby tego przewodnika Szybki start. Dodaj następujący kod do index.js:
// Make sure to install the necessary dependencies
const { CallClient, VideoStreamRenderer, LocalVideoStream } = require('@azure/communication-calling');
const { AzureCommunicationTokenCredential } = require('@azure/communication-common');
const { AzureLogger, setLogLevel } = require("@azure/logger");
// Set the log level and output
setLogLevel('verbose');
AzureLogger.log = (...args) => {
console.log(...args);
};
// Calling web sdk objects
let callAgent;
let deviceManager;
let call;
let localVideoStream;
let localVideoStreamRenderer;
// UI widgets
let userAccessToken = document.getElementById('user-access-token');
let acsRoomId = document.getElementById('acs-room-id');
let initializeCallAgentButton = document.getElementById('initialize-call-agent');
let startCallButton = document.getElementById('join-room-call-button');
let hangUpCallButton = document.getElementById('hangup-call-button');
let startVideoButton = document.getElementById('start-video-button');
let stopVideoButton = document.getElementById('stop-video-button');
let connectedLabel = document.getElementById('connectedLabel');
let remoteVideosGallery = document.getElementById('remoteVideosGallery');
let localVideoContainer = document.getElementById('localVideoContainer');
/**
* Using the CallClient, initialize a CallAgent instance with a CommunicationUserCredential which enable us to join a rooms call.
*/
initializeCallAgentButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const callClient = new CallClient();
tokenCredential = new AzureCommunicationTokenCredential(userAccessToken.value.trim());
callAgent = await callClient.createCallAgent(tokenCredential)
// Set up a camera device to use.
deviceManager = await callClient.getDeviceManager();
await deviceManager.askDevicePermission({ video: true });
await deviceManager.askDevicePermission({ audio: true });
startCallButton.disabled = false;
initializeCallAgentButton.disabled = true;
} catch(error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
startCallButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const localVideoStream = await createLocalVideoStream();
const videoOptions = localVideoStream ? { localVideoStreams: [localVideoStream] } : undefined;
const roomCallLocator = { roomId: acsRoomId.value.trim() };
call = callAgent.join(roomCallLocator, { videoOptions });
// Subscribe to the call's properties and events.
subscribeToCall(call);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a call obj.
* Listen for property changes and collection updates.
*/
subscribeToCall = (call) => {
try {
// Inspect the initial call.id value.
console.log(`Call Id: ${call.id}`);
//Subscribe to call's 'idChanged' event for value changes.
call.on('idChanged', () => {
console.log(`Call Id changed: ${call.id}`);
});
// Inspect the initial call.state value.
console.log(`Call state: ${call.state}`);
// Subscribe to call's 'stateChanged' event for value changes.
call.on('stateChanged', async () => {
console.log(`Call state changed: ${call.state}`);
if(call.state === 'Connected') {
connectedLabel.hidden = false;
startCallButton.disabled = true;
hangUpCallButton.disabled = false;
startVideoButton.disabled = false;
stopVideoButton.disabled = false;
remoteVideosGallery.hidden = false;
} else if (call.state === 'Disconnected') {
connectedLabel.hidden = true;
startCallButton.disabled = false;
hangUpCallButton.disabled = true;
startVideoButton.disabled = true;
stopVideoButton.disabled = true;
remoteVideosGallery.hidden = true;
console.log(`Call ended, call end reason={code=${call.callEndReason.code}, subCode=${call.callEndReason.subCode}}`);
}
});
call.on('isLocalVideoStartedChanged', () => {
console.log(`isLocalVideoStarted changed: ${call.isLocalVideoStarted}`);
});
console.log(`isLocalVideoStarted: ${call.isLocalVideoStarted}`);
call.localVideoStreams.forEach(async (lvs) => {
localVideoStream = lvs;
await displayLocalVideoStream();
});
call.on('localVideoStreamsUpdated', e => {
e.added.forEach(async (lvs) => {
localVideoStream = lvs;
await displayLocalVideoStream();
});
e.removed.forEach(lvs => {
removeLocalVideoStream();
});
});
// Inspect the call's current remote participants and subscribe to them.
call.remoteParticipants.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
subscribeToRemoteParticipant(remoteParticipant);
});
// Subscribe to the call's 'remoteParticipantsUpdated' event to be
// notified when new participants are added to the call or removed from the call.
call.on('remoteParticipantsUpdated', e => {
// Subscribe to new remote participants that are added to the call.
e.added.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
subscribeToRemoteParticipant(remoteParticipant)
});
// Unsubscribe from participants that are removed from the call
e.removed.forEach(remoteParticipant => {
console.log('Remote participant removed from the call.');
});
});
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a remote participant obj.
* Listen for property changes and collection updates.
*/
subscribeToRemoteParticipant = (remoteParticipant) => {
try {
// Inspect the initial remoteParticipant.state value.
console.log(`Remote participant state: ${remoteParticipant.state}`);
// Subscribe to remoteParticipant's 'stateChanged' event for value changes.
remoteParticipant.on('stateChanged', () => {
console.log(`Remote participant state changed: ${remoteParticipant.state}`);
});
// Inspect the remoteParticipants's current videoStreams and subscribe to them.
remoteParticipant.videoStreams.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream(remoteVideoStream)
});
// Subscribe to the remoteParticipant's 'videoStreamsUpdated' event to be
// notified when the remoteParticipant adds new videoStreams and removes video streams.
remoteParticipant.on('videoStreamsUpdated', e => {
// Subscribe to new remote participant's video streams that were added.
e.added.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream(remoteVideoStream)
});
// Unsubscribe from remote participant's video streams that were removed.
e.removed.forEach(remoteVideoStream => {
console.log('Remote participant video stream was removed.');
})
});
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Subscribe to a remote participant's remote video stream obj.
* You have to subscribe to the 'isAvailableChanged' event to render the remoteVideoStream. If the 'isAvailable' property
* changes to 'true', a remote participant is sending a stream. Whenever availability of a remote stream changes
* you can choose to destroy the whole 'Renderer', a specific 'RendererView' or keep them, but this will result in displaying blank video frame.
*/
subscribeToRemoteVideoStream = async (remoteVideoStream) => {
let renderer = new VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream);
let view;
let remoteVideoContainer = document.createElement('div');
remoteVideoContainer.className = 'remote-video-container';
const createView = async () => {
// Create a renderer view for the remote video stream.
view = await renderer.createView();
// Attach the renderer view to the UI.
remoteVideoContainer.appendChild(view.target);
remoteVideosGallery.appendChild(remoteVideoContainer);
}
// Remote participant has switched video on/off
remoteVideoStream.on('isAvailableChanged', async () => {
try {
if (remoteVideoStream.isAvailable) {
await createView();
} else {
view.dispose();
remoteVideosGallery.removeChild(remoteVideoContainer);
}
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
});
// Remote participant has video on initially.
if (remoteVideoStream.isAvailable) {
try {
await createView();
} catch (e) {
console.error(e);
}
}
}
/**
* Start your local video stream.
* This will send your local video stream to remote participants so they can view it.
*/
startVideoButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
const localVideoStream = await createLocalVideoStream();
await call.startVideo(localVideoStream);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Stop your local video stream.
* This will stop your local video stream from being sent to remote participants.
*/
stopVideoButton.onclick = async () => {
try {
await call.stopVideo(localVideoStream);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* To render a LocalVideoStream, you need to create a new instance of VideoStreamRenderer, and then
* create a new VideoStreamRendererView instance using the asynchronous createView() method.
* You may then attach view.target to any UI element.
*/
createLocalVideoStream = async () => {
const camera = (await deviceManager.getCameras())[0];
if (camera) {
return new LocalVideoStream(camera);
} else {
console.error(`No camera device found on the system`);
}
}
/**
* Display your local video stream preview in your UI
*/
displayLocalVideoStream = async () => {
try {
localVideoStreamRenderer = new VideoStreamRenderer(localVideoStream);
const view = await localVideoStreamRenderer.createView();
localVideoContainer.hidden = false;
localVideoContainer.appendChild(view.target);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* Remove your local video stream preview from your UI
*/
removeLocalVideoStream = async() => {
try {
localVideoStreamRenderer.dispose();
localVideoContainer.hidden = true;
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
}
}
/**
* End current room call
*/
hangUpCallButton.addEventListener("click", async () => {
await call.hangUp();
});
Dodawanie kodu serwera lokalnego webpack
Utwórz plik w katalogu głównym projektu o nazwie webpack.config.js zawierający logikę serwera lokalnego dla tego przewodnika Szybki start. Dodaj następujący kod, aby webpack.config.js:
const path = require('path');
const CopyPlugin = require("copy-webpack-plugin");
module.exports = {
mode: 'development',
entry: './index.js',
output: {
filename: 'main.js',
path: path.resolve(__dirname, 'dist'),
},
devServer: {
static: {
directory: path.join(__dirname, './')
},
},
plugins: [
new CopyPlugin({
patterns: [
'./index.html'
]
}),
]
};
Uruchamianie kodu
Użyj polecenia , webpack-dev-server aby skompilować i uruchomić aplikację. Uruchom następujące polecenie, aby utworzyć pakiet hosta aplikacji na lokalnym serwerze internetowym:
`npx webpack serve --config webpack.config.js`
- Otwórz przeglądarkę, przejdź do http://localhost:8080/.
- W pierwszym polu wejściowym wprowadź prawidłowy token dostępu użytkownika.
- Kliknij pozycję "Zainicjuj agenta połączeń" i wprowadź swój identyfikator pokoju.
- Kliknij pozycję "Dołącz do połączenia w pokoju"
Połączenie z pokojem zostało pomyślnie dołączone!
Informacje na temat dołączania do połączenia z pokojem
Cały kod dodany w aplikacji Szybki start umożliwił pomyślne uruchomienie i dołączenie połączenia pokoju. Poniżej znajduje się więcej informacji na temat dodatkowych metod/procedur obsługi, do których można uzyskać dostęp w usłudze Rooms w celu rozszerzenia funkcji w aplikacji.
Aby wyświetlić rolę uczestników lokalnego lub zdalnego wywołania, zasubskrybuj procedurę obsługi poniżej.
// Subscribe to changes for your role in a call
const callRoleChangedHandler = () => {
console.log(call.role);
};
call.on('roleChanged', callRoleChangedHandler);
// Subscribe to role changes for remote participants
const subscribeToRemoteParticipant = (remoteParticipant) => {
remoteParticipant.on('roleChanged', () => {
console.log(remoteParticipant.role);
});
}
Więcej informacji na temat ról uczestników rozmów w pokoju można dowiedzieć się w dokumentacji koncepcji pomieszczeń.
Dołącz do połączenia z pokojem
Aby wykonać czynności opisane w tym przewodniku Szybki start, możesz pobrać przewodnik Szybki start dotyczący połączenia z pokojem w witrynie GitHub.
Konfigurowanie
Tworzenie projektu Xcode
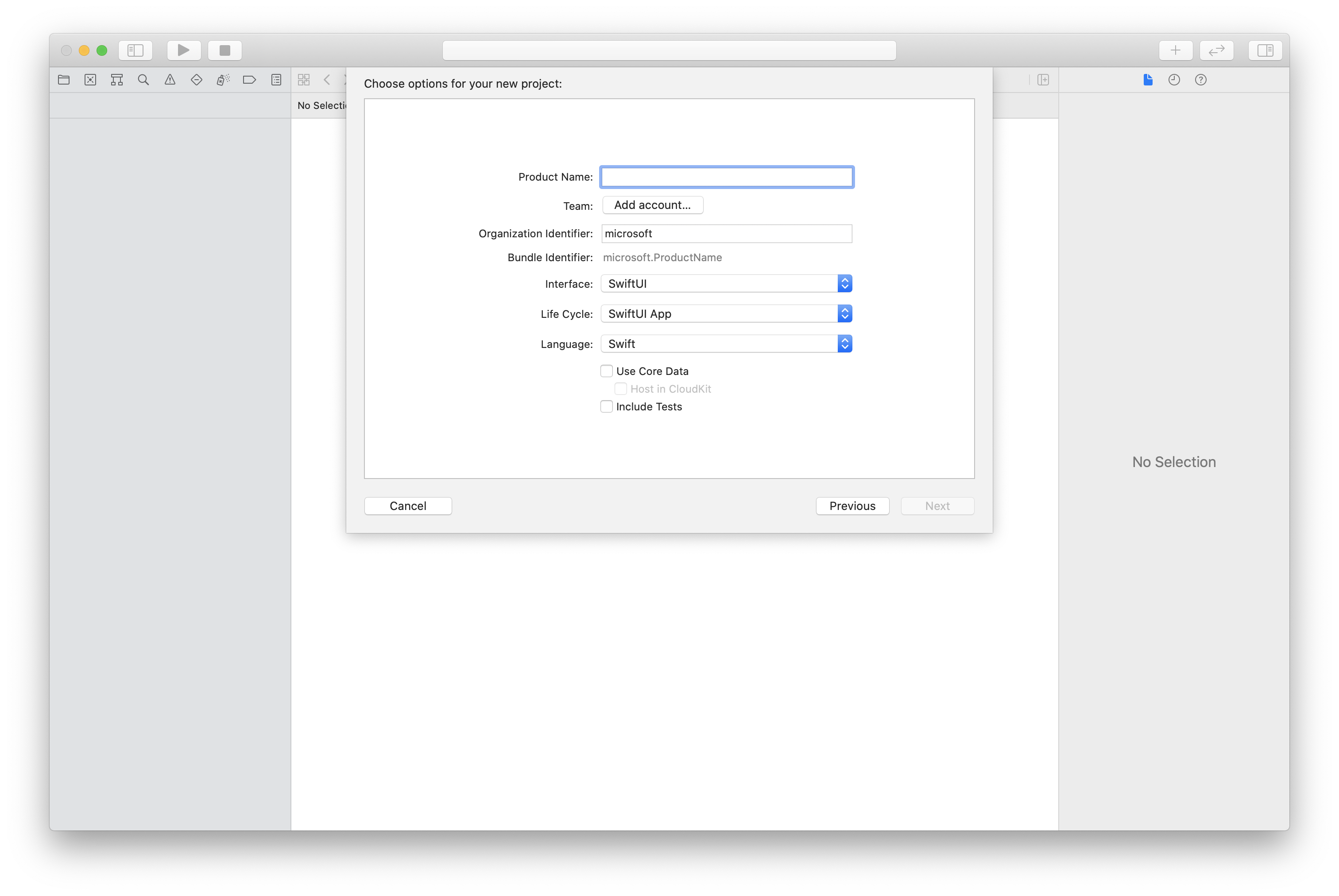
W programie Xcode utwórz nowy projekt systemu iOS i wybierz szablon Aplikacja z jednym widokiem. W tym samouczku jest używana struktura SwiftUI, dlatego należy ustawić język na swift i interfejs użytkownika na swiftUI.
Instalowanie platformy CocoaPods
Skorzystaj z tego przewodnika, aby zainstalować narzędzie CocoaPods na komputerze Mac.
Instalowanie pakietu i zależności za pomocą narzędzia CocoaPods
Aby utworzyć plik Podfile dla aplikacji, otwórz terminal i przejdź do folderu projektu i uruchom init zasobnika.
Dodaj następujący kod do pliku Podfile i zapisz:
platform :ios, '13.0'
use_frameworks!
target 'roomsquickstart' do
pod 'AzureCommunicationCalling', '~> 2.5.0'
end
Uruchom instalację zasobnika.
Otwórz plik za
.xcworkspacepomocą programu Xcode.
Żądanie dostępu do mikrofonu i kamery
Aby uzyskać dostęp do mikrofonu i aparatu urządzenia, należy zaktualizować listę właściwości informacji aplikacji za pomocą elementów NSMicrophoneUsageDescription i NSCameraUsageDescription. Ustaw skojarzona wartość na ciąg, który zostanie uwzględniony w oknie dialogowym używanym przez system do żądania dostępu od użytkownika.
Kliknij prawym przyciskiem myszy Info.plist wpis drzewa projektu i wybierz pozycję Otwórz jako > kod źródłowy. Dodaj następujące wiersze sekcji najwyższego poziomu <dict> , a następnie zapisz plik.
<key>NSMicrophoneUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need microphone access for VOIP calling.</string>
<key>NSCameraUsageDescription</key>
<string>Need camera access for video calling</string>
Konfigurowanie struktury aplikacji
Otwórz plik projektu ContentView.swift i dodaj deklarację importu na początku pliku, aby zaimportować bibliotekę AzureCommunicationCalling i AVFoundation. Funkcja AVFoundation służy do przechwytywania uprawnień dźwięku z kodu.
import AzureCommunicationCalling
import AVFoundation
Model obiektów
Następujące klasy i interfejsy obsługują niektóre główne funkcje zestawu SDK wywołującego usługi Azure Communication Services dla systemu iOS.
| Nazwa/nazwisko | opis |
|---|---|
| CallClient | Obiekt CallClient jest głównym punktem wejścia do zestawu Sdk wywołującego. |
| CallAgent | CallAgent służy do uruchamiania wywołań i zarządzania nimi. |
| CommunicationTokenCredential | Element CommunicationTokenCredential jest używany jako poświadczenie tokenu do utworzenia wystąpienia obiektu CallAgent. |
| CommunicationIdentifier | Element CommunicationIdentifier służy do reprezentowania tożsamości użytkownika i może mieć jedną z następujących wartości: CommunicationUserIdentifier/PhoneNumberIdentifier/CallingApplication. |
| RoomCallLocator | Funkcja RoomCallLocator jest używana przez callAgent do dołączenia do połączenia pokoju |
Tworzenie agenta połączeń
Zastąp implementację struktury ContentView prostymi kontrolkami interfejsu użytkownika, które umożliwiają użytkownikowi zainicjowanie i zakończenie wywołania. W tym przewodniku Szybki start dołączymy logikę biznesową do tych kontrolek.
struct ContentView: View {
@State var roomId: String = ""
@State var callObserver:CallObserver?
@State var previewRenderer: VideoStreamRenderer? = nil
@State var previewView: RendererView? = nil
@State var sendingLocalVideo: Bool = false
@State var speakerEnabled: Bool = false
@State var muted: Bool = false
@State var callClient: CallClient?
@State var call: Call?
@State var callHandler: CallHandler?
@State var callAgent: CallAgent?
@State var deviceManager: DeviceManager?
@State var localVideoStreams: [LocalVideoStream]?
@State var callState: String = "Unknown"
@State var showAlert: Bool = false
@State var alertMessage: String = ""
@State var participants: [[Participant]] = [[]]
var body: some View {
NavigationView {
ZStack {
if (call == nil) {
Form {
Section {
TextField("Room ID", text: $roomId)
Button(action: joinRoomCall) {
Text("Join Room Call")
}
}
}
.navigationBarTitle("Rooms Quickstart")
} else {
ZStack {
VStack {
ForEach(participants, id:\.self) { array in
HStack {
ForEach(array, id:\.self) { participant in
ParticipantView(self, participant)
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: 200, alignment: .topLeading)
}
}
.background(Color.black)
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity, alignment: .topLeading)
VStack {
if (sendingLocalVideo) {
HStack {
RenderInboundVideoView(view: $previewView)
.frame(width:90, height:160)
.padding(10)
.background(Color.green)
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .trailing)
}
HStack {
Button(action: toggleMute) {
HStack {
Text(muted ? "Unmute" : "Mute")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.lightGray))
}
Button(action: toggleLocalVideo) {
HStack {
Text(sendingLocalVideo ? "Video-Off" : "Video-On")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.lightGray))
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .leading)
.padding(.horizontal, 10)
.padding(.vertical, 5)
HStack {
Button(action: leaveRoomCall) {
HStack {
Text("Leave Room Call")
}
.frame(width:80)
.padding(.vertical, 10)
.background(Color(.red))
}
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, alignment: .leading)
.padding(.horizontal, 10)
.padding(.vertical, 5)
HStack {
Text("Status:")
Text(callState)
}
.padding(.vertical, 10)
}
.frame(maxWidth: .infinity, maxHeight: .infinity, alignment: .bottomLeading)
}
}
}
}
.onAppear{
// Authenticate the client
// Initialize the CallAgent and access Device Manager
// Ask for permissions
}
}
}
//Functions and Observers
struct HomePageView_Previews: PreviewProvider {
static var previews: some View {
HomePageView()
}
}
Uwierzytelnianie użytkownika
Aby zainicjować wystąpienie callAgent, potrzebujemy tokenu dostępu użytkownika, który umożliwi nam dołączanie wywołań pokoju.
Po utworzeniu tokenu dodaj następujący kod do wywołania zwrotnego onAppear w pliku ContentView.swift. Musisz zastąpić <USER ACCESS TOKEN> prawidłowym tokenem dostępu użytkownika dla zasobu:
var userCredential: CommunicationTokenCredential?
do {
userCredential = try CommunicationTokenCredential(token: "<USER ACCESS TOKEN>")
} catch {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create user credential.")
return
}
Inicjowanie klasy CallAgent i uzyskiwanie dostępu do Menedżer urządzeń
Aby utworzyć wystąpienie callAgent z obiektu CallClient, użyj callClient.createCallAgent metody, która asynchronicznie zwraca obiekt CallAgent po zainicjowaniu. DeviceManager umożliwia wyliczanie urządzeń lokalnych, które mogą być używane w wywołaniu do przesyłania strumieni audio/wideo. Umożliwia również zażądanie uprawnień od użytkownika w celu uzyskania dostępu do mikrofonu/kamery.
self.callClient = CallClient()
self.callClient?.createCallAgent(userCredential: userCredential!) { (agent, error) in
if error != nil {
print("ERROR: It was not possible to create a call agent.")
return
} else {
self.callAgent = agent
print("Call agent successfully created.")
self.callAgent!.delegate = callHandler
self.callClient?.getDeviceManager { (deviceManager, error) in
if (error == nil) {
print("Got device manager instance")
self.deviceManager = deviceManager
} else {
print("Failed to get device manager instance")
}
}
}
}
Poproś o uprawnienia
Musimy dodać następujący kod do wywołania zwrotnego onAppear , aby poprosić o uprawnienia do audio i wideo.
AVAudioSession.sharedInstance().requestRecordPermission { (granted) in
if granted {
AVCaptureDevice.requestAccess(for: .video) { (videoGranted) in
/* NO OPERATION */
}
}
}
Dołączanie do połączenia pokoju
Metoda joinRoomCall jest ustawiana jako akcja, która będzie wykonywana po naciśnięciu przycisku Dołącz do wywołania pokoju. W tym przewodniku Szybki start połączenia są domyślnie tylko audio, ale mogą mieć włączone wideo po dołączeniu pokoju.
func joinRoomCall() {
if self.callAgent == nil {
print("CallAgent not initialized")
return
}
if (self.roomId.isEmpty) {
print("Room ID not set")
return
}
// Join a call with a Room ID
let options = JoinCallOptions()
let audioOptions = AudioOptions()
audioOptions.muted = self.muted
options.audioOptions = audioOptions
let roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId: roomId)
self.callAgent!.join(with: roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions: options) { (call, error) in
self.setCallAndObserver(call: call, error: error)
}
}
CallObserver służy do zarządzania zdarzeniami w połowie połączenia i uczestnikami zdalnymi. Ustawimy obserwatorów w setCallAndObserver funkcji .
func setCallAndObserver(call:Call!, error:Error?) {
if (error == nil) {
self.call = call
self.callObserver = CallObserver(view:self)
self.call!.delegate = self.callObserver
if (self.call!.state == CallState.connected) {
self.callObserver!.handleInitialCallState(call: call)
}
} else {
print("Failed to get call object")
}
}
Opuszczanie połączenia z pokojem
Metoda leaveRoomCall jest ustawiana jako akcja, która będzie wykonywana po naciśnięciu przycisku Opuść wywołanie pokoju. Obsługuje opuszczanie wywołania i czyszczenie wszystkich utworzonych zasobów.
private func leaveRoomCall() {
if (self.sendingLocalVideo) {
self.call!.stopVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Failed to stop video")
} else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = false
self.previewView = nil
self.previewRenderer?.dispose()
self.previewRenderer = nil
}
}
}
self.call?.hangUp(options: nil) { (error) in }
self.participants.removeAll()
self.call?.delegate = nil
self.call = nil
}
Emisja wideo
Podczas rozmowy w pokoju możemy użyć startVideo lub uruchomić lub stopVideo zatrzymać wysyłanie LocalVideoStream do uczestników zdalnych.
func toggleLocalVideo() {
if (self.sendingLocalVideo) {
self.call!.stopVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Cannot stop video")
} else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = false
self.previewView = nil
self.previewRenderer!.dispose()
self.previewRenderer = nil
}
}
} else {
let availableCameras = self.deviceManager!.cameras
let scalingMode:ScalingMode = .crop
if (self.localVideoStreams == nil) {
self.localVideoStreams = [LocalVideoStream]()
}
self.localVideoStreams!.append(LocalVideoStream(camera: availableCameras.first!))
self.previewRenderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(localVideoStream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!)
self.previewView = try! previewRenderer!.createView(withOptions: CreateViewOptions(scalingMode:scalingMode))
self.call!.startVideo(stream: self.localVideoStreams!.first!) { (error) in
if (error != nil) {
print("Cannot start video")
}
else {
self.sendingLocalVideo = true
}
}
}
}
Wyciszanie lokalnego dźwięku
Podczas rozmowy w pokoju możemy użyć mute lub unMute wyciszyć lub wyciszyć mikrofon.
func toggleMute() {
if (self.muted) {
call!.unmuteOutgoingAudio(completionHandler: { (error) in
if error == nil {
self.muted = false
}
})
} else {
call!.muteOutgoingAudio(completionHandler: { (error) in
if error == nil {
self.muted = true
}
})
}
}
Obsługa aktualizacji wywołań
Aby obsługiwać aktualizacje wywołań, zaimplementuj element CallHandler do obsługi zdarzeń aktualizacji. Umieść następującą implementację w pliku CallHandler.swift.
final class CallHandler: NSObject, CallAgentDelegate {
public var owner: ContentView?
private static var instance: CallHandler?
static func getOrCreateInstance() -> CallHandler {
if let c = instance {
return c
}
instance = CallHandler()
return instance!
}
private override init() {}
public func callAgent(_ callAgent: CallAgent, didUpdateCalls args: CallsUpdatedEventArgs) {
if let removedCall = args.removedCalls.first {
owner?.call = nil
}
}
}
Musimy utworzyć wystąpienie klasy CallHandler , dodając następujący kod do wywołania zwrotnego onAppear w pliku ContentView.swift:
self.callHandler = CallHandler.getOrCreateInstance()
self.callHandler.owner = self
Ustaw delegata na callAgent po pomyślnym utworzeniu callAgent:
self.callAgent!.delegate = callHandler
Zdalne zarządzanie uczestnikami
Wszyscy uczestnicy zdalni są reprezentowani przez RemoteParticipant typ i są dostępne za pośrednictwem remoteParticipants kolekcji w wystąpieniu wywołania. Możemy zaimplementować klasę Participant do zarządzania aktualizacjami na zdalnych strumieniach wideo zdalnych uczestników między innymi.
class Participant: NSObject, RemoteParticipantDelegate, ObservableObject {
private var videoStreamCount = 0
private let innerParticipant:RemoteParticipant
private let call:Call
private var renderedRemoteVideoStream:RemoteVideoStream?
@Published var state:ParticipantState = ParticipantState.disconnected
@Published var isMuted:Bool = false
@Published var isSpeaking:Bool = false
@Published var hasVideo:Bool = false
@Published var displayName:String = ""
@Published var videoOn:Bool = true
@Published var renderer:VideoStreamRenderer? = nil
@Published var rendererView:RendererView? = nil
@Published var scalingMode: ScalingMode = .fit
init(_ call: Call, _ innerParticipant: RemoteParticipant) {
self.call = call
self.innerParticipant = innerParticipant
self.displayName = innerParticipant.displayName
super.init()
self.innerParticipant.delegate = self
self.state = innerParticipant.state
self.isMuted = innerParticipant.isMuted
self.isSpeaking = innerParticipant.isSpeaking
self.hasVideo = innerParticipant.videoStreams.count > 0
if(self.hasVideo) {
handleInitialRemoteVideo()
}
}
deinit {
self.innerParticipant.delegate = nil
}
func getMri() -> String {
Utilities.toMri(innerParticipant.identifier)
}
func set(scalingMode: ScalingMode) {
if self.rendererView != nil {
self.rendererView!.update(scalingMode: scalingMode)
}
self.scalingMode = scalingMode
}
func handleInitialRemoteVideo() {
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
}
func toggleVideo() {
if videoOn {
rendererView = nil
renderer?.dispose()
videoOn = false
}
else {
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: innerParticipant.videoStreams[0])
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
videoOn = true
}
}
func remoteParticipant(_ remoteParticipant: RemoteParticipant, didUpdateVideoStreams args: RemoteVideoStreamsEventArgs) {
let hadVideo = hasVideo
hasVideo = innerParticipant.videoStreams.count > 0
if videoOn {
if hadVideo && !hasVideo {
// Remote user stopped sharing
rendererView = nil
renderer?.dispose()
} else if hasVideo && !hadVideo {
// remote user started sharing
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
} else if hadVideo && hasVideo {
if args.addedRemoteVideoStreams.count > 0 {
if renderedRemoteVideoStream?.id == args.addedRemoteVideoStreams[0].id {
return
}
// remote user added a second video, so switch to the latest one
guard let rendererTemp = renderer else {
return
}
rendererTemp.dispose()
renderedRemoteVideoStream = args.addedRemoteVideoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
} else if args.removedRemoteVideoStreams.count > 0 {
if args.removedRemoteVideoStreams[0].id == renderedRemoteVideoStream!.id {
// remote user stopped sharing video that we were rendering but is sharing
// another video that we can render
renderer!.dispose()
renderedRemoteVideoStream = innerParticipant.videoStreams[0]
renderer = try! VideoStreamRenderer(remoteVideoStream: renderedRemoteVideoStream!)
rendererView = try! renderer!.createView()
}
}
}
}
}
func remoteParticipant(_ remoteParticipant: RemoteParticipant, didChangeDisplayName args: PropertyChangedEventArgs) {
self.displayName = innerParticipant.displayName
}
}
class Utilities {
@available(*, unavailable) private init() {}
public static func toMri(_ id: CommunicationIdentifier?) -> String {
if id is CommunicationUserIdentifier {
let communicationUserIdentifier = id as! CommunicationUserIdentifier
return communicationUserIdentifier.identifier
} else {
return "<nil>"
}
}
}
Strumienie wideo uczestnika zdalnego
Możemy utworzyć element ParticipantView do obsługi renderowania strumieni wideo uczestników zdalnych. Umieść implementację w ParticipantView.swift
struct ParticipantView : View, Hashable {
static func == (lhs: ParticipantView, rhs: ParticipantView) -> Bool {
return lhs.participant.getMri() == rhs.participant.getMri()
}
private let owner: HomePageView
@State var showPopUp: Bool = false
@State var videoHeight = CGFloat(200)
@ObservedObject private var participant:Participant
var body: some View {
ZStack {
if (participant.rendererView != nil) {
HStack {
RenderInboundVideoView(view: $participant.rendererView)
}
.background(Color(.black))
.frame(height: videoHeight)
.animation(Animation.default)
} else {
HStack {
Text("No incoming video")
}
.background(Color(.red))
.frame(height: videoHeight)
}
}
}
func hash(into hasher: inout Hasher) {
hasher.combine(participant.getMri())
}
init(_ owner: HomePageView, _ participant: Participant) {
self.owner = owner
self.participant = participant
}
func resizeVideo() {
videoHeight = videoHeight == 200 ? 150 : 200
}
func showAlert(_ title: String, _ message: String) {
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.1) {
self.owner.alertMessage = message
self.owner.showAlert = true
}
}
}
struct RenderInboundVideoView: UIViewRepresentable {
@Binding var view:RendererView!
func makeUIView(context: Context) -> UIView {
return UIView()
}
func updateUIView(_ uiView: UIView, context: Context) {
for view in uiView.subviews {
view.removeFromSuperview()
}
if (view != nil) {
uiView.addSubview(view)
}
}
}
Subskrybowanie zdarzeń
Możemy zaimplementować klasę CallObserver , aby subskrybować kolekcję zdarzeń, aby otrzymywać powiadomienia, gdy wartości, takie jak remoteParticipants, zmieniają się podczas wywołania.
public class CallObserver : NSObject, CallDelegate
{
private var owner: ContentView
private var firstTimeCallConnected: Bool = true
init(view: ContentView) {
owner = view
super.init()
}
public func call(_ call: Call, didChangeState args: PropertyChangedEventArgs) {
let state = CallObserver.callStateToString(state:call.state)
owner.callState = state
if (call.state == CallState.disconnected) {
owner.leaveRoomCall()
}
else if (call.state == CallState.connected) {
if(self.firstTimeCallConnected) {
self.handleInitialCallState(call: call);
}
self.firstTimeCallConnected = false;
}
}
public func handleInitialCallState(call: Call) {
// We want to build a matrix with max 2 columns
owner.callState = CallObserver.callStateToString(state:call.state)
var participants = [Participant]()
// Add older/existing participants
owner.participants.forEach { (existingParticipants: [Participant]) in
participants.append(contentsOf: existingParticipants)
}
owner.participants.removeAll()
// Add new participants to the collection
for remoteParticipant in call.remoteParticipants {
let mri = Utilities.toMri(remoteParticipant.identifier)
let found = participants.contains { (participant) -> Bool in
participant.getMri() == mri
}
if !found {
let participant = Participant(call, remoteParticipant)
participants.append(participant)
}
}
// Convert 1-D array into a 2-D array with 2 columns
var indexOfParticipant = 0
while indexOfParticipant < participants.count {
var newParticipants = [Participant]()
newParticipants.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
if (indexOfParticipant < participants.count) {
newParticipants.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
}
owner.participants.append(newParticipants)
}
}
public func call(_ call: Call, didUpdateRemoteParticipant args: ParticipantsUpdatedEventArgs) {
var participants = [Participant]()
// Add older/existing participants
owner.participants.forEach { (existingParticipants: [Participant]) in
participants.append(contentsOf: existingParticipants)
}
owner.participants.removeAll()
// Remove deleted participants from the collection
args.removedParticipants.forEach { p in
let mri = Utilities.toMri(p.identifier)
participants.removeAll { (participant) -> Bool in
participant.getMri() == mri
}
}
// Add new participants to the collection
for remoteParticipant in args.addedParticipants {
let mri = Utilities.toMri(remoteParticipant.identifier)
let found = participants.contains { (view) -> Bool in
view.getMri() == mri
}
if !found {
let participant = Participant(call, remoteParticipant)
participants.append(participant)
}
}
// Convert 1-D array into a 2-D array with 2 columns
var indexOfParticipant = 0
while indexOfParticipant < participants.count {
var array = [Participant]()
array.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
if (indexOfParticipant < participants.count) {
array.append(participants[indexOfParticipant])
indexOfParticipant += 1
}
owner.participants.append(array)
}
}
private static func callStateToString(state:CallState) -> String {
switch state {
case .connected: return "Connected"
case .connecting: return "Connecting"
case .disconnected: return "Disconnected"
case .disconnecting: return "Disconnecting"
case .none: return "None"
default: return "Unknown"
}
}
}
Uruchamianie kodu
Aplikację można skompilować i uruchomić w symulatorze systemu iOS, wybierając pozycję Uruchom produkt > lub za pomocą skrótu klawiaturowego (⌘-R).
Możliwość dołączenia do połączenia pokoju i wyświetlania ról uczestników połączeń jest dostępna w zestawie iOS Mobile Calling SDK w wersji 2.5.0 lub nowszej.
Więcej informacji na temat ról uczestników rozmów w pokoju można dowiedzieć się w dokumentacji koncepcji pomieszczeń.
Przykładowa aplikacja
Aby wykonać czynności opisane w tym przewodniku Szybki start, możesz pobrać przewodnik Szybki start dotyczący połączenia z pokojem w witrynie GitHub.
Konfigurowanie projektu
Tworzenie aplikacji systemu Android z pustym działaniem
W programie Android Studio utwórz nowy projekt:
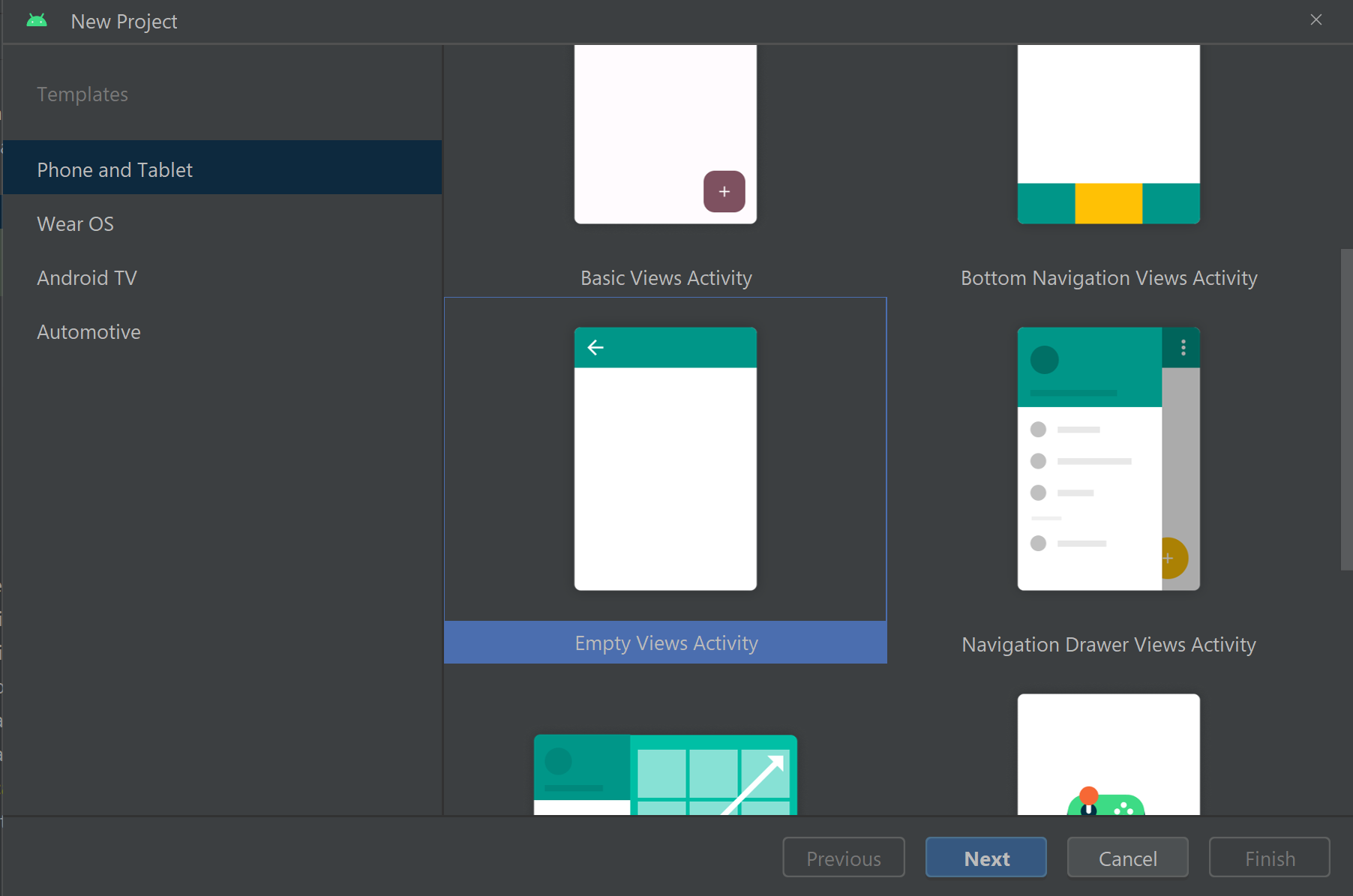
Nadaj projektowi nazwę Room Call Quickstart i wybierz pozycję Kotlin.
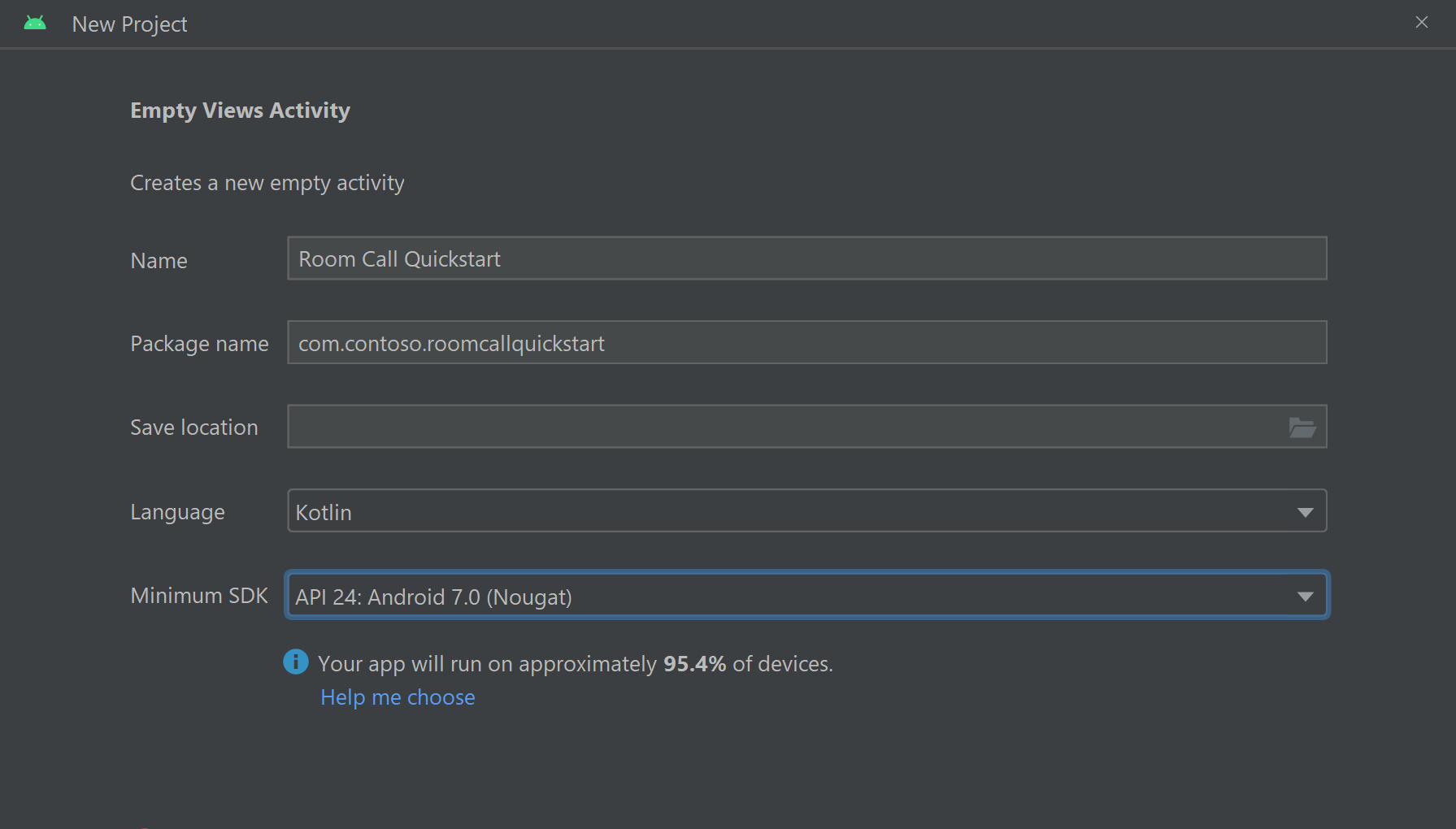
Instalowanie pakietu
Na poziomie build.gradlemodułu dependencies dodaj następujący wiersz do sekcji .
dependencies {
...
//Ability to join a Rooms calls is available in 2.4.0 or above.
implementation 'com.azure.android:azure-communication-calling:2.4.0'
...
}
Dodawanie uprawnień do manifestu aplikacji
Aby zażądać uprawnień wymaganych do wykonania wywołania, musisz najpierw zadeklarować uprawnienia w manifeście aplikacji (app/src/main/AndroidManifest.xml). Skopiuj następujące elementy do pliku manifestu:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.camera"
android:required="false" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_WIFI_STATE" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.RECORD_AUDIO" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.CAMERA" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/Theme.AppTheme">
<!--Our Calling SDK depends on the Apache HTTP SDK.
When targeting Android SDK 28+, this library needs to be explicitly referenced.
See https://developer.android.com/about/versions/pie/android-9.0-changes-28#apache-p-->
<uses-library android:name="org.apache.http.legacy" android:required="false"/>
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:exported="true">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
Konfigurowanie układu aplikacji
Potrzebujesz wprowadzania tekstu dla identyfikatora pokoju, przycisku do umieszczenia połączenia i dodatkowego przycisku w celu zawieszenia połączenia.
Przejdź do app/src/main/res/layout/activity_main.xmlpliku i zastąp zawartość pliku następującym kodem:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_role"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Role:"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/text_call_status"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Call Status"
android:textSize="16sp"
android:textStyle="bold"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
android:layout_marginTop="48dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/room_id"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:ems="10"
android:hint="Room ID"
android:inputType="textPersonName"
android:layout_marginTop="100dp"
android:layout_marginHorizontal="20dp"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="260dp"
android:gravity="center"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent">
<Button
android:id="@+id/call_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="32dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Start Call" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/hangup_button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Hangup" />
</LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
Tworzenie głównego działania
Po utworzeniu układu możesz dodać logikę, aby uruchomić wywołanie pokoju. Działanie obsługuje żądanie uprawnień środowiska uruchomieniowego, tworzenie agenta wywołania i umieszczanie wywołania po naciśnięciu przycisku.
Metoda onCreate wywołuje metodę getAllPermissions i createAgent, i dodaje powiązania dla przycisku wywołania.
To zdarzenie występuje tylko raz po utworzeniu działania. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji na temat onCreateprogramu , zobacz przewodnik Omówienie cyklu życia działania.
Przejdź do pliku MainActivity.kt i zastąp zawartość następującym kodem:
package com.contoso.roomscallquickstart
import android.Manifest
import android.annotation.SuppressLint
import android.content.pm.PackageManager
import android.media.AudioManager
import android.os.Bundle
import android.widget.Button
import android.widget.EditText
import android.widget.TextView
import android.widget.Toast
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity
import androidx.core.app.ActivityCompat
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.Call
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallAgent
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.CallClient
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.HangUpOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.JoinCallOptions
import com.azure.android.communication.calling.RoomCallLocator
import com.azure.android.communication.common.CommunicationTokenCredential
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException
class MainActivity : AppCompatActivity() {
private val allPermissions = arrayOf(
Manifest.permission.RECORD_AUDIO,
Manifest.permission.CAMERA,
Manifest.permission.READ_PHONE_STATE
)
private val userToken = "<ACS_USER_TOKEN>"
private lateinit var callAgent: CallAgent
private var call: Call? = null
private lateinit var roleTextView: TextView
private lateinit var statusView: TextView
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main)
getAllPermissions()
createCallAgent()
val callButton: Button = findViewById(R.id.call_button)
callButton.setOnClickListener { startCall() }
val hangupButton: Button = findViewById(R.id.hangup_button)
hangupButton.setOnClickListener { endCall() }
roleTextView = findViewById(R.id.text_role)
statusView = findViewById(R.id.text_call_status)
volumeControlStream = AudioManager.STREAM_VOICE_CALL
}
/**
* Start a call
*/
private fun startCall() {
if (userToken.startsWith("<")) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter token in source code", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return
}
val roomIdView: EditText = findViewById(R.id.room_id)
val roomId = roomIdView.text.toString()
if (roomId.isEmpty()) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Please enter room ID", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
return
}
val joinCallOptions = JoinCallOptions()
val roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId)
call = callAgent.join(applicationContext, roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions)
call?.addOnStateChangedListener { setCallStatus(call?.state.toString()) }
call?.addOnRoleChangedListener { setRoleText(call?.callParticipantRole.toString()) }
}
/**
* Ends the call previously started
*/
private fun endCall() {
try {
call?.hangUp(HangUpOptions())?.get()
} catch (e: ExecutionException) {
Toast.makeText(this, "Unable to hang up call", Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show()
}
}
/**
* Create the call callAgent
*/
private fun createCallAgent() {
try {
val credential = CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken)
callAgent = CallClient().createCallAgent(applicationContext, credential).get()
} catch (ex: Exception) {
Toast.makeText(
applicationContext,
"Failed to create call callAgent.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
}
}
/**
* Request each required permission if the app doesn't already have it.
*/
private fun getAllPermissions() {
val permissionsToAskFor = mutableListOf<String>()
for (permission in allPermissions) {
if (ActivityCompat.checkSelfPermission(this, permission) != PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED) {
permissionsToAskFor.add(permission)
}
}
if (permissionsToAskFor.isNotEmpty()) {
ActivityCompat.requestPermissions(this, permissionsToAskFor.toTypedArray(), 1)
}
}
/**
* Ensure all permissions were granted, otherwise inform the user permissions are missing.
*/
override fun onRequestPermissionsResult(
requestCode: Int,
permissions: Array<out String>,
grantResults: IntArray
) {
super.onRequestPermissionsResult(requestCode, permissions, grantResults)
var allPermissionsGranted = true
for (result in grantResults) {
allPermissionsGranted = allPermissionsGranted && (result == PackageManager.PERMISSION_GRANTED)
}
if (!allPermissionsGranted) {
Toast.makeText(this, "All permissions are needed to make the call.", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show()
finish()
}
}
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun setCallStatus(status: String?) {
runOnUiThread {
statusView.text = "Call Status: $status"
}
}
@SuppressLint("SetTextI18n")
private fun setRoleText(role: String?) {
runOnUiThread {
roleTextView.text = "Role: $role"
}
}
}
Uwaga
Podczas projektowania aplikacji należy wziąć pod uwagę, kiedy należy zażądać tych uprawnień. Uprawnienia powinny być wymagane, ponieważ są potrzebne, a nie przed upływem czasu. Aby uzyskać więcej informacji, zobacz Przewodnik po uprawnieniach systemu Android.
Uruchamianie projektu
Przed uruchomieniem projektu zastąp wartość <ACS_USER_TOKEN> w pliku MainActivity.kt tokenem dostępu użytkownika usług Azure Communication Services.
private val userToken = "<ACS_USER_TOKEN>"
Uruchom projekt na emulatorze lub urządzeniu fizycznym.
Powinno zostać wyświetlone pole, aby wprowadzić identyfikator pokoju i przycisk, aby rozpocząć połączenie pokoju. Wprowadź identyfikator pokoju i sprawdź, czy stan połączenia został zmieniony wraz z rolą.
Informacje na temat dołączania do połączenia z pokojem
Cały kod dodany w aplikacji Szybki start umożliwił pomyślne uruchomienie i dołączenie połączenia pokoju. Musimy zagłębić się w to, jak to wszystko działa i jakie są więcej metod/procedur obsługi, do których można uzyskać dostęp w przypadku pokoi.
Połączenia pokoju są dołączane, za pomocą CallAgent którego jest tworzony prawidłowy token użytkownika:
private fun createCallAgent() {
try {
val credential = CommunicationTokenCredential(userToken)
callAgent = CallClient().createCallAgent(applicationContext, credential).get()
} catch (ex: Exception) {
Toast.makeText(
applicationContext,
"Failed to create call callAgent.",
Toast.LENGTH_SHORT
).show()
}
}
Za pomocą CallAgent metod i RoomCallLocatormożemy dołączyć wywołanie pomieszczenia przy użyciu CallAgent.join metody, która zwraca Call obiekt:
val joinCallOptions = JoinCallOptions()
val roomCallLocator = RoomCallLocator(roomId)
call = callAgent.join(applicationContext, roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions)
Dalsze dostosowywanie poza plikiem MainActivity.ktobejmuje subskrybowanie Call zdarzeń w celu pobrania aktualizacji:
call.addOnRemoteParticipantsUpdatedListener { args: ParticipantsUpdatedEvent? ->
handleRemoteParticipantsUpdate(
args!!
)
}
call.addOnStateChangedListener { args: PropertyChangedEvent? ->
this.handleCallOnStateChanged(
args!!
)
}
Możesz dodatkowo rozszerzyć MainActivity.kt , aby wyświetlić rolę uczestników lokalnego lub zdalnego wywołania, korzystając z poniższych metod i procedur obsługi.
// Get your role in the call
call.getCallParticipantRole();
// Subscribe to changes for your role in a call
private void isCallRoleChanged(PropertyChangedEvent propertyChangedEvent) {
// handle self-role change
}
call.addOnRoleChangedListener(isCallRoleChanged);
// Subscribe to role changes for remote participants
private void isRoleChanged(PropertyChangedEvent propertyChangedEvent) {
// handle remote participant role change
}
remoteParticipant.addOnRoleChangedListener(isRoleChanged);
// Get role of the remote participant
remoteParticipant.getCallParticipantRole();
Możliwość dołączenia do połączenia pokoju i wyświetlania ról uczestników połączeń jest dostępna w zestawie Android Mobile Calling SDK w wersji 2.4.0 lub nowszej.
Więcej informacji na temat ról uczestników rozmów w pokoju można dowiedzieć się w dokumentacji koncepcji pomieszczeń.
Dołącz do połączenia z pokojem
Aby dołączyć do wywołania pokoju, skonfiguruj aplikację systemu Windows przy użyciu przewodnika Dodawanie wywołania wideo do aplikacji klienckiej. Alternatywnie możesz pobrać przewodnik Szybki start dotyczący wywoływania wideo w witrynie GitHub.
Utwórz element callAgent z prawidłowym tokenem użytkownika:
var creds = new CallTokenCredential("<user-token>");
CallAgentOptions callAgentOptions = new CallAgentOptions();
callAgentOptions.DisplayName = "<display-name>";
callAgent = await callClient.CreateCallAgentAsync(creds, callAgentOptions);
callAgent Użyj metody i RoomCallLocator , aby dołączyć wywołanie pokoju, CallAgent.JoinAsync metoda zwróci CommunicationCall obiekt:
RoomCallLocator roomCallLocator = new RoomCallLocator('<RoomId>');
CommunicationCall communicationCall = await callAgent.JoinAsync(roomCallLocator, joinCallOptions);
Subskrybowanie zdarzeń w CommunicationCall celu pobrania aktualizacji:
private async void CommunicationCall_OnStateChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args) {
var call = sender as CommunicationCall;
if (sender != null)
{
switch (call.State){
// Handle changes in call state
}
}
}
Aby wyświetlić rolę uczestników połączeń, zasubskrybuj zmiany roli:
private void RemoteParticipant_OnRoleChanged(object sender, Azure.Communication.Calling.WindowsClient.PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
_ = Windows.ApplicationModel.Core.CoreApplication.MainView.CoreWindow.Dispatcher.RunAsync(CoreDispatcherPriority.Normal, () =>
{
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine("Raising Role change, new Role: " + remoteParticipant_.Role);
PropertyChanged(this, new System.ComponentModel.PropertyChangedEventArgs("RemoteParticipantRole"));
});
}
Możliwość dołączenia do połączenia pokoju i wyświetlania ról uczestników połączeń jest dostępna w wersji NuGet systemu Windows w wersji 1.1.0 lub nowszej.
Więcej informacji na temat ról uczestników rozmów w pokoju można dowiedzieć się w dokumentacji koncepcji pomieszczeń.
Następne kroki
W tej sekcji przedstawiono, jak wykonać następujące działania:
- Dodawanie wywołania wideo do aplikacji
- Przekazywanie identyfikatora pokoju do zestawu SDK wywołującego
- Dołączanie połączenia pokoju z aplikacji
Możesz również wykonać następujące czynności:
- Dowiedz się więcej na temat koncepcji pomieszczeń
- Dowiedz się więcej o pojęciach dotyczących połączeń głosowych i wideo
- Dowiedz się więcej o pojęciach dotyczących uwierzytelniania