WinUSB architecture and modules
WinUSB consists of two primary components:
- Winusb.sys is a kernel-mode driver that can be installed as either a filter or function driver, above the protocol drivers in a USB device's kernel-mode device stack.
- Winusb.dll is a user-mode DLL that exposes WinUSB functions. Applications can use these functions to communicate with Winusb.sys when it's installed as a device's function driver.
For devices that don't require a custom function driver, Winusb.sys can be installed in the device's kernel-mode stack as the function driver. User-mode processes can then communicate with Winusb.sys by using a set of device I/O control requests or by calling WinUSB functions.
The following figure shows a USB driver stack that contains several instances of Winusb.sys.
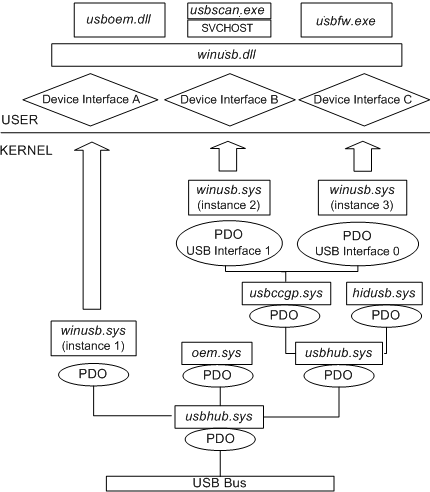
The preceding figure shows an example WinUSB configuration that implements three device interface classes, each of which has a single registered device interface:
- Instance 1 of Winusb.sys registers device interface A, which supports a user-mode driver (Usboem.dll).
- Instance 2 of Winusb.sys registers device interface B, which supports a user-mode driver for a scanner (Usbscan.exe) that communicates with Winusb.dll by using a system service (SVCHOST).
- Instance 3 of Winusb.sys registers device interface C, which supports a firmware update utility (Usbfw.exe).
There's exactly one loaded instance of Winusb.sys. A physical device object (PDO) can represent a noncomposite device (instance 1 in the diagram) or it can represent an interface or interface collection on a composite device (instances 2 and 3). For USB wireless mobile communication device class (WMCDC) devices, a PDO can even represent several interface collections. (For more information about PDOs for WMCDC devices, see Support for the Wireless Mobile Communication Device Class.)
Any user-mode application can communicate with the USB stack by loading the WinUSB dynamic link library (Winusb.dll) and calling the WinUSB functions that are exposed by this module.