Halting a PF Miniport Driver
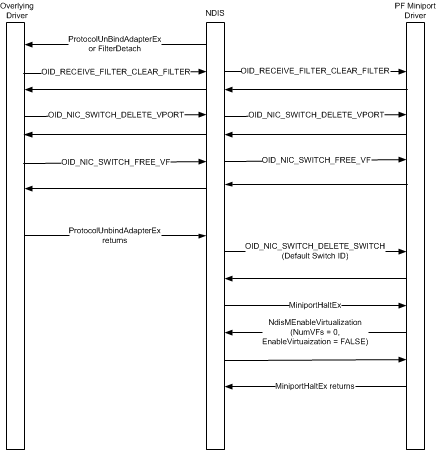
This topic discusses the steps that are involved with halting the miniport driver for a PCI Express (PCIe) Physical Function (PF) on an adapter that supports single root I/O virtualization (SR-IOV). These steps are shown in the following figure.
This topic contains the following information:
Actions Performed by NDIS and Overlying Drivers Before MiniportHaltEx is Called
Actions Performed by the PF Miniport Driver When MiniportHaltEx is Called
Actions Performed by NDIS and Overlying Drivers Before MiniportHaltEx is Called
Before NDIS calls the PF miniport driver's MiniportHaltEx function, it first does the following:
NDIS unbinds all protocol drivers that have previously bound to the underlying PF miniport driver. NDIS does this by calling the protocol driver's ProtocolUnbindAdapterEx function.
NDIS detaches all filter drivers that have previously bound to the underlying PF miniport driver. NDIS does this by calling the filter driver's FilterDetach function.
When an overlying protocol or filter driver is being unbound or detached from the PF miniport driver, it must follow these steps:
The driver must issue an object identifier (OID) set request of OID_RECEIVE_FILTER_CLEAR_FILTER to clear any receive filters that it previously set. The driver sets these filters on the default virtual port (VPort) or any nondefault VPorts of the NIC switch on the network adapter. The driver sets these filters by issuing OID method requests of OID_RECEIVE_FILTER_SET_FILTER to the PF miniport driver.
The driver must issue an OID set request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_VPORT to delete any nondefault VPorts that it previously created on the NIC switch. The driver sets these VPorts by issuing OID method requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_CREATE_VPORT to the PF miniport driver.
The driver must issue an OID set request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_FREE_VF to free the resources for any PCIe Virtual Functions (VFs) that it previously allocated on the NIC switch. The driver allocates resources for the VF by issuing OID method requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_ALLOCATE_VF to the PF miniport driver.
For more information, see Freeing Resources for a Virtual Function.
Note When resources for the VF are freed, NDIS calls the MiniportHaltEx function of the VF miniport driver. For more information, see Halting a VF Miniport Driver.
After all receive filters, nondefault VPorts, and VFs have been deleted from the NIC switch, NDIS follows these steps:
NDIS deletes all NIC switches by issuing OID set requests of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_SWITCH to the PF miniport driver. For more information on how a NIC switch is deleted, see Deleting a NIC Switch.
Note Starting with Windows Server 2012, the SR-IOV interface only supports the default NIC switch on the network adapter.
After all NIC switches have been successfully deleted, NDIS calls the MiniportHaltEx function of the PF miniport driver.
Actions Performed by the PF Miniport Driver When MiniportHaltEx is Called
When NDIS calls MiniportHaltEx, the PF miniport driver must follow these steps:
If the PF miniport driver supports the static creation of NIC switches and all the NIC switches have been deleted, the driver must disable the virtualization on the adapter by calling NdisMEnableVirtualization with EnableVirtualization parameter set to FALSE and the NumVFs parameter set to zero.
NdisMEnableVirtualization clears the NumVFs member and the VF Enable bit in the SR-IOV Extended Capability structure in the PCIe configuration space of the network adapter's PF.
Note If the PF miniport driver supports dynamic creation and configuration of NIC switches, it must call NdisMEnableVirtualization when the driver handles the OID set request of OID_NIC_SWITCH_DELETE_SWITCH. This OID request is issued before MiniportHaltEx is called.
The PF miniport driver performs the other tasks associated with a miniport halt operation. For more information, see Halting a Miniport Adapter.