Overview of the Microsoft 365 Copilot orchestrator
Microsoft 365 Copilot is your personal assistant for work. It helps with various general tasks, such as writing, summarizing, researching, and more. Copilot has different skills that correspond to these different types of tasks. For example, Copilot can summarize action items from a meeting, suggest edits to a file, or track down resources and experts on a given topic within your organization. Each skill has its own parameters and outputs that are tailored to the specific task.
Like any copilot, Microsoft 365 Copilot is trained with data at a point in time. To retrieve and process new and real-time information, especially data that's specific to your organization and workflows, agents require plugins. Plugins within an agent extend Microsoft 365 Copilot's skills and utility for end users, enabling it to choose the right skill from its full repertoire.
But how does your agent know which skill to use when you ask for help? How does it interpret your request and match it to the best skill available? That's the job of the Microsoft 365 Copilot orchestrator.
This article explains the logic behind Copilot's skill selection process and how you can ensure that Copilot uses the right plugin from your agent at every opportunity to benefit your users.
Important
- API plugins are currently only supported as actions within declarative agents. They aren't enabled in Microsoft 365 Copilot. For an example that shows how to add an API plugin to a declarative agent, see Add a plugin.
- The capability is enabled by default in all Microsoft 365 Copilot-licensed tenants. Admins can disable this functionality on a user and group basis and control how individual plugins are approved for use, and which plugins are enabled. For more information, see Manage Agents in Integrated Apps.
Copilot orchestrator
Between the user's natural language input and Copilot's natural language output, the Copilot orchestrator works behind the scenes to select and run the right skills from the right plugins for the user's task.
The orchestration layer represents the interface between foundation Large Language Models (LLMs) and the many ways you can extend, enrich, and customize Copilot for the way your customers work.
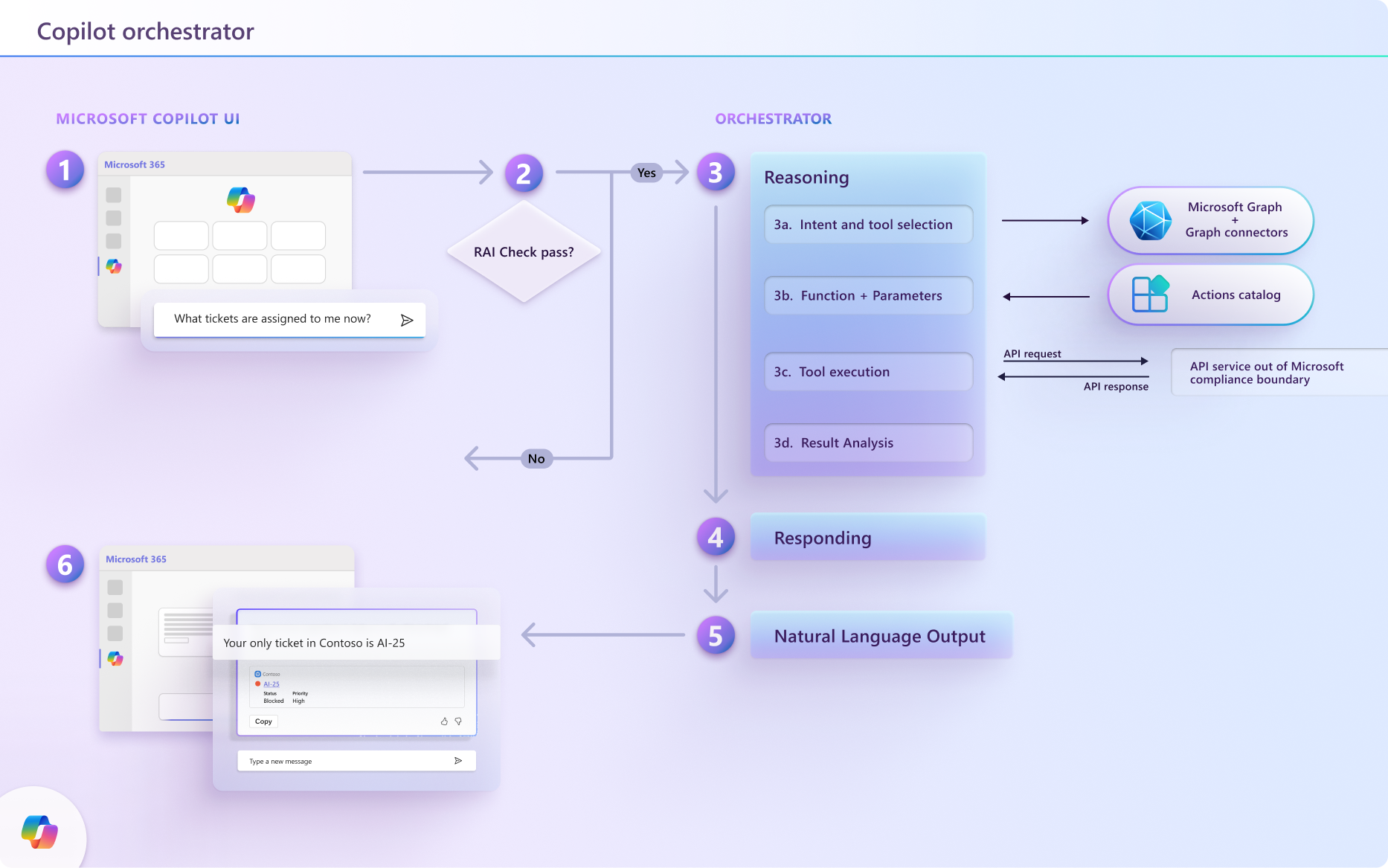
The following diagram illustrates how the Microsoft 365 Copilot orchestrator selects the right plugin, with the right skill, at the right time, even when there are multiple options to choose from.
Natural language input: The user submits a query to your agent, such as "What tickets are assigned to me right now?"
Preliminary checks: Copilot conducts several checks on the query, including responsible AI checks and security measures to ensure it doesn't pose any risks. If the query fails any of these checks, Copilot terminates the interaction.
Reasoning: The Copilot orchestrator formulates a plan comprised of multiple actions that it performs in an attempt to respond to the user's prompt.
Context and tool selection: The orchestrator retrieves the user's conversation context from the context store and integrates data from Microsoft Graph to refine the context. It then adjusts the initial query based on this updated context and forwards it to the LLM (large language model) to guide the next steps.
The LLM might proceed to generating a response using Copilot's built-in capabilities, or it might determine that additional data is necessary.
If more information is needed, the orchestrator does a search for the plugins (tools) with the right skill for the task from the agent's enabled plugins based on the descriptions of the plugins and their functions.
Function matching and parameter determination: The orchestrator formulates a new prompt that incorporates the user's initial query, the updated context, and the selected plugins, and presents it to the LLM. The LLM evaluates the input and specifies the optimal plugin and function within that plugin to address the task. It then provides the orchestrator with the necessary function details and parameters required to gather the needed information.
Tool initiation: The orchestrator uses the response from the LLM to construct an API request and send the request to the tool initiator, which securely retrieves the requested information located outside of Copilot's infrastructure. It runs the request and sends the results back to the orchestrator for further processing.
Result analysis and response formulation: The orchestrator integrates the API response into the ongoing context and consults the LLM in a continuous reasoning loop until the LLM deems it appropriate to generate a final response.
Responding: The orchestrator compiles all the information gathered during the reasoning process and submits it to the LLM to create a final response. After ensuring the response complies with Responsible AI guidelines, it sends the response back to the orchestrator, which logs it in the context store and delivers it to the user via the Copilot UI.
Natural language output: Finally, the orchestrator delivers the response to the user and updates the conversation state. Copilot is ready for its next prompt.
How Copilot's orchestrator matches plugins to user queries
When a user submits a query to your agent, the orchestrator searches the agent's full catalog of skills (functions) from installed plugins to identify up to five skills that best match the query. The orchestrator first tries to match on exact words (lexical match) and expands its search scope as needed to include matches on descriptive meanings (semantic match), working from specific function names to general plugin descriptions, until all five function candidate slots are filled. Specifically, the following list shows the hierarchy of matching mechanisms for Copilot plugin function selection:
- Lexical match on function name.
- Semantic match on function description.
- Lexical match on plugin name (adds all plugin functions to candidate list).
- Semantic match on plugin name (adds all plugin functions to candidate list).
The orchestrator works through this list until all five function candidate slots are filled.
Check out Validation guidelines for agents to learn more about writing good descriptions to ensure that Copilot chooses the right skill for each user query to your agent.