Configure process architecture for a unit test
This article provides information on the process architecture used for running unit tests, how to set the process architecture, and how to run unit tests as a 64-bit process.
This article provides information on how to set the process architecture for unit tests and how to run unit tests as a 64-bit process.
Configure process architecture for MSTest projects
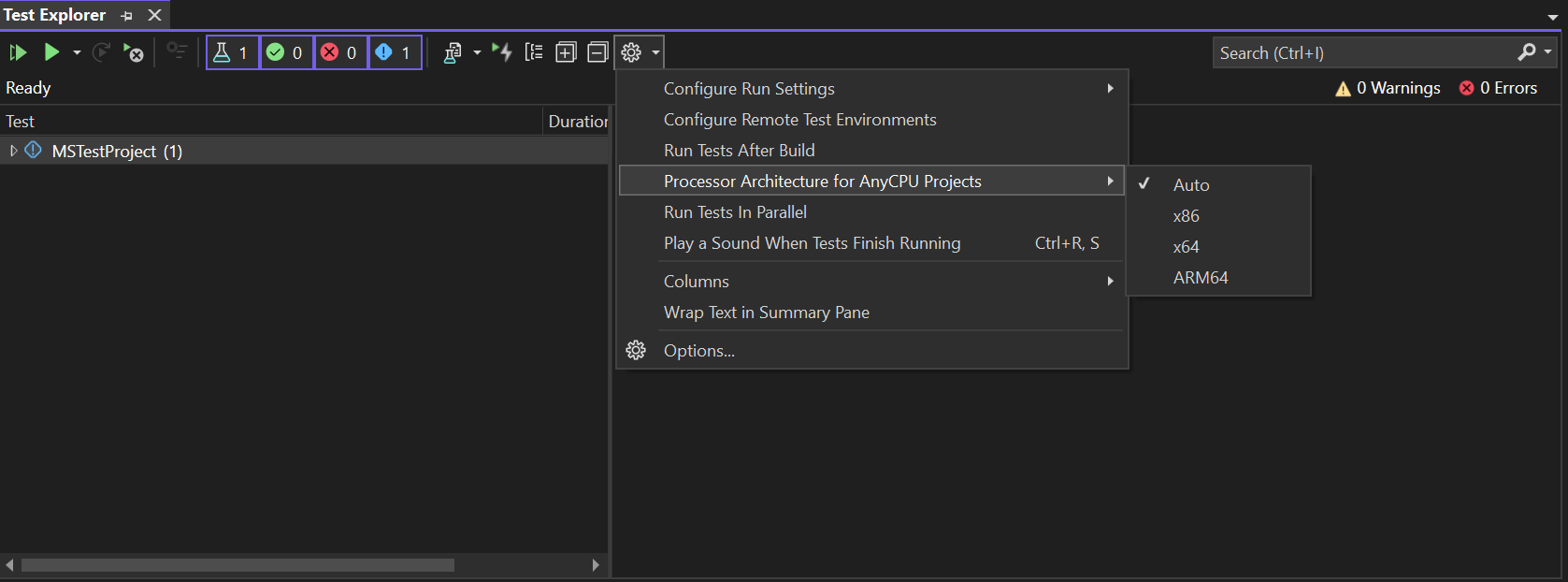
For MSTest projects using Visual Studio Testing Platform (VSTest) as the test runner, the default target platform (process architecture) matches the operating system's architecture. You can override this behavior for projects set to Any CPU as the target platform using either the Test Explorer Settings, as shown in the following illustration, or using the Test menu.
From the Test menu, select Processor Architecture for AnyCPU Projects.
For projects using MSTest as the test runner instead of VSTest, the architecture is determined strictly by MSBuild and runtime rules. Executables are generated based on the preferred architecture specified in MSBuild/runtime settings. You can adjust this preference using MSBuild properties (for example, PreferNativeArm64), but the setting Processor Architecture for AnyCPU Projects cannot be used to change the architecture for these projects.
Note
You can set the test runner when you create a unit test project using the MSTest project template, or by using MSBuild properties. For more information on the difference between MSTest and VSTest test runners, see Microsoft.Testing.Platform and VSTest comparison.
PreferNativeArm64 (MSTest)
When using the PreferNativeArm64 MSBuild property, the project prefers running natively on ARM64 architecture if it's available. This property is applicable to projects that generate executables and follow MSBuild runtime rules. This setting is ignored for Visual Studio Test Platform (VSTest) test runners and only applies to MSTest projects with MSTest configured as the test runner.
Run a unit test as a 64-bit process
If you have a 64-bit machine, you can run unit tests and capture code coverage information as a 64-bit process.
To run a unit test as a 64-bit process:
If your code or tests were compiled as 32-bit/x86, but you now want to run them as a 64-bit process, recompile them as Any CPU.
Tip
For maximum flexibility, compile your test projects with the Any CPU configuration. Then you can run on both 32-bit and 64-bit agents. There's no advantage to compiling test projects with the 64-bit configuration, unless you are calling code that is only supported on 64-bit.
Set the unit tests to run as a 64-bit process.
From the Visual Studio menu, choose Test, then choose Processor Architecture for AnyCPU projects. Choose x64 to run the tests as a 64-bit process.
- or -
Specify
<TargetPlatform>x64</TargetPlatform>in a .runsettings file. An advantage of this method is that you can specify groups of settings in different files and quickly switch between different settings. You can also copy settings between solutions. For more information, see Configure unit tests by using a .runsettings file.Note
The Processor Architecture for AnyCPU projects setting is not supported in an MSTest project if you set MSTest as the test runner instead of VSTest.