Software updates planning guide for managed Android Enterprise devices in Microsoft Intune
Patches, major & minor updates, and new operating system versions are released frequently. Organizations must keep devices updated to get the latest security updates.
Devices with Android Google Mobile Services (GMS) include all the Google apps and Google services. These apps and services are on top of the OEMs own firmware features and apps. These devices receive a different type of updates and they're updated randomly, depending on the behaviors by Google, the OEM, and the service carrier/telecommunication company.
Intune has built-in policies that can manage software updates.
This article includes an admin checklist for enrolled and managed Android Enterprise devices. Use this information to help manage software updates on your organization-owned devices.
This article applies to:
- Android Enterprise devices enrolled in Intune
Tip
If your devices are personally owned, then go to the software updates planning guide for personal devices.
Before you begin
To avoid delays in devices receiving updates, make sure devices are:
- Powered on
- Plugged in
- Connected to the Internet
- Idle and not actively being used
Admin checklist for corporate devices
Corporate or organization-owned devices should be enrolled and managed by the organization. For Android Enterprise, you can manage software updates on the following device types:
- Dedicated devices
- Fully managed devices
- Fully managed devices with a work profile
This section lists the Microsoft-recommended policies to install software updates on managed Android devices.
✅ Manage updates with policies
Do create policies that update your devices. Don't put this responsibility on end users.
When users install their own updates (instead of admins managing the updates), it can disrupt user productivity and business tasks. For example:
Users can start an update when they want, and might not be able to work while an update is installing.
Users can apply updates that your organization hasn't approved. This decision can cause issues with application compatibility, changes to the operating system, or changes to the user experience that disrupt device use.
Users can avoid applying required updates that affect security or app compatibility. This situation can leave the devices at risk and/or prevent the devices from functioning.
✅ Configure the system update setting
Manage OS updates using the System update setting in an Intune device configuration profile (Devices > Manage devices > Configuration > Create > Device restrictions > General).
For enrolled Android Enterprise devices, you can configure this setting and choose when the updates are installed. For example, you can:
Use the device's default behavior, which automatically installs updates if the device is connected to Wi-Fi, is charging, and is idle.
Automatically install updates without user interaction. Pending updates install immediately.
Postpone updates for 30 days and then prompt users to install updates. Expect your device manufacturer and/or carrier to prevent important security updates from being postponed.
Create a maintenance window to automatically install updates during a specific time frame.

For more specific information on this setting and the values you can configure, go to Android Enterprise device settings list to allow or restrict features on corporate-owned devices using Intune.
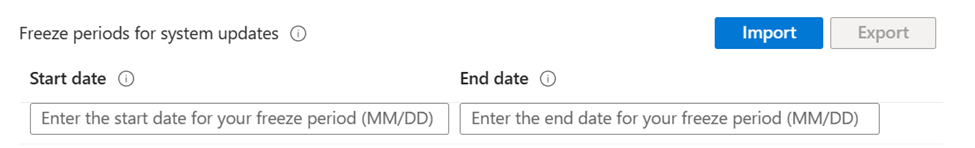
✅ Use freeze periods during critical times
Configure the Freeze periods for system updates setting in an Intune device configuration profile (Devices > Manage devices > Configuration > Create > Device restrictions > General).
During critical periods of the year, like holidays and other events, a freeze period prevents devices from receiving system updates, security patches, and notifications about pending updates. Users can't manually check for updates:
For more information on this setting, go to Android Enterprise device settings list to allow or restrict features on corporate-owned devices using Intune.
✅ Use OEMConfig for firmware updates
For some rugged Android devices, you can use OEMConfig to configure firmware updates and other settings that are specific to that OEM. If an OEM provides an OEMConfig app, then in Intune, you can deploy the app and configure its settings using a configuration profile.
To get started, go to Use and manage Android Enterprise devices with OEMConfig in Intune. This article also lists the Intune-supported OEMConfig apps.
Contact the manufacturer for the firmware and other settings available in the configuration schema.
Upgrade older devices
As of January 7, 2022, the minimum supported versions are:
- Android 8.0 for mobile device management (MDM)
- Android 9.0 for mobile application management (MAM)
Android devices running older versions that are currently enrolled in Intune don't receive updates to the Android Company Portal app or the Intune app. These apps aren't available in the Google Play Store. If these apps were downloaded before this change, then the devices aren't blocked from enrollment. Policies applied to these devices continue to be deployed, but the devices aren't in a supported state.
If you currently have devices running older Android versions in your organization, then upgrade or replace them. Use the information in this article to help you define an update strategy. Using newer OS versions provide better productivity and security to your users and your organization.
For more version information, go to Supported operating systems and browsers in Intune.