hll() (aggregation function)
Applies to: ✅ Microsoft Fabric ✅ Azure Data Explorer ✅ Azure Monitor ✅ Microsoft Sentinel
The hll() function is a way to estimate the number of unique values in a set of values. It does this by calculating intermediate results for aggregation within the summarize operator for a group of data using the dcount function.
Read about the underlying algorithm (HyperLogLog) and the estimation accuracy.
Note
This function is used in conjunction with the summarize operator.
Tip
- Use the hll_merge function to merge the results of multiple
hll()functions. - Use the dcount_hll function to calculate the number of distinct values from the output of the
hll()orhll_mergefunctions.
Important
The results of hll(), hll_if(), and hll_merge() can be stored and later retrieved. For example, you may want to create a daily unique users summary, which can then be used to calculate weekly counts. However, the precise binary representation of these results may change over time. There's no guarantee that these functions will produce identical results for identical inputs, and therefore we don't advise relying on them.
Syntax
hll (expr [, accuracy])
Learn more about syntax conventions.
Parameters
| Name | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| expr | string |
✔️ | The expression used for the aggregation calculation. |
| accuracy | int |
The value that controls the balance between speed and accuracy. If unspecified, the default value is 1. For supported values, see Estimation accuracy. |
Returns
Returns the intermediate results of distinct count of expr across the group.
Example
In the following example, the hll() function is used to estimate the number of unique values of the DamageProperty column within each 10-minute time bin of the StartTime column.
StormEvents
| summarize hll(DamageProperty) by bin(StartTime,10m)
The results table shown includes only the first 10 rows.
| StartTime | hll_DamageProperty |
|---|---|
| 2007-01-01T00:20:00Z | [[1024,14],["3803688792395291579"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T01:00:00Z | [[1024,14],["7755241107725382121","-5665157283053373866","3803688792395291579","-1003235211361077779"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T02:00:00Z | [[1024,14],["-1003235211361077779","-5665157283053373866","7755241107725382121"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T02:20:00Z | [[1024,14],["7755241107725382121"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T03:30:00Z | [[1024,14],["3803688792395291579"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T03:40:00Z | [[1024,14],["-5665157283053373866"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T04:30:00Z | [[1024,14],["3803688792395291579"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T05:30:00Z | [[1024,14],["3803688792395291579"],[]] |
| 2007-01-01T06:30:00Z | [[1024,14],["1589522558235929902"],[]] |
Estimation accuracy
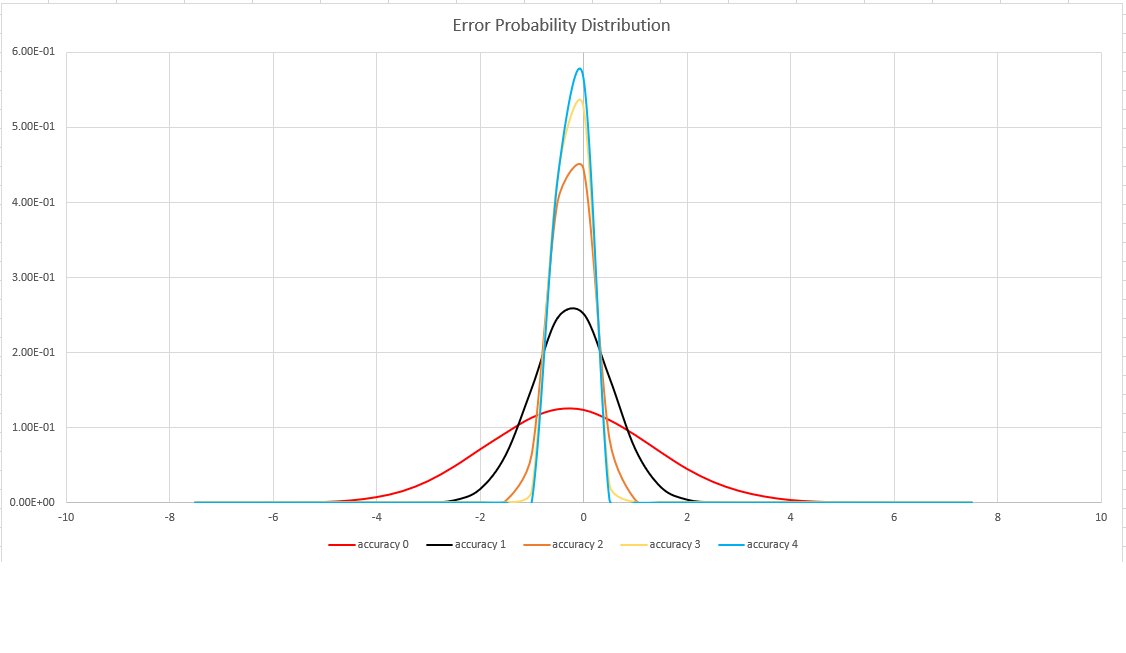
This function uses a variant of the HyperLogLog (HLL) algorithm, which does a stochastic estimation of set cardinality. The algorithm provides a "knob" that can be used to balance accuracy and execution time per memory size:
| Accuracy | Error (%) | Entry count |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1.6 | 212 |
| 1 | 0.8 | 214 |
| 2 | 0.4 | 216 |
| 3 | 0.28 | 217 |
| 4 | 0.2 | 218 |
Note
The "entry count" column is the number of 1-byte counters in the HLL implementation.
The algorithm includes some provisions for doing a perfect count (zero error), if the set cardinality is small enough:
- When the accuracy level is
1, 1000 values are returned - When the accuracy level is
2, 8000 values are returned
The error bound is probabilistic, not a theoretical bound. The value is the standard deviation of error distribution (the sigma), and 99.7% of the estimations will have a relative error of under 3 x sigma.
The following image shows the probability distribution function of the relative estimation error, in percentages, for all supported accuracy settings: