Configure a user-assigned managed identity to trust an external identity provider
This article describes how to manage a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity in Microsoft Entra ID. The federated identity credential creates a trust relationship between a user-assigned managed identity and an external identity provider (IdP). Configuring a federated identity credential on a system-assigned managed identity isn't supported.
After you configure your user-assigned managed identity to trust an external IdP, configure your external software workload to exchange a token from the external IdP for an access token from Microsoft identity platform. The external workload uses the access token to access Microsoft Entra protected resources without needing to manage secrets (in supported scenarios). To learn more about the token exchange workflow, read about workload identity federation.
In this article, you learn how to create, list, and delete federated identity credentials on a user-assigned managed identity.
Important considerations and restrictions
A maximum of 20 federated identity credentials can be added to an application or user-assigned managed identity.
When you configure a federated identity credential, there are several important pieces of information to provide:
issuer and subject are the key pieces of information needed to set up the trust relationship. The combination of
issuerandsubjectmust be unique on the app. When the external software workload requests Microsoft identity platform to exchange the external token for an access token, the issuer and subject values of the federated identity credential are checked against theissuerandsubjectclaims provided in the external token. If that validation check passes, Microsoft identity platform issues an access token to the external software workload.issuer is the URL of the external identity provider and must match the
issuerclaim of the external token being exchanged. Required. If theissuerclaim has leading or trailing whitespace in the value, the token exchange is blocked. This field has a character limit of 600 characters.subject is the identifier of the external software workload and must match the
sub(subject) claim of the external token being exchanged. subject has no fixed format, as each IdP uses their own - sometimes a GUID, sometimes a colon delimited identifier, sometimes arbitrary strings. This field has a character limit of 600 characters.Important
The subject setting values must exactly match the configuration on the GitHub workflow configuration. Otherwise, Microsoft identity platform will look at the incoming external token and reject the exchange for an access token. You won't get an error, the exchange fails without error.
Important
If you accidentally add the incorrect external workload information in the subject setting the federated identity credential is created successfully without error. The error does not become apparent until the token exchange fails.
audiences lists the audiences that can appear in the external token. Required. You must add a single audience value, which has a limit of 600 characters. The recommended value is "api://AzureADTokenExchange". It says what Microsoft identity platform must accept in the
audclaim in the incoming token.name is the unique identifier for the federated identity credential. Required. This field has a character limit of 3-120 characters and must be URL friendly. Alphanumeric, dash, or underscore characters are supported, the first character must be alphanumeric only. It's immutable once created.
description is the user-provided description of the federated identity credential. Optional. The description isn't validated or checked by Microsoft Entra ID. This field has a limit of 600 characters.
Wildcard characters aren't supported in any federated identity credential property value.
To learn more about supported regions, time to propagate federated credential updates, supported issuers and more, read Important considerations and restrictions for federated identity credentials.
Prerequisites
- If you're unfamiliar with managed identities for Azure resources, check out the overview section. Be sure to review the difference between a system-assigned and user-assigned managed identity.
- If you don't already have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- Get the information for your external IdP and software workload, which you need in the following steps.
- To create a user-assigned managed identity and configure a federated identity credential, your account needs the Contributor or Owner role assignment.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity
- Find the name of the user-assigned managed identity, which you need in the following steps.
Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
In the Microsoft Azure portal, navigate to the user-assigned managed identity you created. Under Settings in the left nav bar, select Federated credentials and then Add Credential.
In the Federated credential scenario dropdown box, select your scenario.
GitHub Actions deploying Azure resources
To add a federated identity for GitHub actions, follow these steps:
For Entity type, select Environment, Branch, Pull request, or Tag and specify the value. The values must exactly match the configuration in the GitHub workflow. For more info, read the examples.
Add a Name for the federated credential.
The Issuer, Audiences, and Subject identifier fields autopopulate based on the values you entered.
Select Add to configure the federated credential.
Use the following values from your Microsoft Entra managed identity for your GitHub workflow:
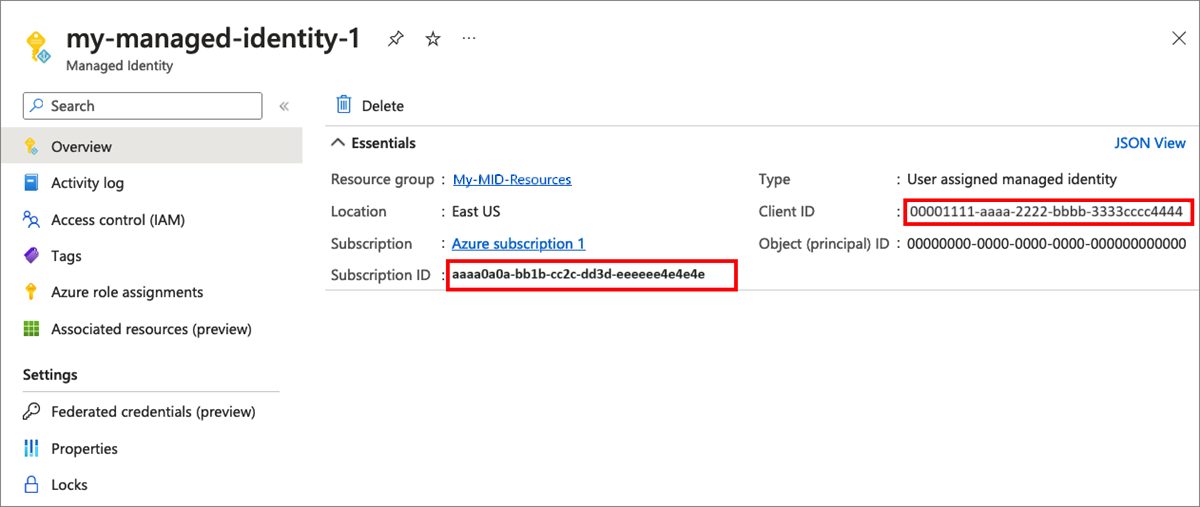
AZURE_CLIENT_IDthe managed identity Client IDAZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_IDthe Subscription ID.The following screenshot demonstrates how to copy the managed identity ID and subscription ID.
AZURE_TENANT_IDthe Directory (tenant) ID. Learn how to find your Microsoft Entra tenant ID.
Entity type examples
Branch example
For a workflow triggered by a push or pull request event on the main branch:
on:
push:
branches: [ main ]
pull_request:
branches: [ main ]
Specify an Entity type of Branch and a GitHub branch name of "main".
Environment example
For Jobs tied to an environment named "production":
on:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
deployment:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
environment: production
steps:
- name: deploy
# ...deployment-specific steps
Specify an Entity type of Environment and a GitHub environment name of "production".
Tag example
For example, for a workflow triggered by a push to the tag named "v2":
on:
push:
# Sequence of patterns matched against refs/heads
branches:
- main
- 'mona/octocat'
- 'releases/**'
# Sequence of patterns matched against refs/tags
tags:
- v2
- v1.*
Specify an Entity type of Tag and a GitHub tag name of "v2".
Pull request example
For a workflow triggered by a pull request event, specify an Entity type of Pull request
Kubernetes accessing Azure resources
Fill in the Cluster issuer URL, Namespace, Service account name, and Name fields:
- Cluster issuer URL is the OIDC issuer URL for the managed cluster or the OIDC Issuer URL for a self-managed cluster.
- Service account name is the name of the Kubernetes service account, which provides an identity for processes that run in a Pod.
- Namespace is the service account namespace.
- Name is the name of the federated credential, which can't be changed later.
Select Add to configure the federated credential.
Other
Select the Other issuer scenario from the dropdown menu.
Specify the following fields (using a software workload running in Google Cloud as an example):
- Name is the name of the federated credential, which can't be changed later.
- Subject identifier: must match the
subclaim in the token issued by the external identity provider. In this example using Google Cloud, subject is the Unique ID of the service account you plan to use. - Issuer: must match the
issclaim in the token issued by the external identity provider. A URL that complies with the OIDC Discovery spec. Microsoft Entra ID uses this issuer URL to fetch the keys that are necessary to validate the token. For Google Cloud, the issuer is "https://accounts.google.com".
Select Add to configure the federated credential.
List federated identity credentials on a user-assigned managed identity
In the Microsoft Azure portal, navigate to the user-assigned managed identity you created. Under Settings in the left nav bar and select Federated credentials.
The federated identity credentials configured on that user-assigned managed identity are listed.
Delete a federated identity credential from a user-assigned managed identity
In the Microsoft Azure portal, navigate to the user-assigned managed identity you created. Under Settings in the left nav bar and select Federated credentials.
The federated identity credentials configured on that user-assigned managed identity are listed.
To delete a specific federated identity credential, select the Delete icon for that credential.
Prerequisites
- If you're unfamiliar with managed identities for Azure resources, check out the overview section. Be sure to review the difference between a system-assigned and user-assigned managed identity.
- If you don't already have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- Get the information for your external IdP and software workload, which you need in the following steps.
- To create a user-assigned managed identity and configure a federated identity credential, your account needs the Contributor or Owner role assignment.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity
- Find the name of the user-assigned managed identity, which you need in the following steps.
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the az login command. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.
When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the az identity federated-credential create command to create a new federated identity credential on your user-assigned managed identity (specified by the name). Specify the name, issuer, subject, and other parameters.
az login
# set variables
location="centralus"
subscription="{subscription-id}"
rg="fic-test-rg"
# user assigned identity name
uaId="fic-test-ua"
# federated identity credential name
ficId="fic-test-fic-name"
# create prerequisites if required.
# otherwise make sure that existing resources names are set in variables above
az account set --subscription $subscription
az group create --location $location --name $rg
az identity create --name $uaId --resource-group $rg --location $location --subscription $subscription
# Create/update a federated identity credential
az identity federated-credential create --name $ficId --identity-name $uaId --resource-group $rg --issuer 'https://aks.azure.com/issuerGUID' --subject 'system:serviceaccount:ns:svcaccount' --audiences 'api://AzureADTokenExchange'
List federated identity credentials on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the az identity federated-credential list command to read all the federated identity credentials configured on a user-assigned managed identity:
az login
# Set variables
rg="fic-test-rg"
# User assigned identity name
uaId="fic-test-ua"
# Read all federated identity credentials assigned to the user-assigned managed identity
az identity federated-credential list --identity-name $uaId --resource-group $rg
Get a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the az identity federated-credential show command to show a federated identity credential (by ID):
az login
# Set variables
rg="fic-test-rg"
# User assigned identity name
uaId="fic-test-ua"
# Federated identity credential name
ficId="fic-test-fic-name"
# Show the federated identity credential
az identity federated-credential show --name $ficId --identity-name $uaId --resource-group $rg
Delete a federated identity credential from a user-assigned managed identity
Run the az identity federated-credential delete command to delete a federated identity credential under an existing user assigned identity.
az login
# Set variables
# in Linux shell remove $ from set variable statement
$rg="fic-test-rg"
# User assigned identity name
$uaId="fic-test-ua"
# Federated identity credential name
$ficId="fic-test-fic-name"
az identity federated-credential delete --name $ficId --identity-name $uaId --resource-group $rg
Prerequisites
- If you're unfamiliar with managed identities for Azure resources, check out the overview section. Be sure to review the difference between a system-assigned and user-assigned managed identity.
- If you don't already have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- Get the information for your external IdP and software workload, which you need in the following steps.
- To create a user-assigned managed identity and configure a federated identity credential, your account needs the Contributor or Owner role assignment.
- To run the example scripts, you have two options:
- Use Azure Cloud Shell, which you can open by using the Try It button in the upper-right corner of code blocks.
- Run scripts locally with Azure PowerShell, as described in the next section.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity
- Find the name of the user-assigned managed identity, which you need in the following steps.
Configure Azure PowerShell locally
To use Azure PowerShell locally for this article instead of using Cloud Shell:
Install the latest version of Azure PowerShell if you haven't already.
Sign in to Azure.
Connect-AzAccountInstall the latest version of PowerShellGet.
Install-Module -Name PowerShellGet -AllowPrereleaseYou might need to
Exitout of the current PowerShell session after you run this command for the next step.Install the
Az.ManagedServiceIdentitymodule to perform the user-assigned managed identity operations in this article.Install-Module -Name Az.ManagedServiceIdentity
Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the New-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials command to create a new federated identity credential on your user-assigned managed identity (specified by the name). Specify the name, issuer, subject, and other parameters.
New-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials -ResourceGroupName azure-rg-test -IdentityName uai-pwsh01 `
-Name fic-pwsh01 -Issuer "https://kubernetes-oauth.azure.com" -Subject "system:serviceaccount:ns:svcaccount"
List federated identity credentials on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the Get-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials command to read all the federated identity credentials configured on a user-assigned managed identity:
Get-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials -ResourceGroupName azure-rg-test -IdentityName uai-pwsh01
Get a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Run the Get-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials command to show a federated identity credential (by name):
Get-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials -ResourceGroupName azure-rg-test -IdentityName uai-pwsh01 -Name fic-pwsh01
Delete a federated identity credential from a user-assigned managed identity
Run the Remove-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials command to delete a federated identity credential under an existing user assigned identity.
Remove-AzFederatedIdentityCredentials -ResourceGroupName azure-rg-test -IdentityName uai-pwsh01 -Name fic-pwsh01
Prerequisites
- If you're unfamiliar with managed identities for Azure resources, check out the overview section. Be sure to review the difference between a system-assigned and user-assigned managed identity.
- If you don't already have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- Get the information for your external IdP and software workload, which you need in the following steps.
- To create a user-assigned managed identity and configure a federated identity credential, your account needs the Contributor or Owner role assignment.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity
- Find the name of the user-assigned managed identity, which you need in the following steps.
Template creation and editing
Resource Manager templates help you deploy new or modified resources defined by an Azure resource group. Several options are available for template editing and deployment, both local and portal-based. You can:
- Use a custom template from Azure Marketplace to create a template from scratch or base it on an existing common or quickstart template.
- Derive from an existing resource group by exporting a template. You can export them from either the original deployment or from the current state of the deployment.
- Use a local JSON editor (such as VS Code), and then upload and deploy by using PowerShell or the Azure CLI.
- Use the Visual Studio Azure Resource Group project to create and deploy a template.
Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Federated identity credential and parent user assigned identity can be created or updated be means of template below. You can deploy ARM templates from the Azure portal.
All of the template parameters are mandatory.
There's a limit of 3-120 characters for a federated identity credential name length. It must be alphanumeric, dash, underscore. First symbol is alphanumeric only.
You must add exactly one audience to a federated identity credential. The audience is verified during token exchange. Use "api://AzureADTokenExchange" as the default value.
List, Get, and Delete operations aren't available with template. Refer to Azure CLI for these operations. By default, all child federated identity credentials are created in parallel, which triggers concurrency detection logic and causes the deployment to fail with a 409-conflict HTTP status code. To create them sequentially, specify a chain of dependencies using the dependsOn property.
Make sure that any kind of automation creates federated identity credentials under the same parent identity sequentially. Federated identity credentials under different managed identities can be created in parallel without any restrictions.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2019-04-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"variables": {},
"parameters": {
"location": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "westcentralus",
"metadata": {
"description": "Location for identities resources. FIC should be enabled in this region."
}
},
"userAssignedIdentityName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "FIC_UA",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of the User Assigned identity (parent identity)"
}
},
"federatedIdentityCredential": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "testCredential",
"metadata": {
"description": "Name of the Federated Identity Credential"
}
},
"federatedIdentityCredentialIssuer": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "https://aks.azure.com/issuerGUID",
"metadata": {
"description": "Federated Identity Credential token issuer"
}
},
"federatedIdentityCredentialSubject": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "system:serviceaccount:ns:svcaccount",
"metadata": {
"description": "Federated Identity Credential token subject"
}
},
"federatedIdentityCredentialAudience": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": " api://AzureADTokenExchange",
"metadata": {
"description": "Federated Identity Credential audience. Single value is only supported."
}
}
},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities",
"apiVersion": "2018-11-30",
"name": "[parameters('userAssignedIdentityName')]",
"location": "[parameters('location')]",
"tags": {
"firstTag": "ficTest"
},
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/federatedIdentityCredentials",
"apiVersion": "2022-01-31-PREVIEW",
"name": "[concat(parameters('userAssignedIdentityName'), '/', parameters('federatedIdentityCredential'))]",
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities', parameters('userAssignedIdentityName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"issuer": "[parameters('federatedIdentityCredentialIssuer')]",
"subject": "[parameters('federatedIdentityCredentialSubject')]",
"audiences": [
"[parameters('federatedIdentityCredentialAudience')]"
]
}
}
]
}
]
}
Prerequisites
- If you're unfamiliar with managed identities for Azure resources, check out the overview section. Be sure to review the difference between a system-assigned and user-assigned managed identity.
- If you don't already have an Azure account, sign up for a free account before you continue.
- Get the information for your external IdP and software workload, which you need in the following steps.
- To create a user-assigned managed identity and configure a federated identity credential, your account needs the Contributor or Owner role assignment.
- You can run all the commands in this article either in the cloud or locally:
- To run in the cloud, use Azure Cloud Shell.
- To run locally, install curl and the Azure CLI.
- Create a user-assigned managed identity
- Find the name of the user-assigned managed identity, which you need in the following steps.
Obtain a bearer access token
If you're running locally, sign in to Azure through the Azure CLI.
az loginObtain an access token by using az account get-access-token.
az account get-access-token
Configure a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Create or update a federated identity credential on the specified user-assigned managed identity.
curl 'https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/provider
s/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/federatedIdenti
tyCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL NAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview' -X PUT -d '{"properties": "{ "properties": { "issuer": "<ISSUER>", "subject": "<SUBJECT>", "audiences": [ "api://AzureADTokenExchange" ] }}"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS TOKEN>"
PUT https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL NAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview
{
"properties": {
"issuer": "https://oidc.prod-aks.azure.com/IssuerGUID",
"subject": "system:serviceaccount:ns:svcaccount",
"audiences": [
"api://AzureADTokenExchange"
]
}
}
Request headers
| Request header | Description |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | Required. Set to application/json. |
| Authorization | Required. Set to a valid Bearer access token. |
Request body
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| properties.audiences | Required. The list of audiences that can appear in the issued token. |
| properties.issuer | Required. The URL of the issuer to be trusted. |
| properties.subject | Required. The identifier of the external identity. |
List federated identity credentials on a user-assigned managed identity
List all the federated identity credentials on the specified user-assigned managed identity.
curl 'https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials?api-version=2022-01-31-preview' -H "Content-Type: application/json" -X GET -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS TOKEN>"
GET
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials?api-version=2022-01-31-preview
Request headers
| Request header | Description |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | Required. Set to application/json. |
| Authorization | Required. Set to a valid Bearer access token. |
Get a federated identity credential on a user-assigned managed identity
Get a federated identity credential on the specified user-assigned managed identity.
curl 'https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL RESOURCENAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview' -X GET -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS TOKEN>"
GET
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL RESOURCENAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview
Request headers
| Request header | Description |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | Required. Set to application/json. |
| Authorization | Required. Set to a valid Bearer access token. |
Delete a federated identity credential from a user-assigned managed identity
Delete a federated identity credential on the specified user-assigned managed identity.
curl 'https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL RESOURCENAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview' -X DELETE -H "Content-Type: application/json" -H "Authorization: Bearer <ACCESS TOKEN>"
DELETE
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/<SUBSCRIPTION ID>/resourceGroups/<RESOURCE GROUP>/providers/Microsoft.ManagedIdentity/userAssignedIdentities/<USER ASSIGNED IDENTITY NAME>/<RESOURCE NAME>/federatedIdentityCredentials/<FEDERATED IDENTITY CREDENTIAL RESOURCENAME>?api-version=2022-01-31-preview
Request headers
| Request header | Description |
|---|---|
| Content-Type | Required. Set to application/json. |
| Authorization | Required. Set to a valid Bearer access token. |
Next steps
- For information about the required format of JWTs created by external identity providers, read about the assertion format.