Analyze data with Azure Machine Learning
This tutorial uses Azure Machine Learning designer to build a predictive machine learning model. The model is based on the data stored in Azure Synapse. The scenario for the tutorial is to predict if a customer is likely to buy a bike or not so Adventure Works, the bike shop, can build a targeted marketing campaign.
Prerequisites
To step through this tutorial, you need:
- a SQL pool pre-loaded with AdventureWorksDW sample data. To provision this SQL Pool, see Create a SQL pool and choose to load the sample data. If you already have a data warehouse but don't have sample data, you can load sample data manually.
- an Azure Machine learning workspace. Follow this tutorial to create a new one.
Get the data
The data used is in the dbo.vTargetMail view in AdventureWorksDW. To use Datastore in this tutorial, the data is first exported to Azure Data Lake Storage account as Azure Synapse doesn't currently support datasets. Azure Data Factory can be used to export data from the data warehouse to Azure Data Lake Storage using the copy activity. Use the following query for import:
SELECT [CustomerKey]
,[GeographyKey]
,[CustomerAlternateKey]
,[MaritalStatus]
,[Gender]
,cast ([YearlyIncome] as int) as SalaryYear
,[TotalChildren]
,[NumberChildrenAtHome]
,[EnglishEducation]
,[EnglishOccupation]
,[HouseOwnerFlag]
,[NumberCarsOwned]
,[CommuteDistance]
,[Region]
,[Age]
,[BikeBuyer]
FROM [dbo].[vTargetMail]
Once the data is available in Azure Data Lake Storage, Datastores in Azure Machine Learning is used to connect to Azure storage services. Follow the steps below to create a Datastore and a corresponding Dataset:
Launch Azure Machine Learning studio either from Azure portal or sign in at Azure Machine Learning studio.
Click on Datastores on the left pane in the Manage section and then click on New Datastore.
Provide a name for the datastore, select the type as 'Azure Blob Storage', provide location and credentials. Then, click Create.
Next, click on Datasets on the left pane in the Assets section. Select Create dataset with the option From datastore.
Specify the name of the dataset and select the type to be Tabular. Then, click Next to move forward.
In Select or create a datastore section, select the option Previously created datastore. Select the datastore that was created earlier. Click Next and specify the path and file settings. Make sure to specify column header if the files contain one.
Finally, click Create to create the dataset.
Configure designer experiment
Next, follow steps below for designer configuration:
Click on Designer tab on the left pane in the Author section.
Select Easy-to-use prebuilt components to build a new pipeline.
In the settings pane on the right, specify the name of the pipeline.
Also, select a target compute cluster for the whole experiment in settings button to a previously provisioned cluster. Close the Settings pane.
Import the data
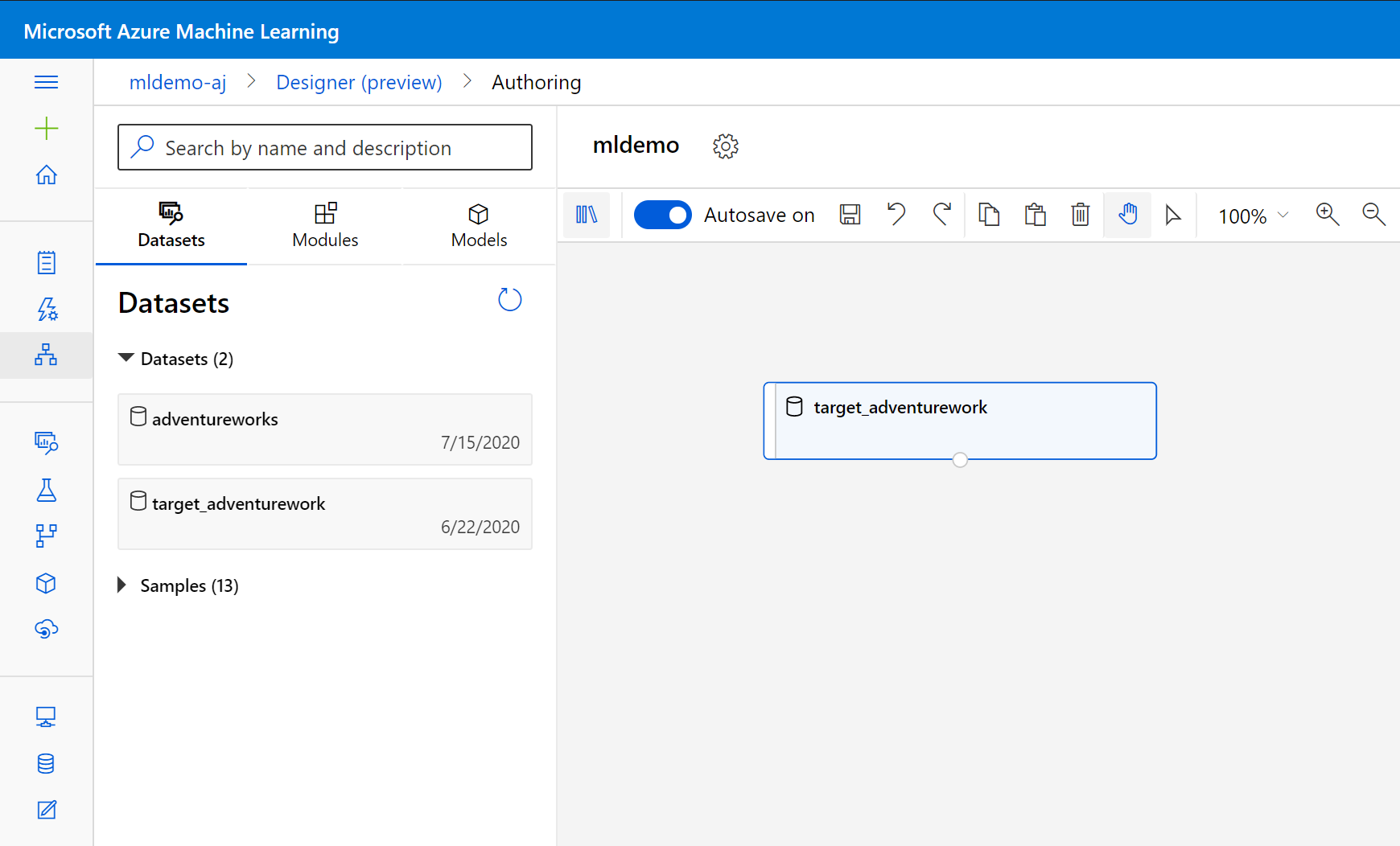
Select the Datasets subtab in the left pane below the search box.
Drag the dataset your created earlier into the canvas.
Clean the data
To clean the data, drop columns that aren't relevant for the model. Follow the steps below:
Select the Components subtab in the left pane.
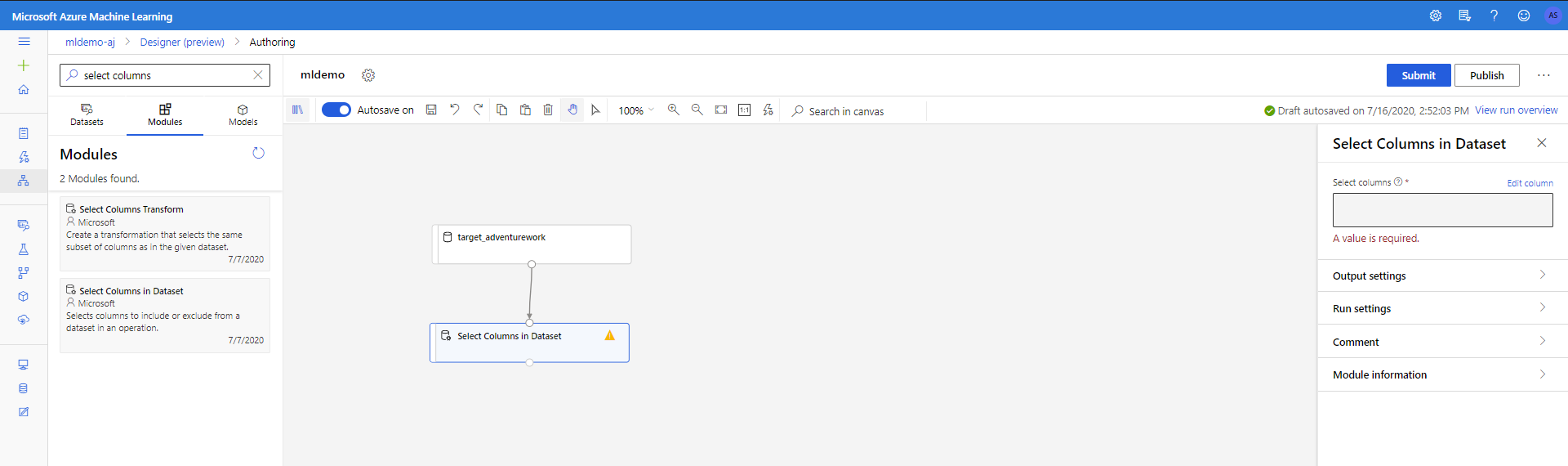
Drag the Select Columns in Dataset component under Data Transformation < Manipulation into the canvas. Connect this component to the Dataset component.
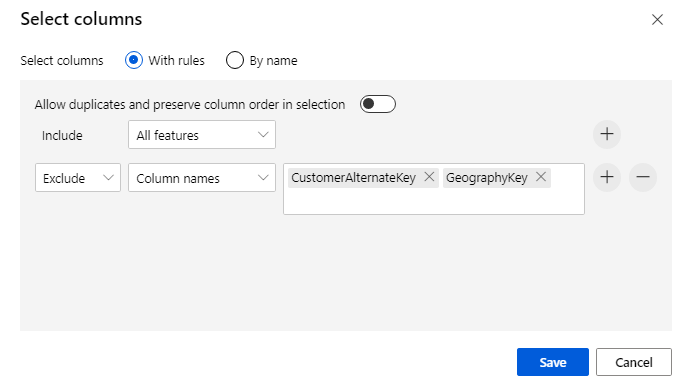
Click on the component to open properties pane. Click on Edit column to specify which columns you wish to drop.
Exclude two columns: CustomerAlternateKey and GeographyKey. Click Save
Build the model
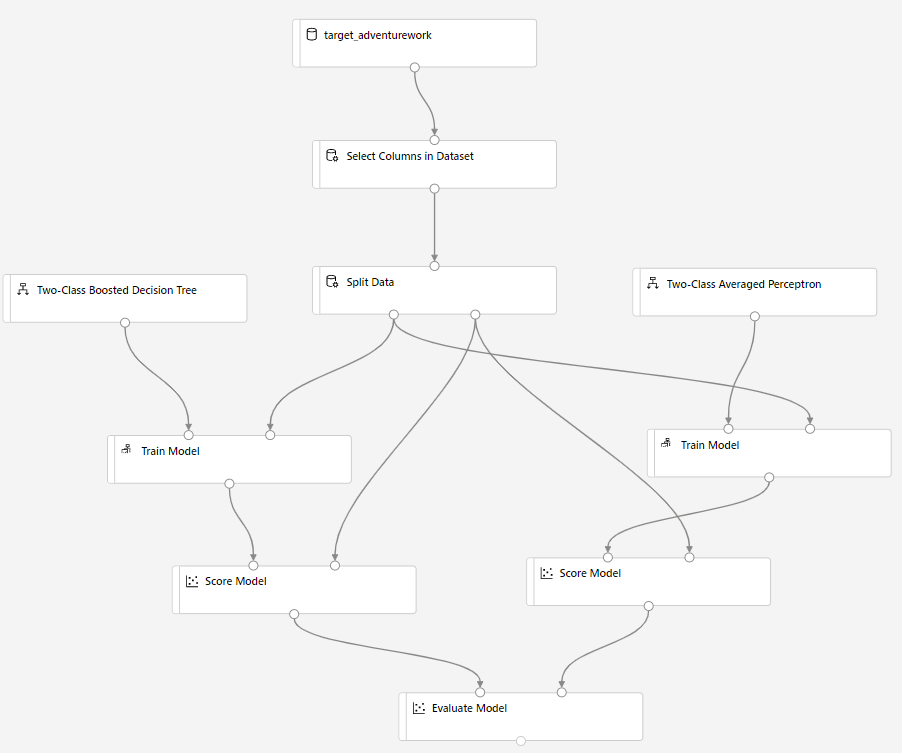
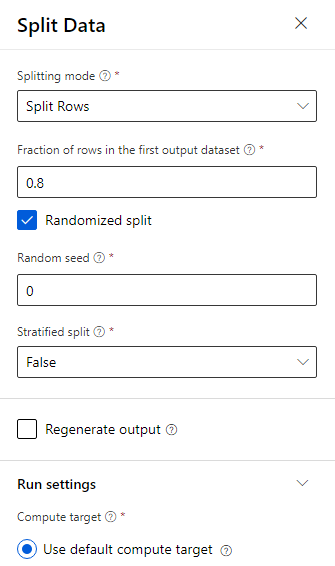
The data is split 80-20: 80% to train a machine learning model and 20% to test the model. "Two-Class" algorithms are used in this binary classification problem.
Drag the Split Data component into the canvas.
In the properties pane, enter 0.8 for Fraction of rows in the first output dataset.
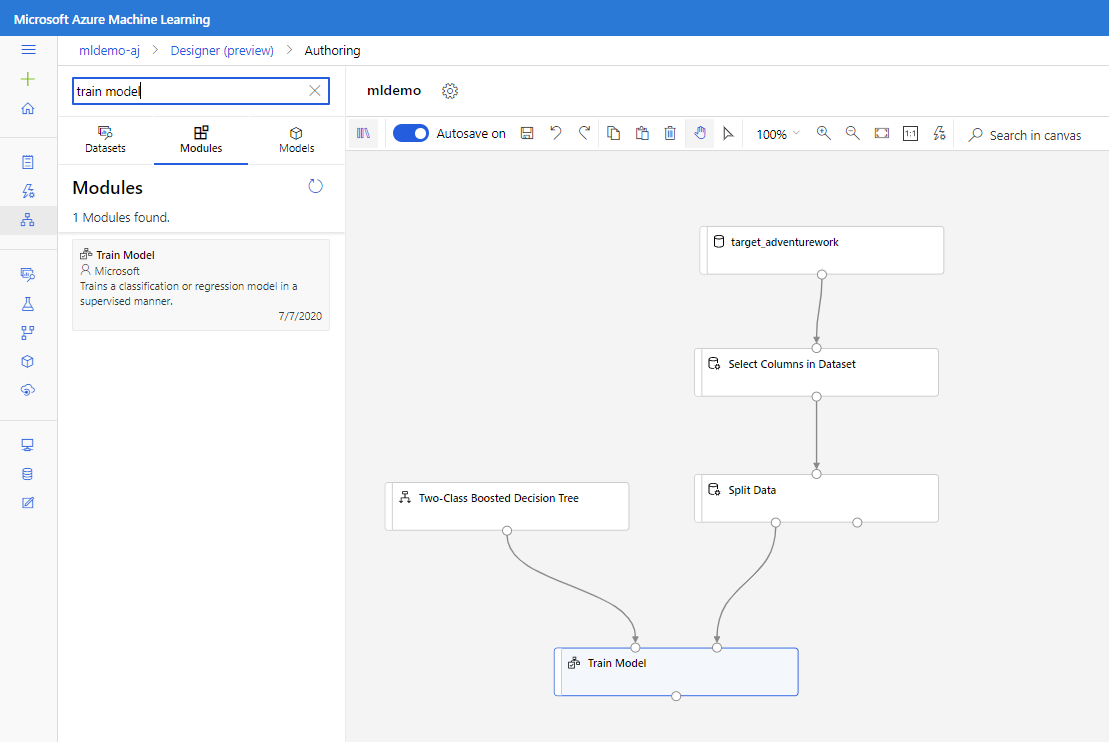
Drag the Two-Class Boosted Decision Tree component into the canvas.
Drag the Train Model component into the canvas. Specify inputs by connecting it to the Two-Class Boosted Decision Tree (ML algorithm) and Split Data (data to train the algorithm on) components.
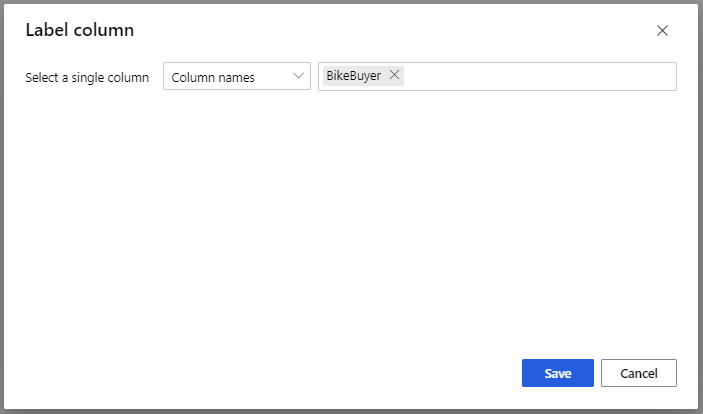
For Train Model model, in Label column option in the Properties pane, select Edit column. Select the BikeBuyer column as the column to predict and select Save.
Score the model
Now, test how does the model perform on test data. Two different algorithms will be compared to see which one performs better. Follow the steps below:
Drag Score Model component into the canvas and connect it to Train Model and Split Data components.
Drag the Two-Class Bayes Averaged Perceptron into the experiment canvas. You'll compare how this algorithm performs in comparison to the Two-Class Boosted Decision Tree.
Copy and paste the components Train Model and Score Model in the canvas.
Drag the Evaluate Model component into the canvas to compare the two algorithms.
Click submit to set up the pipeline run.
Once the run finishes, right-click on the Evaluate Model component and click Visualize Evaluation results.
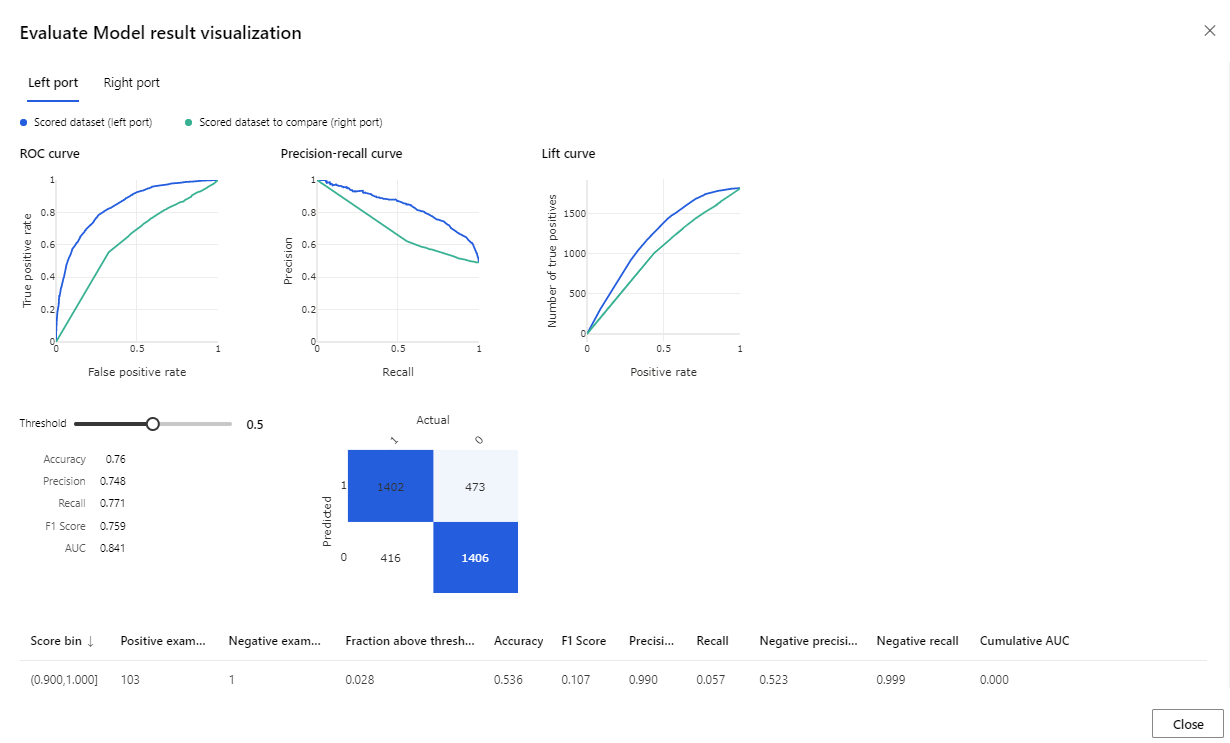
The metrics provided are the ROC curve, precision-recall diagram, and lift curve. Look at these metrics to see that the first model performed better than the second one. To look at what the first model predicted, right-click on the Score Model component and click Visualize Scored dataset to see the predicted results.
You'll see two more columns added to your test dataset.
- Scored Probabilities: the likelihood that a customer is a bike buyer.
- Scored Labels: the classification done by the model – bike buyer (1) or not (0). This probability threshold for labeling is set to 50% and can be adjusted.
Compare the column BikeBuyer (actual) with the Scored Labels (prediction), to see how well the model has performed. Next, you can use this model to make predictions for new customers. You can publish this model as a web service or write results back to Azure Synapse.
Next steps
To learn more about Azure Machine Learning, refer to Introduction to Machine Learning on Azure.
Learn about built-in scoring in the data warehouse, here.