Manage libraries for Apache Spark pools in Azure Synapse Analytics
After you identify the Scala, Java, R (Preview), or Python packages that you would like to use or update for your Spark application, you can install or remove them from a Spark pool. Pool-level libraries are available to all notebooks and jobs running on the pool.
There are two primary ways to install a library on a Spark pool:
- Install a workspace library that's been uploaded as a workspace package.
- To update Python libraries, provide a requirements.txt or Conda environment.yml environment specification file to install packages from repositories like PyPI or Conda-Forge. For more information, see the Environment specification formats section.
After the changes are saved, a Spark job runs the installation and caches the resulting environment for later reuse. Once the job is complete, new Spark jobs or notebook sessions use the updated pool libraries.
Important
- If the package you're installing is large or takes a long time to install, the Spark instance startup time is affected.
- Altering the PySpark, Python, Scala/Java, .NET, R, or Spark version isn't supported.
- Installing packages from external repositories like PyPI, Conda-Forge, or the default Conda channels isn't supported within data exfiltration protection enabled workspaces.
Manage packages from Synapse Studio or Azure portal
Spark pool libraries can be managed either from Synapse Studio or the Azure portal.
In the Azure portal, navigate to your Azure Synapse Analytics workspace.
From the Analytics pools section, select the Apache Spark pools tab and select a Spark pool from the list.
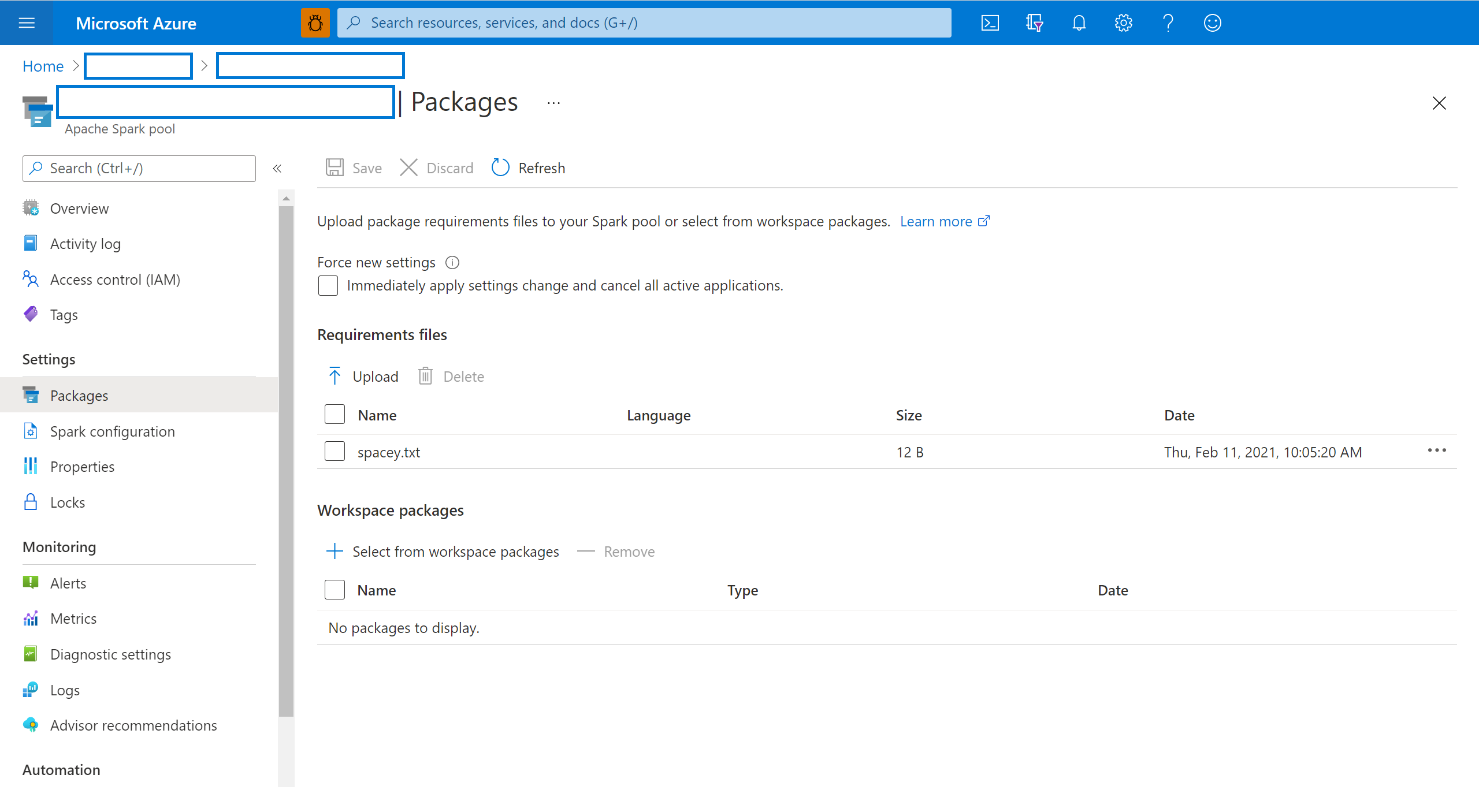
Select the Packages from the Settings section of the Spark pool.
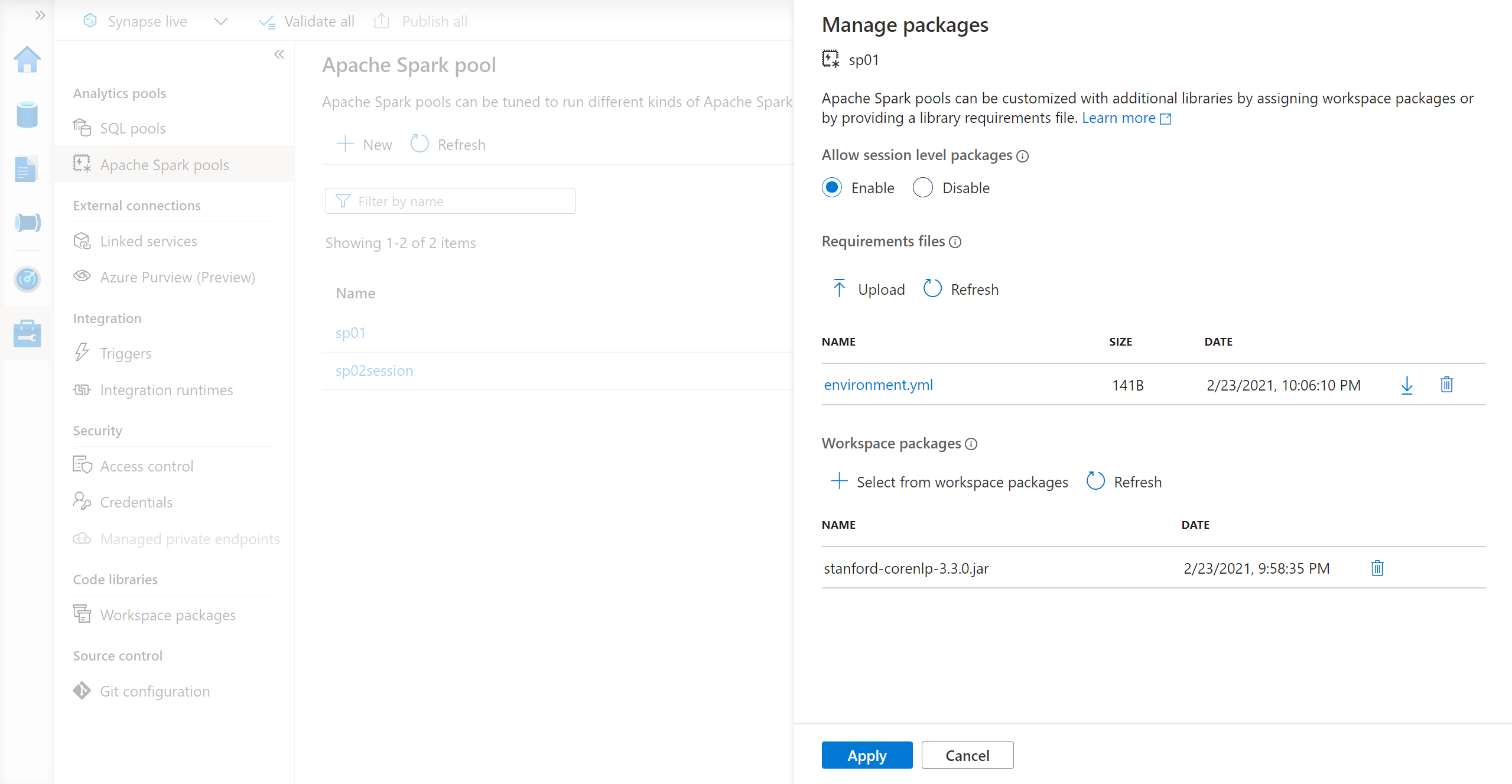
For Python feed libraries, upload the environment configuration file using the file selector in the Packages section of the page.
You can also select additional workspace packages to add Jar, Wheel, or Tar.gz files to your pool.
You can also remove deprecated packages from Workspace packages section, then your pool no longer attaches these packages.
After you save your changes, a system job is triggered to install and cache the specified libraries. This process helps reduce overall session startup time.
After the job successfully completes, all new sessions pick up the updated pool libraries.
Important
By selecting the option to Force new settings, you're ending all current sessions for the selected Spark pool. Once the sessions are ended, you must wait for the pool to restart.
If this setting is unchecked, then you need to wait for the current Spark session to end or stop it manually. After the session ends, you need to let the pool restart.
Track installation progress
A system reserved Spark job is initiated each time a pool is updated with a new set of libraries. This Spark job helps monitor the status of the library installation. If the installation fails due to library conflicts or other issues, the Spark pool reverts to its previous or default state.
In addition, users can inspect the installation logs to identify dependency conflicts or see which libraries were installed during the pool update.
To view these logs:
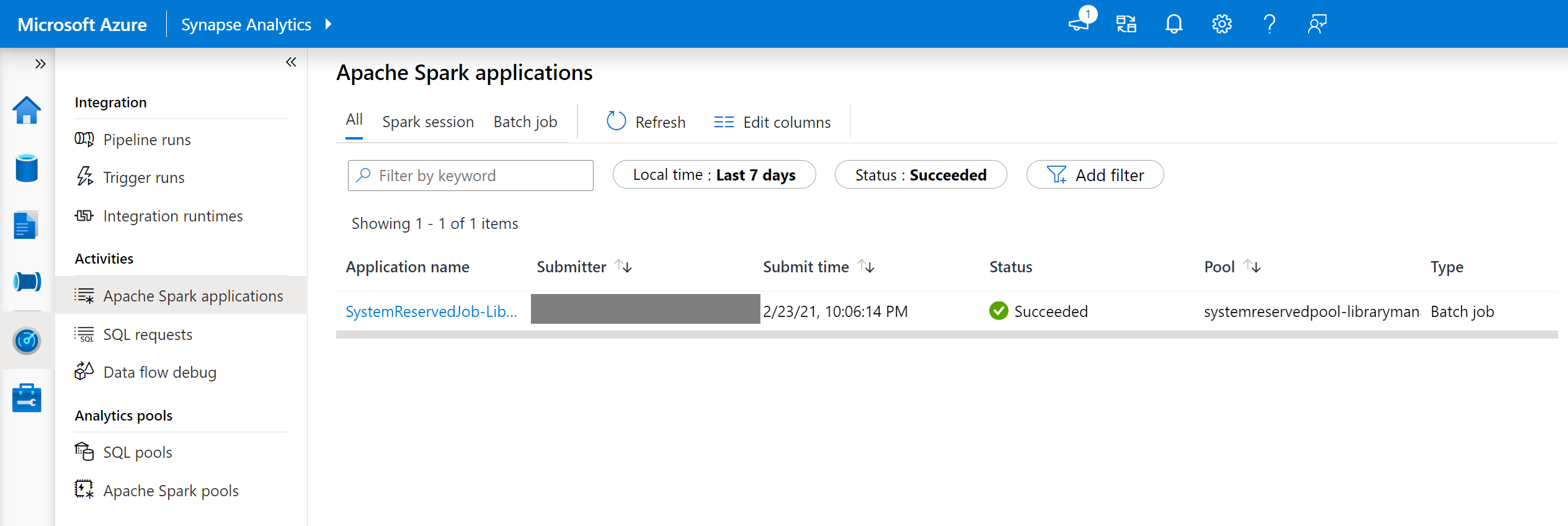
In Synapse Studio, navigate to the Spark applications list in the Monitor tab.
Select the system Spark application job that corresponds to your pool update. These system jobs run under the SystemReservedJob-LibraryManagement title.
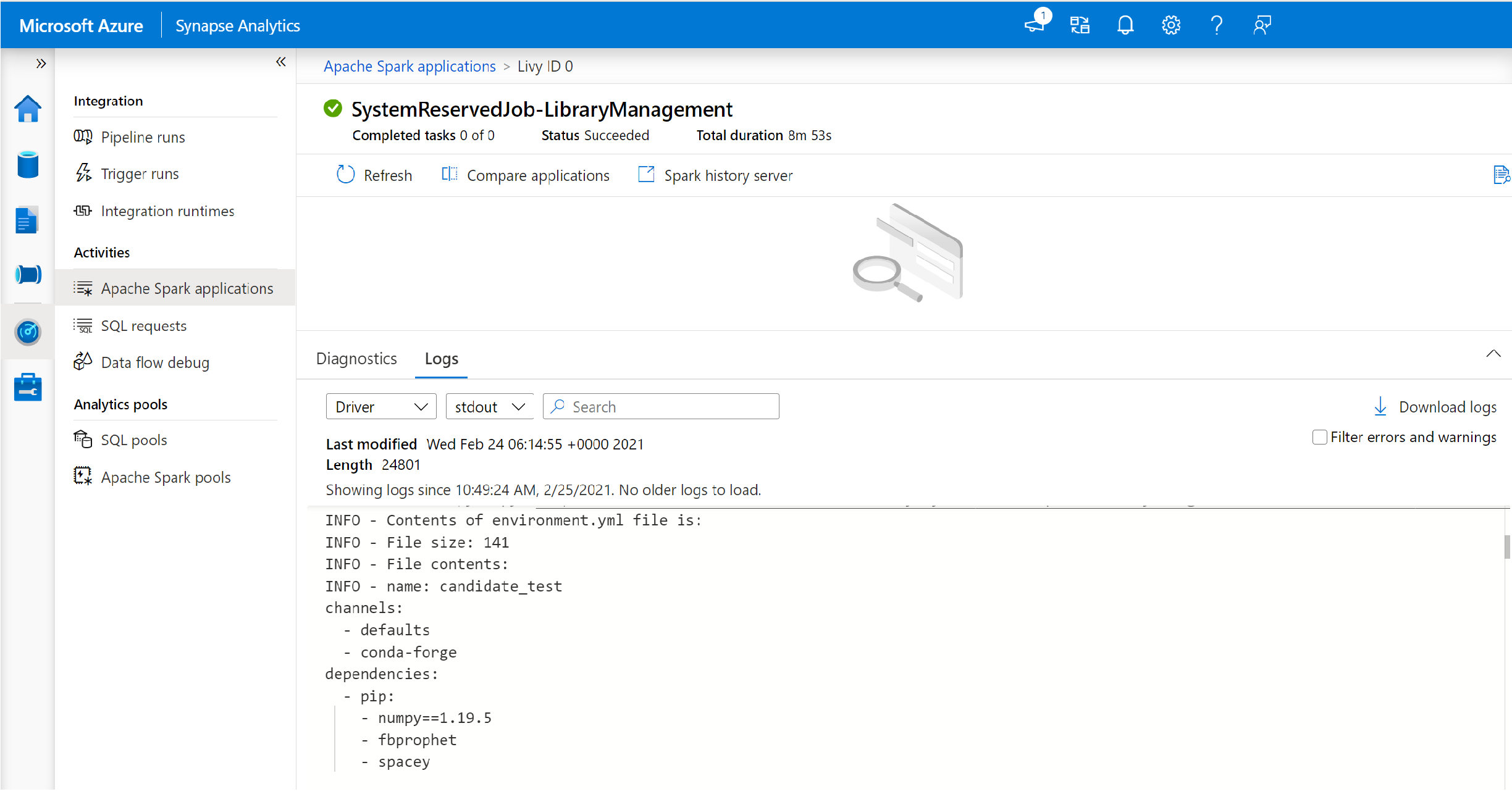
Switch to view the driver and stdout logs.
The results contain the logs related to the installation of your dependencies.
Environment specification formats
PIP requirements.txt
A requirements.txt file (output from the pip freeze command) can be used to upgrade the environment. When a pool is updated, the packages listed in this file are downloaded from PyPI. The full dependencies are then cached and saved for later reuse of the pool.
The following snippet shows the format for the requirements file. The PyPI package name is listed along with an exact version. This file follows the format described in the pip freeze reference documentation.
This example pins a specific version.
absl-py==0.7.0
adal==1.2.1
alabaster==0.7.10
YML format
In addition, you can provide an environment.yml file to update the pool environment. The packages listed in this file are downloaded from the default Conda channels, Conda-Forge, and PyPI. You can specify other channels or remove the default channels by using the configuration options.
This example specifies the channels and Conda/PyPI dependencies.
name: stats2
channels:
- defaults
dependencies:
- bokeh
- numpy
- pip:
- matplotlib
- koalas==1.7.0
For details on creating an environment from this environment.yml file, see Activating an environment.