Retrieval Augmented Generation using Azure Machine Learning prompt flow (preview)
Important
This feature is currently in public preview. This preview version is provided without a service-level agreement, and we don't recommend it for production workloads. Certain features might not be supported or might have constrained capabilities.
For more information, see Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews.
Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) is a pattern that works with pretrained Large Language Models (LLM) and your own data to generate responses. In Azure Machine Learning, you can now implement RAG in a prompt flow. Support for RAG is currently in public preview.
This article lists some of the benefits of RAG, provides a technical overview, and describes RAG support in Azure Machine Learning.
Note
New to LLM and RAG concepts? This video clip from a Microsoft presentation offers a simple explanation.
Why use RAG?
Traditionally, a base model is trained with point-in-time data to ensure its effectiveness in performing specific tasks and adapting to the desired domain. However, sometimes you need to work with newer or more current data. Two approaches can supplement the base model: fine-tuning or further training of the base model with new data, or RAG that uses prompt engineering to supplement or guide the model in real time.
Fine-tuning is suitable for continuous domain adaptation, enabling significant improvements in model quality but often incurring higher costs. Conversely, RAG offers an alternative approach, allowing the use of the same model as a reasoning engine over new data provided in a prompt. This technique enables in-context learning without the need for expensive fine-tuning, empowering businesses to use LLMs more efficiently.
RAG allows businesses to achieve customized solutions while maintaining data relevance and optimizing costs. By adopting RAG, companies can use the reasoning capabilities of LLMs, utilizing their existing models to process and generate responses based on new data. RAG facilitates periodic data updates without the need for fine-tuning, streamlining the integration of LLMs into businesses.
- Provide supplemental data as a directive or a prompt to the LLM
- Adds a fact checking component on your existing models
- Train your model on up-to-date data without incurring the extra time and costs associated with fine-tuning
- Train on your business specific data
Technical overview of using RAG on Large Language Models (LLMs)
In information retrieval, RAG is an approach that enables you to harness the power of LLMs with your own data. Enabling an LLM to access custom data involves the following steps. First, the large data should be chunked into manageable pieces. Second, the chunks need to be converted into a searchable format. Third, the converted data should be stored in a location that allows efficient access. Additionally, it's important to store relevant metadata for citations or references when the LLM provides responses.
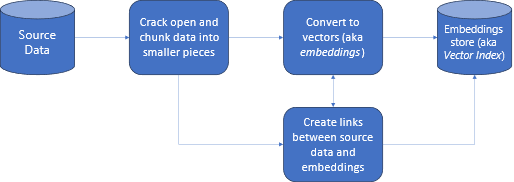
Let us look at the diagram in more detail.
Source data: this is where your data exists. It could be a file/folder on your machine, a file in cloud storage, an Azure Machine Learning data asset, a Git repository, or an SQL database.
Data chunking: The data in your source needs to be converted to plain text. For example, word documents or PDFs need to be cracked open and converted to text. The text is then chunked into smaller pieces.
Converting the text to vectors: called embeddings. Vectors are numerical representations of concepts converted to number sequences, which make it easy for computers to understand the relationships between those concepts.
Links between source data and embeddings: this information is stored as metadata on the chunks created which are then used to assist the LLMs to generate citations while generating responses.
RAG with Azure Machine Learning (preview)
RAG in Azure Machine Learning is enabled by integration with Azure OpenAI Service for large language models and vectorization, with support for Faiss and Azure AI Search (formerly Cognitive Search) as vector stores, and support for open source offerings tools and frameworks such as LangChain for data chunking.
To implement RAG, a few key requirements must be met. First, data should be formatted in a manner that allows efficient searchability before sending it to the LLM, which ultimately reduces token consumption. To ensure the effectiveness of RAG, it's also important to regularly update your data on a periodic basis. Furthermore, having the capability to evaluate the output from the LLM using your data enables you to measure the efficacy of your techniques. Azure Machine Learning not only allows you to get started easily on these aspects, but also enables you to improve and productionize RAG. Azure Machine Learning offers:
- Samples for starting RAG-based Q&A scenarios.
- Wizard-based UI experience to create and manage data and incorporate it into prompt flows.
- Ability to measure and enhance RAG workflows, including test data generation, automatic prompt creation, and visualized prompt evaluation metrics.
- Advanced scenarios with more control using the new built-in RAG components for creating custom pipelines in notebooks.
- Code experience, which allows utilization of data created with open source offerings like LangChain.
- Seamless integration of RAG workflows into MLOps workflows using pipelines and jobs.
Conclusion
Azure Machine Learning allows you to incorporate RAG in your AI using the Azure Machine Learning studio or using code with Azure Machine Learning pipelines. It offers several value additions like the ability to measure and enhance RAG workflows, test data generation, automatic prompt creation, and visualize prompt evaluation metrics. It enables the integration of RAG workflows into MLOps workflows using pipelines. You can also use your data with open source offerings like LangChain.
Next steps
Use Vector Stores with Azure Machine Learning (preview)
How to create vector index in Azure Machine Learning prompt flow (preview)