Quickstart: Create Apache Hadoop cluster in Azure HDInsight using Azure portal
In this article, you learn how to create Apache Hadoop clusters in HDInsight using Azure portal, and then run Apache Hive jobs in HDInsight. Most of Hadoop jobs are batch jobs. You create a cluster, run some jobs, and then delete the cluster. In this article, you perform all the three tasks. For in-depth explanations of available configurations, see Set up clusters in HDInsight. For more information regarding the use of the portal to create clusters, see Create clusters in the portal.
In this quickstart, you use the Azure portal to create an HDInsight Hadoop cluster. You can also create a cluster using the Azure Resource Manager template.
Currently, HDInsight comes with seven different cluster types. Each cluster type supports a different set of components. All cluster types support Hive. For a list of supported components in HDInsight, see What's new in the Apache Hadoop cluster versions provided by HDInsight?
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Create an Apache Hadoop cluster
In this section, you create a Hadoop cluster in HDInsight using the Azure portal.
Sign in to the Azure portal.
From the top menu, select + Create a resource.
Select Analytics > Azure HDInsight to go to the Create HDInsight cluster page.
From the Basics tab, provide the following information:
Property Description Subscription From the drop-down list, select the Azure subscription that's used for the cluster. Resource group From the drop-down list, select your existing resource group, or select Create new. Cluster name Enter a globally unique name. The name can consist of up to 59 characters including letters, numbers, and hyphens. The first and last characters of the name can't be hyphens. Region From the drop-down list, select a region where the cluster is created. Choose a location closer to you for better performance. Cluster type Select Select cluster type. Then select Hadoop as the cluster type. Version From the drop-down list, select a version. Use the default version if you don't know what to choose. Cluster sign in username and password The default sign in name is admin. The password must be at least 10 characters in length and must contain at least one digit, one uppercase, and one lower case letter, one nonalphanumeric character (except characters ' ` "). Make sure you do not provide common passwords such as "Pass@word1".Secure Shell (SSH) username The default username is sshuser. You can provide another name for the SSH username.Use cluster sign in password for SSH Select this check box to use the same password for SSH user as the one you provided for the cluster sign in user. 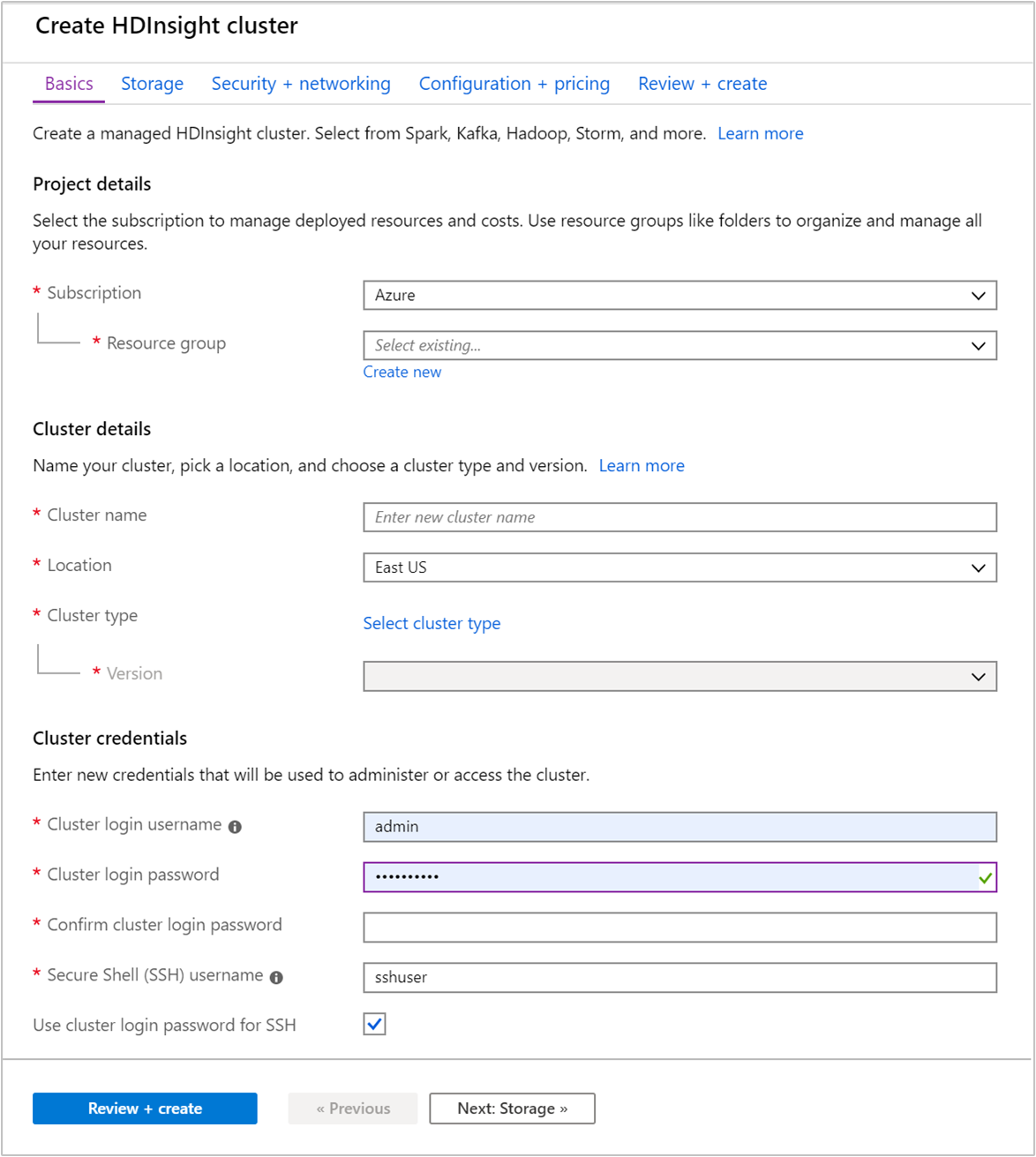
Select the Next: Storage >> to advance to the storage settings.
From the Storage tab, provide the following values:
Property Description Primary storage type Use the default value Azure Storage. Selection method Use the default value Select from list. Primary storage account Use the drop-down list to select an existing storage account, or select Create new. If you create a new account, the name must be between 3 and 24 characters in length, and can include numbers and lowercase letters only Container Use the autopopulated value. 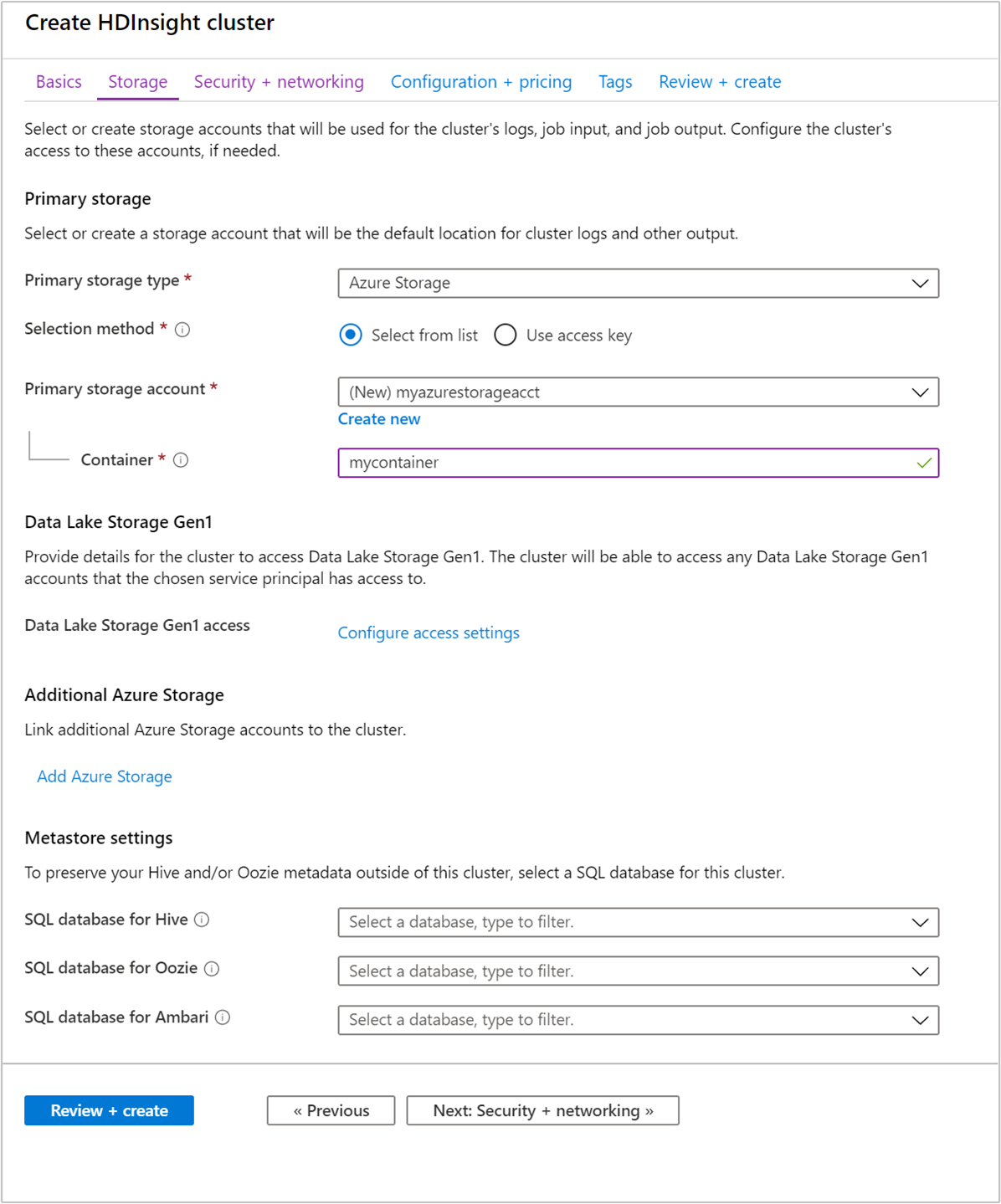
Each cluster has an Azure Storage account, or an
Azure Data Lake Storage Gen2dependency. It's referred as the default storage account. HDInsight cluster and its default storage account must be colocated in the same Azure region. Deleting clusters doesn't delete the storage account.Select the Review + create tab.
From the Review + create tab, verify the values you selected in the earlier steps.
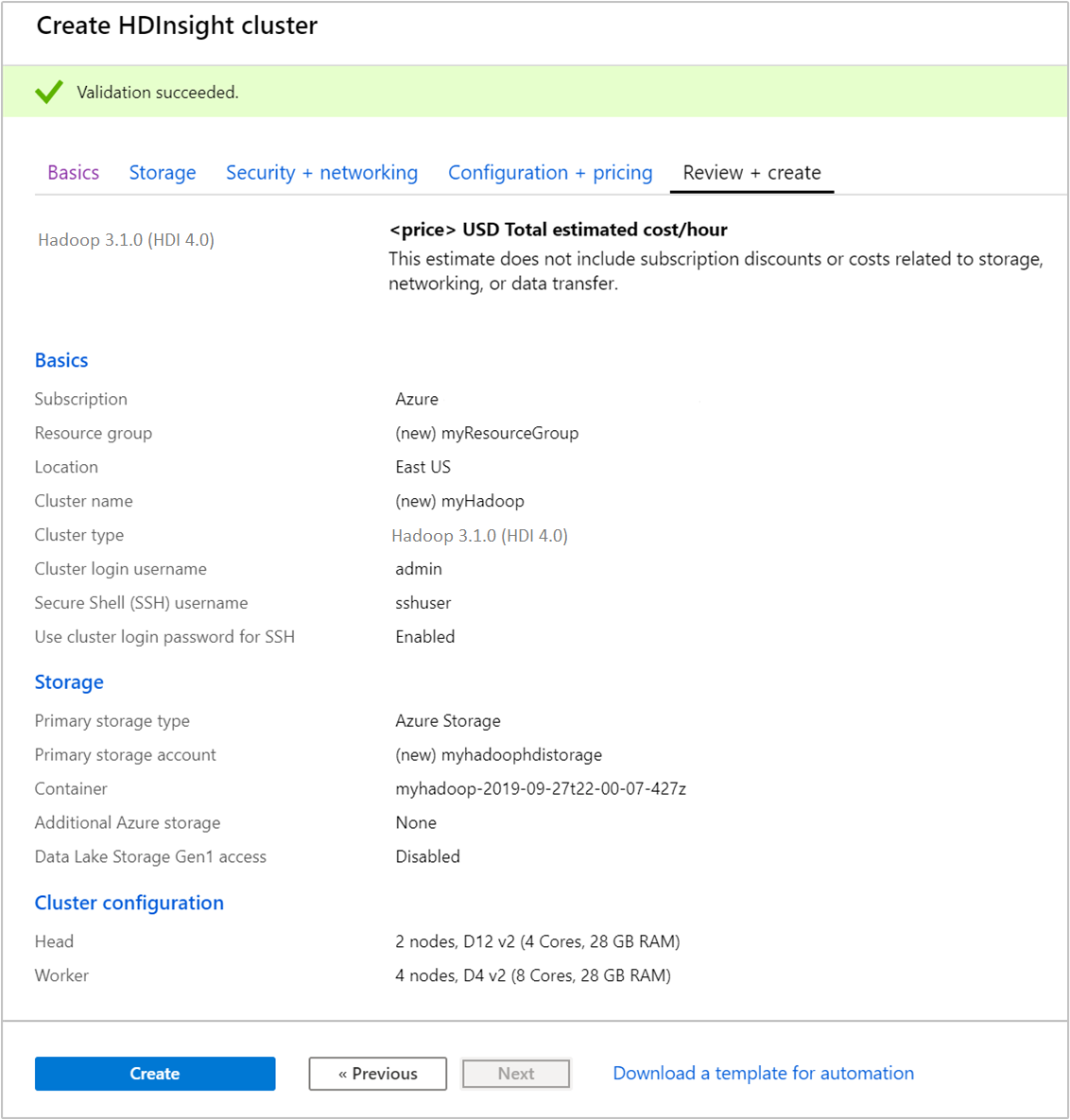
Select Create. It takes about 20 minutes to create a cluster.
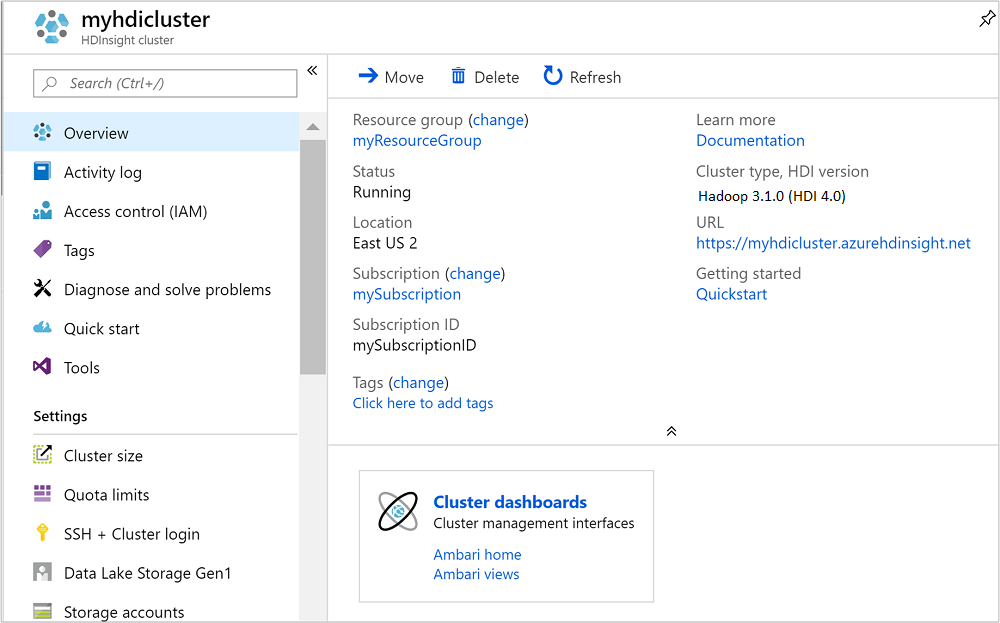
Once the cluster is created, you see the cluster overview page in the Azure portal.
Run Apache Hive queries
Apache Hive is the most popular component used in HDInsight. There are many ways to run Hive jobs in HDInsight. In this quickstart, you use the Ambari Hive view from the portal. For other methods for submitting Hive jobs, see Use Hive in HDInsight.
Note
Apache Hive View is not available in HDInsight 4.0.
To open Ambari, from the previous screenshot, select Cluster Dashboard. You can also browse to
https://ClusterName.azurehdinsight.netwhereClusterNameis the cluster you created in the previous section.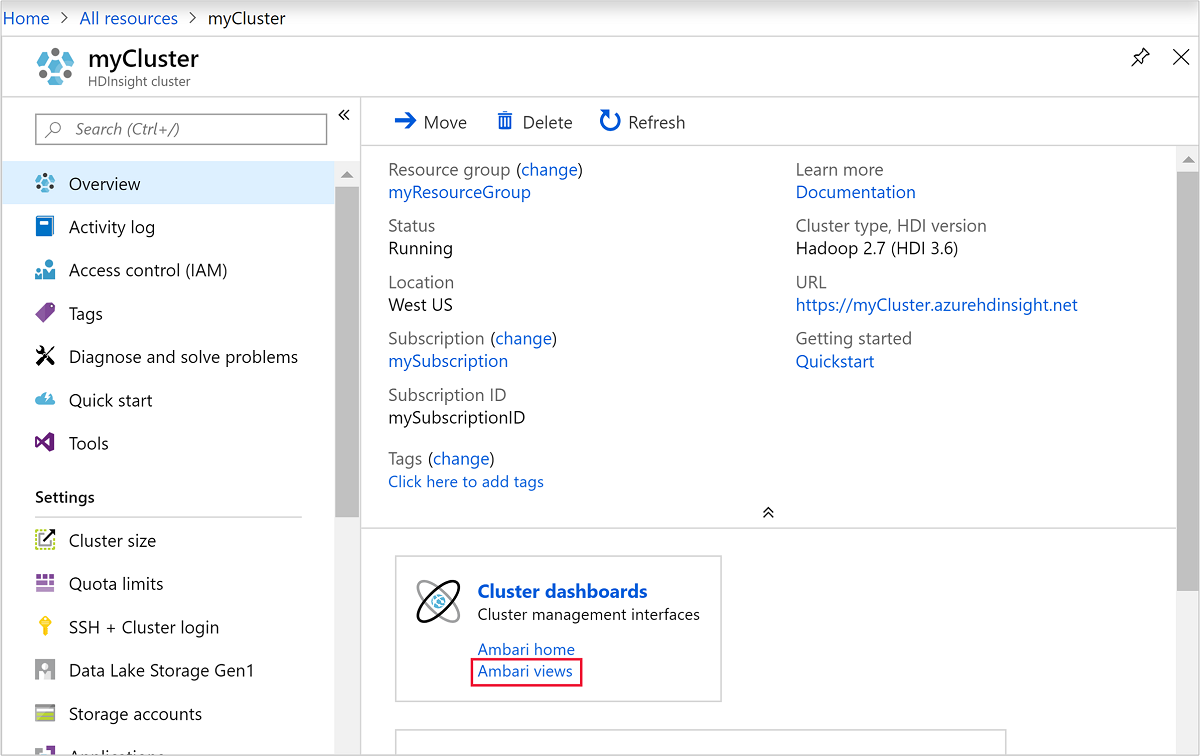
Enter the Hadoop username and password that you specified while creating the cluster. The default username is
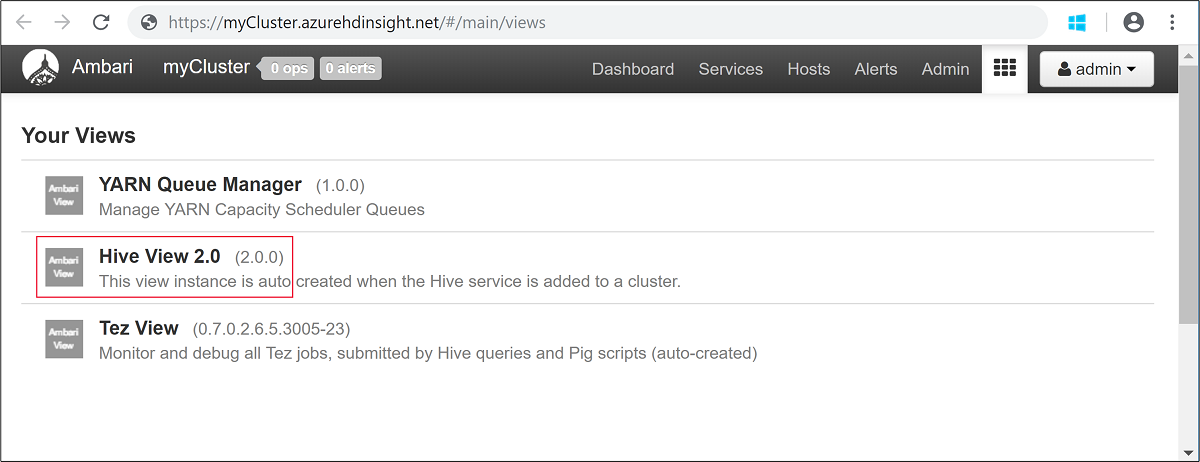
admin.Open Hive View as shown in the following screenshot:
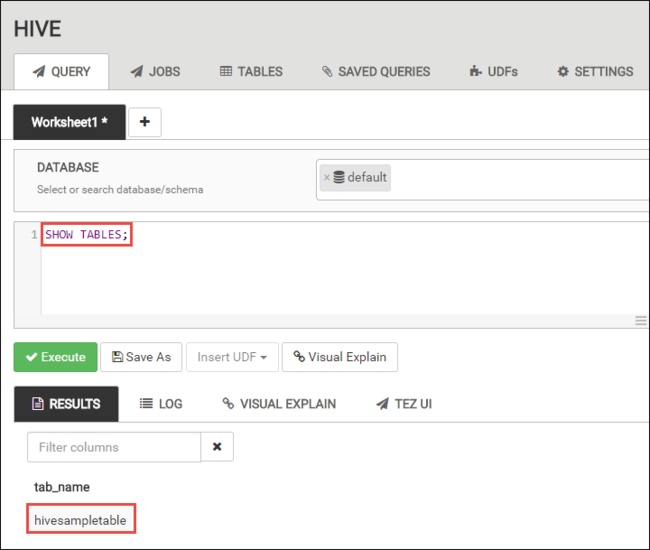
In the QUERY tab, paste the following HiveQL statements into the worksheet:
SHOW TABLES;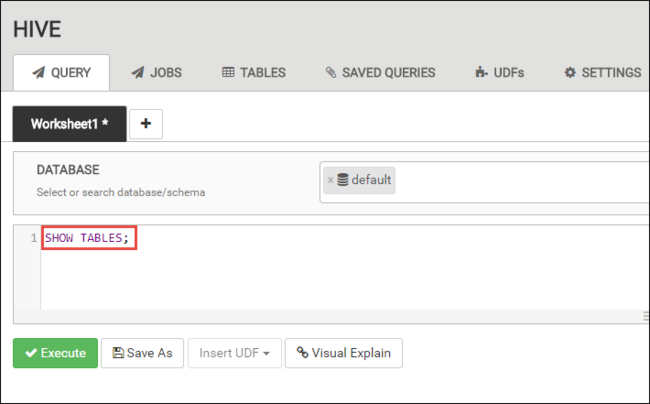
Select Execute. A RESULTS tab appears beneath the QUERY tab and displays information about the job.
Once the query has finished, the QUERY tab displays the results of the operation. You shall see one table called hivesampletable. This sample Hive table comes with all the HDInsight clusters.
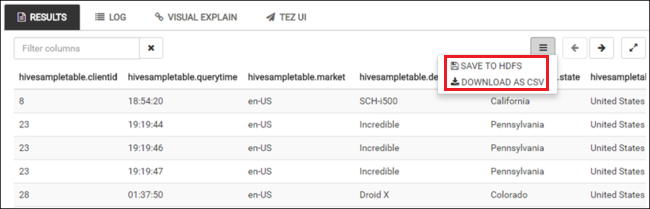
Repeat step 4 and step 5 to run the following query:
SELECT * FROM hivesampletable;You can also save the results of the query. Select the menu button on the right, and specify whether you want to download the results as a CSV file or store it to the storage account associated with the cluster.
After you've completed a Hive job, you can export the results to Azure SQL Database or SQL Server database, you can also visualize the results using Excel. For more information about using Hive in HDInsight, see Use Apache Hive and HiveQL with Apache Hadoop in HDInsight to analyze a sample Apache Log4j file.
Clean up resources
After you complete the quickstart, you may want to delete the cluster. With HDInsight, your data is stored in Azure Storage, so you can safely delete a cluster when it isn't in use. You're also charged for an HDInsight cluster, even when it isn't in use. Since the charges for the cluster are many times more than the charges for storage, it makes economic sense to delete clusters when they aren't in use.
Note
If you are immediately proceeding to the next article to learn how to run ETL operations using Hadoop on HDInsight, you may want to keep the cluster running. This is because in the tutorial you have to create a Hadoop cluster again. However, if you are not going through the next article right away, you must delete the cluster now.
To delete the cluster and/or the default storage account
Go back to the browser tab where you have the Azure portal. You shall be on the cluster overview page. If you only want to delete the cluster but retain the default storage account, select Delete.
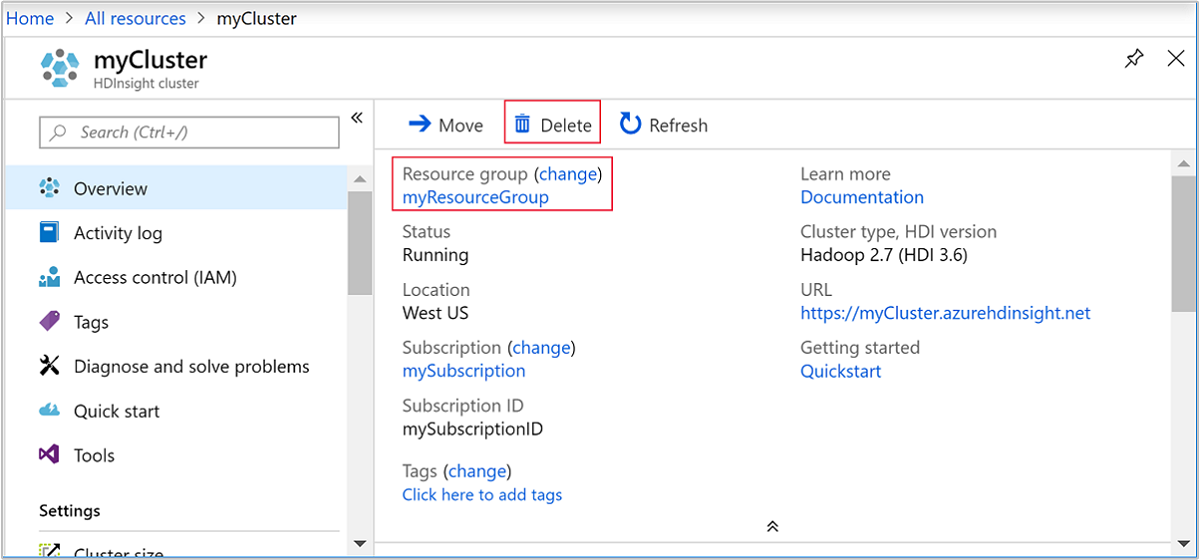
If you want to delete the cluster and the default storage account, select the resource group name (highlighted in the previous screenshot) to open the resource group page.
Select Delete resource group to delete the resource group, which contains the cluster and the default storage account. Note deleting the resource group deletes the storage account. If you want to keep the storage account, choose to delete the cluster only.
Next steps
In this quickstart, you learned how to create a Linux-based HDInsight cluster using a Resource Manager template, and how to perform basic Hive queries. In the next article, you learn how to perform an extract, transform, and load (ETL) operation using Hadoop on HDInsight.