Get answers to common questions about Microsoft Defender for Databases.
If I enable this Microsoft Defender plan on my subscription, are all SQL servers on the subscription protected?
No. To defend a SQL server running on an Azure virtual machine or an Azure Arc-enabled machine, Defender for Cloud requires:
- A Log Analytics agent on the machine.
- The relevant Log Analytics workspace to have Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines enabled.
The subscription status, shown on the SQL server's page in the Azure portal, reflects the default workspace status and applies to all connected machines. Defender for Cloud helps protect only the SQL servers on hosts that have a Log Analytics agent reporting to that workspace.
Is there a performance effect from deploying Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines?
Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines focuses on security, but it has a split architecture to balance data uploading and speed with performance:
- Some of our detectors, including an Extended Events trace named
SQLAdvancedThreatProtectionTraffic, run on the machine for real-time speed advantages. - Other detectors run in the cloud to spare the machine from heavy computational loads.
Lab tests of our solution showed CPU usage averaging 3% for peak slices, compared against benchmark loads. An analysis of our current user data shows a negligible effect on CPU and memory usage.
Performance always varies between environments, machines, and loads. These statements serve as a general guideline, not a guarantee for any individual deployment.
I changed the Log Analytics workspace for Defender for SQL Servers on Machines and lost all my scan results and baselines settings. What happened?
The scan results and baselines are not stored in the Log Analytics workspace but are linked to it. Changing the workspace resets the scan results and baseline settings. However, if you revert to the original workspace within 90 days, the scan results and baseline settings are restored. Read more.
What happens to the old scan results and baselines after I switch to express configuration?
Old results and baseline settings remain available on your storage account, but they won't be updated or used by the system. You don't need to maintain these files for SQL vulnerability assessment to work after you switch to express configuration, but you can keep your old baseline definitions for future reference.
When express configuration is enabled, you don't have direct access to the result and baseline data because it's stored on internal Microsoft storage.
Why is my Azure SQL server marked as unhealthy for "SQL servers should have vulnerability assessment configured," even though I set it up properly by using classic configuration?
The policy behind this recommendation checks for the existence of subassessments for the server. With classic configuration, system databases are scanned only if at least one user database exists. A server without any user databases doesn't have scans or reported scan results, which causes the policy to remain unhealthy.
Switching to express configuration mitigates the issue by enabling scheduled and manual scans for system databases.
Can I set up recurring scans with express configuration?
Express configuration automatically sets up recurring scans for all databases under your server. This behavior is the default, and it isn't configurable at the server or database level.
Is there a way with express configuration to get the weekly email report that's provided in classic configuration?
You can use workflow automation and Logic Apps email scheduling, by following the Microsoft Defender for Cloud processes:
- Time-based triggers
- Scan-based triggers
- Support for disabled rules
Why can't I set database policies anymore?
The SQL vulnerability assessment reports all vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in your environment, so including all databases is helpful. Defender for SQL Servers on Machines is billed per server, not per database.
Can I revert to classic configuration?
Yes. You can revert to classic configuration by using the existing REST APIs and PowerShell cmdlets. When you revert to classic configuration, a notification appears in the Azure portal for changing to express configuration.
Will express configuration become available for other types of SQL?
Stay tuned for updates!
Can I choose which experience is the default?
No. Express configuration is the default for every new, supported Azure SQL database.
Does express configuration change scanning behavior?
No, express configuration provides the same scanning behavior and performance.
Does express configuration have any effect on pricing?
Express configuration doesn't require a storage account, so you don't need to pay extra storage fees unless you choose to keep old scan and baseline data.
What does the 1-MB cap per rule mean?
Any individual rule can't produce results that are more than 1 MB. When results for the rule reach that limit, they stop. You can't set a baseline for the rule, the rule isn't included in the overall recommendation health, and the results appear as Not applicable.
After I enable Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines, how long do I need to wait to see a successful deployment?
It takes approximately 30 minutes to update the protection status via the SQL IaaS Agent Extension, assuming that all the prerequisites are fulfilled.
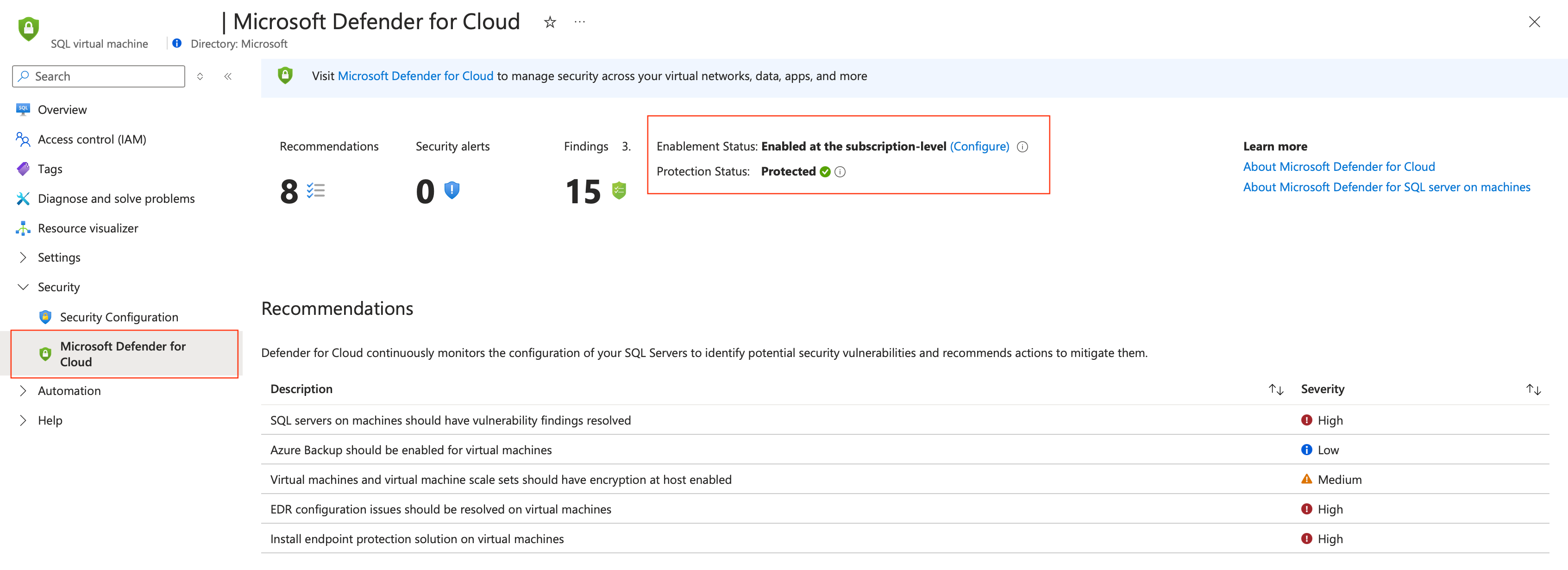
How do I verify that my deployment of Defender for SQL Servers on Machines ended successfully and that my database is now protected?
- In the Azure portal, locate the database on the upper search bar.
- Under Security, select Microsoft Defender for Cloud.
- Check Protection Status. If the status is Protected, the deployment was successful.
What is the purpose of the managed identity created during the installation process on Azure SQL virtual machines?
The managed identity is part of the Azure policy, which pushes out the Azure Monitor Agent. The Azure Monitor Agent uses the managed identity to access the database so that it can collect the data and send it via the Log Analytics workspace to Defender for Cloud. For more information about the use of the managed identity, see Resource Manager template samples for agents in Azure Monitor.
Can I use my own DCR or managed identity instead of the one that Defender for Cloud creates?
Yes. We allow you to bring your own identity or data collection rule (DCR) by using only the script described in Enable Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines at scale.
How many resource groups and Log Analytics workspaces does the autoprovisioning process create?
By default, we create the resource group, workspace, and DCR per region that has the SQL machine. If you choose the custom workspace option, only one resource group or DCR is created in the same location as the workspace.
How can I enable SQL servers on machines with the Azure Monitor Agent at scale?
For the process of how to enable autoprovisioning across multiple subscriptions simultaneously, see Enable Microsoft Defender for SQL Servers on Machines at scale. It's applicable to SQL servers hosted on Azure virtual machines, SQL servers hosted in on-premises environments, and Azure Arc-enabled SQL servers.
Which tables are used in a Log Analytics workspace with the Azure Monitor Agent?
Defender for SQL Servers on Machines (for both SQL virtual machines and Azure Arc-enabled SQL servers) uses the Log Analytics workspace to transfer data from the database to the Defender for Cloud portal. No data is saved locally at the Log Analytics workspace. The tables in the Log Analytics workspace named SQLAtpStatus and SqlVulnerabilityAssessmentScanStatus will be retired when the Microsoft Monitor Agent is deprecated. You can view the status of threat protection and vulnerability assessments in the Defender for Cloud portal.
How does Defender for SQL Servers on Machines collect logs from the SQL server?
Defender for SQL Servers on Machines uses Extended Events, beginning with SQL Server 2017. On previous versions of SQL Server, Defender for SQL Servers on Machines collects the logs by using the SQL Server audit logs.
Does the presence of a parameter named enableCollectionOfSqlQueriesForSecurityResearch in the policy initiative mean that my data is collected for analysis?
The enableCollectionOfSqlQueriesForSecurityResearch parameter isn't in use today. Its default value is false. Unless you proactively change the value, it remains false. This parameter has no effect.