Copy multiple tables in bulk by using Azure Data Factory using PowerShell
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This tutorial demonstrates copying a number of tables from Azure SQL Database to Azure Synapse Analytics. You can apply the same pattern in other copy scenarios as well. For example, copying tables from SQL Server/Oracle to Azure SQL Database/Data Warehouse/Azure Blob, copying different paths from Blob to Azure SQL Database tables.
At a high level, this tutorial involves following steps:
- Create a data factory.
- Create Azure SQL Database, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Azure Storage linked services.
- Create Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics datasets.
- Create a pipeline to look up the tables to be copied and another pipeline to perform the actual copy operation.
- Start a pipeline run.
- Monitor the pipeline and activity runs.
This tutorial uses Azure PowerShell. To learn about using other tools/SDKs to create a data factory, see Quickstarts.
End-to-end workflow
In this scenario, we have a number of tables in Azure SQL Database that we want to copy to Azure Synapse Analytics. Here is the logical sequence of steps in the workflow that happens in pipelines:
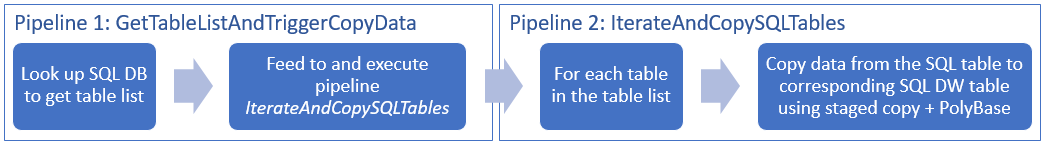
- The first pipeline looks up the list of tables that needs to be copied over to the sink data stores. Alternatively you can maintain a metadata table that lists all the tables to be copied to the sink data store. Then, the pipeline triggers another pipeline, which iterates over each table in the database and performs the data copy operation.
- The second pipeline performs the actual copy. It takes the list of tables as a parameter. For each table in the list, copy the specific table in Azure SQL Database to the corresponding table in Azure Synapse Analytics using staged copy via Blob storage and PolyBase for best performance. In this example, the first pipeline passes the list of tables as a value for the parameter.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. To get started, see Install Azure PowerShell. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
- Azure PowerShell. Follow the instructions in How to install and configure Azure PowerShell.
- Azure Storage account. The Azure Storage account is used as staging blob storage in the bulk copy operation.
- Azure SQL Database. This database contains the source data.
- Azure Synapse Analytics. This data warehouse holds the data copied over from the SQL Database.
Prepare SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics
Prepare the source Azure SQL Database:
Create a database with the Adventure Works LT sample data in SQL Database by following Create a database in Azure SQL Database article. This tutorial copies all the tables from this sample database to Azure Synapse Analytics.
Prepare the sink Azure Synapse Analytics:
If you don't have an Azure Synapse Analytics workspace, see the Get started with Azure Synapse Analytics article for steps to create one.
Create corresponding table schemas in Azure Synapse Analytics. You use Azure Data Factory to migrate/copy data in a later step.
Azure services to access SQL server
For both SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics, allow Azure services to access SQL server. Ensure that Allow access to Azure services setting is turned ON for your server. This setting allows the Data Factory service to read data from your Azure SQL Database and write data to Azure Synapse Analytics. To verify and turn on this setting, do the following steps:
- Click All services on the left and click SQL servers.
- Select your server, and click Firewall under SETTINGS.
- In the Firewall settings page, click ON for Allow access to Azure services.
Create a data factory
Launch PowerShell. Keep Azure PowerShell open until the end of this tutorial. If you close and reopen, you need to run the commands again.
Run the following command, and enter the user name and password that you use to sign in to the Azure portal:
Connect-AzAccountRun the following command to view all the subscriptions for this account:
Get-AzSubscriptionRun the following command to select the subscription that you want to work with. Replace SubscriptionId with the ID of your Azure subscription:
Select-AzSubscription -SubscriptionId "<SubscriptionId>"Run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2 cmdlet to create a data factory. Replace place-holders with your own values before executing the command.
$resourceGroupName = "<your resource group to create the factory>" $dataFactoryName = "<specify the name of data factory to create. It must be globally unique.>" Set-AzDataFactoryV2 -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Location "East US" -Name $dataFactoryNameNote the following points:
The name of the Azure data factory must be globally unique. If you receive the following error, change the name and try again.
The specified Data Factory name 'ADFv2QuickStartDataFactory' is already in use. Data Factory names must be globally unique.To create Data Factory instances, you must be a Contributor or Administrator of the Azure subscription.
For a list of Azure regions in which Data Factory is currently available, select the regions that interest you on the following page, and then expand Analytics to locate Data Factory: Products available by region. The data stores (Azure Storage, Azure SQL Database, etc.) and computes (HDInsight, etc.) used by data factory can be in other regions.
Create linked services
In this tutorial, you create three linked services for source, sink, and staging blob respectively, which includes connections to your data stores:
Create the source Azure SQL Database linked service
Create a JSON file named AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService.json in C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder with the following content: (Create the folder ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy if it does not already exist.)
Important
Replace <servername>, <databasename>, <username>@<servername> and <password> with values of your Azure SQL Database before saving the file.
{ "name": "AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "AzureSqlDatabase", "typeProperties": { "connectionString": "Server=tcp:<servername>.database.windows.net,1433;Database=<databasename>;User ID=<username>@<servername>;Password=<password>;Trusted_Connection=False;Encrypt=True;Connection Timeout=30" } } }In Azure PowerShell, switch to the ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder.
Run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService cmdlet to create the linked service: AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService" -File ".\AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService.json"Here is the sample output:
LinkedServiceName : AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Properties : Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService
Create the sink Azure Synapse Analytics linked service
Create a JSON file named AzureSqlDWLinkedService.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content:
Important
Replace <servername>, <databasename>, <username>@<servername> and <password> with values of your Azure SQL Database before saving the file.
{ "name": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "AzureSqlDW", "typeProperties": { "connectionString": "Server=tcp:<servername>.database.windows.net,1433;Database=<databasename>;User ID=<username>@<servername>;Password=<password>;Trusted_Connection=False;Encrypt=True;Connection Timeout=30" } } }To create the linked service: AzureSqlDWLinkedService, run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "AzureSqlDWLinkedService" -File ".\AzureSqlDWLinkedService.json"Here is the sample output:
LinkedServiceName : AzureSqlDWLinkedService ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Properties : Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.AzureSqlDWLinkedService
Create the staging Azure Storage linked service
In this tutorial, you use Azure Blob storage as an interim staging area to enable PolyBase for a better copy performance.
Create a JSON file named AzureStorageLinkedService.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content:
Important
Replace <accountName> and <accountKey> with name and key of your Azure storage account before saving the file.
{ "name": "AzureStorageLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "AzureStorage", "typeProperties": { "connectionString": "DefaultEndpointsProtocol=https;AccountName=<accountName>;AccountKey=<accountKey>" } } }To create the linked service: AzureStorageLinkedService, run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2LinkedService -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "AzureStorageLinkedService" -File ".\AzureStorageLinkedService.json"Here is the sample output:
LinkedServiceName : AzureStorageLinkedService ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Properties : Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.AzureStorageLinkedService
Create datasets
In this tutorial, you create source and sink datasets, which specify the location where the data is stored:
Create a dataset for source SQL Database
Create a JSON file named AzureSqlDatabaseDataset.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content. The "tableName" is a dummy one as later you use the SQL query in copy activity to retrieve data.
{ "name": "AzureSqlDatabaseDataset", "properties": { "type": "AzureSqlTable", "linkedServiceName": { "referenceName": "AzureSqlDatabaseLinkedService", "type": "LinkedServiceReference" }, "typeProperties": { "tableName": "dummy" } } }To create the dataset: AzureSqlDatabaseDataset, run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2Dataset cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2Dataset -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "AzureSqlDatabaseDataset" -File ".\AzureSqlDatabaseDataset.json"Here is the sample output:
DatasetName : AzureSqlDatabaseDataset ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupname> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Structure : Properties : Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.AzureSqlTableDataset
Create a dataset for sink Azure Synapse Analytics
Create a JSON file named AzureSqlDWDataset.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content: The "tableName" is set as a parameter, later the copy activity that references this dataset passes the actual value into the dataset.
{ "name": "AzureSqlDWDataset", "properties": { "type": "AzureSqlDWTable", "linkedServiceName": { "referenceName": "AzureSqlDWLinkedService", "type": "LinkedServiceReference" }, "typeProperties": { "tableName": { "value": "@{dataset().DWTableName}", "type": "Expression" } }, "parameters":{ "DWTableName":{ "type":"String" } } } }To create the dataset: AzureSqlDWDataset, run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2Dataset cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2Dataset -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "AzureSqlDWDataset" -File ".\AzureSqlDWDataset.json"Here is the sample output:
DatasetName : AzureSqlDWDataset ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupname> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Structure : Properties : Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.AzureSqlDwTableDataset
Create pipelines
In this tutorial, you create two pipelines:
Create the pipeline "IterateAndCopySQLTables"
This pipeline takes a list of tables as a parameter. For each table in the list, it copies data from the table in Azure SQL Database to Azure Synapse Analytics using staged copy and PolyBase.
Create a JSON file named IterateAndCopySQLTables.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content:
{ "name": "IterateAndCopySQLTables", "properties": { "activities": [ { "name": "IterateSQLTables", "type": "ForEach", "typeProperties": { "isSequential": "false", "items": { "value": "@pipeline().parameters.tableList", "type": "Expression" }, "activities": [ { "name": "CopyData", "description": "Copy data from Azure SQL Database to Azure Synapse Analytics", "type": "Copy", "inputs": [ { "referenceName": "AzureSqlDatabaseDataset", "type": "DatasetReference" } ], "outputs": [ { "referenceName": "AzureSqlDWDataset", "type": "DatasetReference", "parameters": { "DWTableName": "[@{item().TABLE_SCHEMA}].[@{item().TABLE_NAME}]" } } ], "typeProperties": { "source": { "type": "SqlSource", "sqlReaderQuery": "SELECT * FROM [@{item().TABLE_SCHEMA}].[@{item().TABLE_NAME}]" }, "sink": { "type": "SqlDWSink", "preCopyScript": "TRUNCATE TABLE [@{item().TABLE_SCHEMA}].[@{item().TABLE_NAME}]", "allowPolyBase": true }, "enableStaging": true, "stagingSettings": { "linkedServiceName": { "referenceName": "AzureStorageLinkedService", "type": "LinkedServiceReference" } } } } ] } } ], "parameters": { "tableList": { "type": "Object" } } } }To create the pipeline: IterateAndCopySQLTables, Run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2Pipeline cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2Pipeline -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "IterateAndCopySQLTables" -File ".\IterateAndCopySQLTables.json"Here is the sample output:
PipelineName : IterateAndCopySQLTables ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Activities : {IterateSQLTables} Parameters : {[tableList, Microsoft.Azure.Management.DataFactory.Models.ParameterSpecification]}
Create the pipeline "GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData"
This pipeline performs two steps:
- Looks up the Azure SQL Database system table to get the list of tables to be copied.
- Triggers the pipeline "IterateAndCopySQLTables" to do the actual data copy.
Create a JSON file named GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData.json in the C:\ADFv2TutorialBulkCopy folder, with the following content:
{ "name":"GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData", "properties":{ "activities":[ { "name": "LookupTableList", "description": "Retrieve the table list from Azure SQL database", "type": "Lookup", "typeProperties": { "source": { "type": "SqlSource", "sqlReaderQuery": "SELECT TABLE_SCHEMA, TABLE_NAME FROM information_schema.TABLES WHERE TABLE_TYPE = 'BASE TABLE' and TABLE_SCHEMA = 'SalesLT' and TABLE_NAME <> 'ProductModel'" }, "dataset": { "referenceName": "AzureSqlDatabaseDataset", "type": "DatasetReference" }, "firstRowOnly": false } }, { "name": "TriggerCopy", "type": "ExecutePipeline", "typeProperties": { "parameters": { "tableList": { "value": "@activity('LookupTableList').output.value", "type": "Expression" } }, "pipeline": { "referenceName": "IterateAndCopySQLTables", "type": "PipelineReference" }, "waitOnCompletion": true }, "dependsOn": [ { "activity": "LookupTableList", "dependencyConditions": [ "Succeeded" ] } ] } ] } }To create the pipeline: GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData, Run the Set-AzDataFactoryV2Pipeline cmdlet.
Set-AzDataFactoryV2Pipeline -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -Name "GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData" -File ".\GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData.json"Here is the sample output:
PipelineName : GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> Activities : {LookupTableList, TriggerCopy} Parameters :
Start and monitor pipeline run
Start a pipeline run for the main "GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData" pipeline and capture the pipeline run ID for future monitoring. Underneath, it triggers the run for pipeline "IterateAndCopySQLTables" as specified in ExecutePipeline activity.
$runId = Invoke-AzDataFactoryV2Pipeline -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -PipelineName 'GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData'Run the following script to continuously check the run status of pipeline GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData, and print out the final pipeline run and activity run result.
while ($True) { $run = Get-AzDataFactoryV2PipelineRun -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -DataFactoryName $DataFactoryName -PipelineRunId $runId if ($run) { if ($run.Status -ne 'InProgress') { Write-Host "Pipeline run finished. The status is: " $run.Status -ForegroundColor "Yellow" Write-Host "Pipeline run details:" -ForegroundColor "Yellow" $run break } Write-Host "Pipeline is running...status: InProgress" -ForegroundColor "Yellow" } Start-Sleep -Seconds 15 } $result = Get-AzDataFactoryV2ActivityRun -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -PipelineRunId $runId -RunStartedAfter (Get-Date).AddMinutes(-30) -RunStartedBefore (Get-Date).AddMinutes(30) Write-Host "Activity run details:" -ForegroundColor "Yellow" $resultHere is the output of the sample run:
Pipeline run details: ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> RunId : 0000000000-00000-0000-0000-000000000000 PipelineName : GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData LastUpdated : 9/18/2017 4:08:15 PM Parameters : {} RunStart : 9/18/2017 4:06:44 PM RunEnd : 9/18/2017 4:08:15 PM DurationInMs : 90637 Status : Succeeded Message : Activity run details: ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> ActivityName : LookupTableList PipelineRunId : 0000000000-00000-0000-0000-000000000000 PipelineName : GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData Input : {source, dataset, firstRowOnly} Output : {count, value, effectiveIntegrationRuntime} LinkedServiceName : ActivityRunStart : 9/18/2017 4:06:46 PM ActivityRunEnd : 9/18/2017 4:07:09 PM DurationInMs : 22995 Status : Succeeded Error : {errorCode, message, failureType, target} ResourceGroupName : <resourceGroupName> DataFactoryName : <dataFactoryName> ActivityName : TriggerCopy PipelineRunId : 0000000000-00000-0000-0000-000000000000 PipelineName : GetTableListAndTriggerCopyData Input : {pipeline, parameters, waitOnCompletion} Output : {pipelineRunId} LinkedServiceName : ActivityRunStart : 9/18/2017 4:07:11 PM ActivityRunEnd : 9/18/2017 4:08:14 PM DurationInMs : 62581 Status : Succeeded Error : {errorCode, message, failureType, target}You can get the run ID of pipeline "IterateAndCopySQLTables", and check the detailed activity run result as the following.
Write-Host "Pipeline 'IterateAndCopySQLTables' run result:" -ForegroundColor "Yellow" ($result | Where-Object {$_.ActivityName -eq "TriggerCopy"}).Output.ToString()Here is the output of the sample run:
{ "pipelineRunId": "7514d165-14bf-41fb-b5fb-789bea6c9e58" }$result2 = Get-AzDataFactoryV2ActivityRun -DataFactoryName $dataFactoryName -ResourceGroupName $resourceGroupName -PipelineRunId <copy above run ID> -RunStartedAfter (Get-Date).AddMinutes(-30) -RunStartedBefore (Get-Date).AddMinutes(30) $result2Connect to your sink Azure Synapse Analytics and confirm that data has been copied from Azure SQL Database properly.
Related content
You performed the following steps in this tutorial:
- Create a data factory.
- Create Azure SQL Database, Azure Synapse Analytics, and Azure Storage linked services.
- Create Azure SQL Database and Azure Synapse Analytics datasets.
- Create a pipeline to look up the tables to be copied and another pipeline to perform the actual copy operation.
- Start a pipeline run.
- Monitor the pipeline and activity runs.
Advance to the following tutorial to learn about copy data incrementally from a source to a destination: