The Wingtip Tickets SaaS application
Applies to:
Azure SQL Database
The same Wingtip Tickets SaaS application is implemented in each of three samples. The app is a simple event listing and ticketing SaaS app targeting small venues: theaters, clubs, and so on. Each venue is a tenant of the app, and has its own data, such as venue details, lists of events, customers, ticket orders, and so on. The app, together with the management scripts and tutorials, showcases an end-to-end SaaS scenario. This includes provisioning tenants, monitoring and managing performance, schema management, and cross-tenant reporting and analytics.
Three SaaS application and tenancy patterns
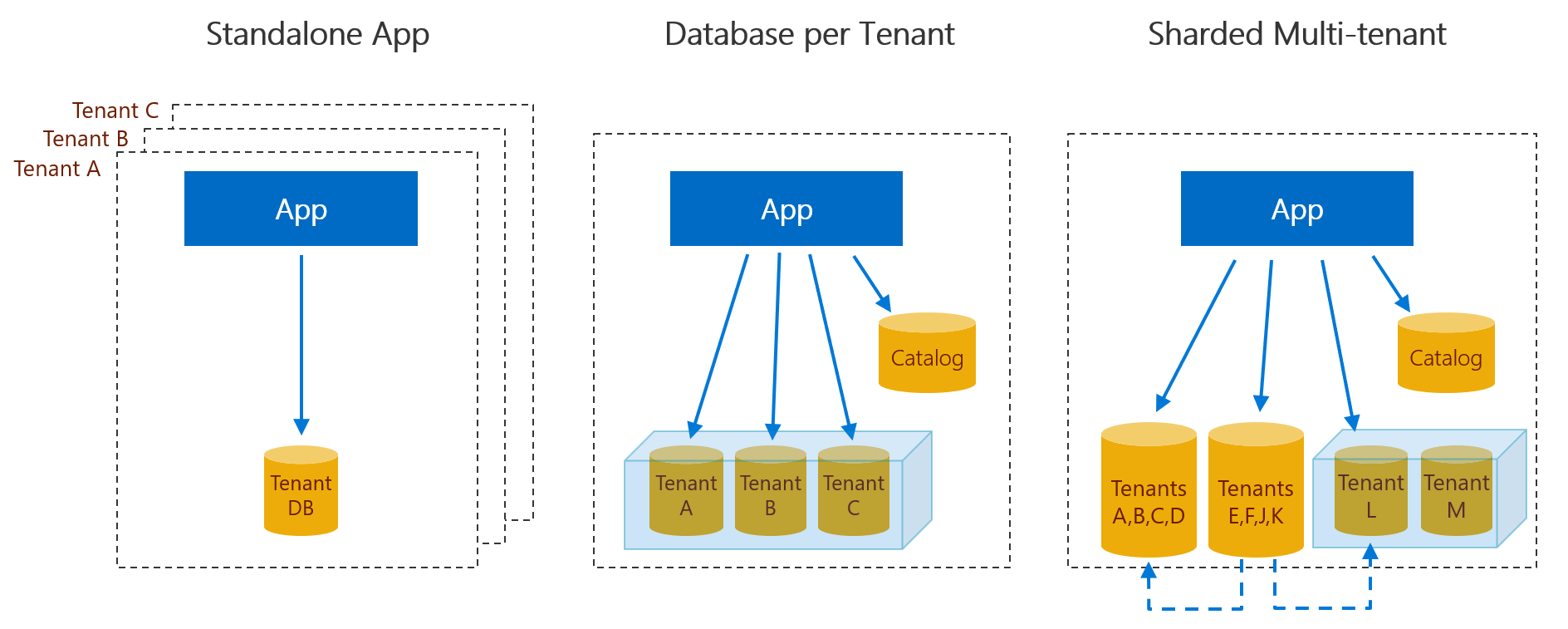
Three versions of the app are available; each explores a different database tenancy pattern on Azure SQL Database. The first uses a standalone application per tenant with its own database. The second uses a multitenant app with a database per tenant. The third sample uses a multitenant app with sharded multitenant databases.
Each sample includes the application code, plus management scripts and tutorials that explore a range of design and management patterns. Each sample deploys in less than five minutes. All three can be deployed side-by-side so you can compare the differences in design and management.
Standalone application per tenant pattern
The standalone app per tenant pattern uses a single tenant application with a database for each tenant. Each tenant's app, including its database, is deployed into a separate Azure resource group. The resource group can be deployed in the service provider's subscription or the tenant's subscription, and managed by the provider on the tenant's behalf. The standalone app per tenant pattern provides the greatest tenant isolation, but is typically the most expensive as there's no opportunity to share resources between multiple tenants. This pattern is well suited to applications that might be more complex and which are deployed to smaller numbers of tenants. With standalone deployments, the app can be customized for each tenant more easily than in other patterns.
Check out the tutorials and code on GitHub .../Microsoft/WingtipTicketsSaaS-StandaloneApp.
Database per tenant pattern
The database per tenant pattern is effective for service providers that are concerned with tenant isolation and want to run a centralized service that allows cost-efficient use of shared resources. A database is created for each venue, or tenant, and all the databases are centrally managed. Databases can be hosted in elastic pools to provide cost-efficient and easy performance management, which manage the unpredictable workload patterns of the tenants. A catalog database holds the mapping between tenants and their databases. This mapping is managed using the shard map management features of the Elastic Database Client Library, which provides efficient connection management to the application.
Check out the tutorials and code on GitHub .../Microsoft/WingtipTicketsSaaS-DbPerTenant.
Sharded multitenant database pattern
Multitenant databases are effective for service providers looking for lower cost per tenant and okay with reduced tenant isolation. This pattern allows packing large numbers of tenants into an individual database, driving the cost-per-tenant down. You can have almost infinite scale by sharding the tenants across multiple databases. A catalog database maps tenants to databases.
This pattern also allows a hybrid model, in which you can optimize for cost with multiple tenants in a database, or optimize for isolation with a single tenant in their own database. The choice can be made on a tenant-by-tenant basis, either when the tenant is provisioned or later, with no effect on the application. This model can be used effectively when groups of tenants need to be treated differently. For example, low-cost tenants can be assigned to shared databases, while premium tenants can be assigned to their own databases.
Check out the Wingtips tutorials and WingtipTicketsSaaS-MultiTenantDB code on GitHub](https://github.com/Microsoft/WingtipTicketsSaaS-MultiTenantDb).
Related content
- Multitenant SaaS database tenancy patterns
- Deploy and explore a standalone single-tenant application that uses Azure SQL Database
- Code for standalone app, on GitHub
- Introduction to a multitenant SaaS app that uses the database-per-tenant pattern with Azure SQL Database
- Code for database per tenant, on GitHub
- Deploy and explore a sharded multitenant application
- Code for sharded multitenant, on GitHub