Quickstart: Create a Java Durable Functions app
Use Durable Functions, a feature of Azure Functions, to write stateful functions in a serverless environment. Durable Functions manages state, checkpoints, and restarts in your application.
In this quickstart, you create and test a "hello world" Durable Functions app in Java.
The most basic Durable Functions app has three functions:
- Orchestrator function: A workflow that orchestrates other functions.
- Activity function: A function that is called by the orchestrator function, performs work, and optionally returns a value.
- Client function: A regular function in Azure that starts an orchestrator function. This example uses an HTTP-triggered function.
This quickstart describes different ways to create this "hello world" app. Use the selector at the top of the page to set your preferred approach.
Prerequisites
To complete this quickstart, you need:
The Java Developer Kit version 8 or later installed.
Apache Maven version 3.0 or later installed.
The latest version of Azure Functions Core Tools.
For Azure Functions 4.x, Core Tools version 4.0.4915 or later is required.
An HTTP test tool that keeps your data secure. For more information, see HTTP test tools.
An Azure subscription. To use Durable Functions, you must have an Azure Storage account.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Add required dependencies and plugins to your project
Add the following code to your pom.xml file:
<properties>
<azure.functions.maven.plugin.version>1.18.0</azure.functions.maven.plugin.version>
<azure.functions.java.library.version>3.0.0</azure.functions.java.library.version>
<durabletask.azure.functions>1.0.0</durabletask.azure.functions>
<functionAppName>your-unique-app-name</functionAppName>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure.functions</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-functions-java-library</artifactId>
<version>${azure.functions.java.library.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft</groupId>
<artifactId>durabletask-azure-functions</artifactId>
<version>${durabletask.azure.functions}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.microsoft.azure</groupId>
<artifactId>azure-functions-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${azure.functions.maven.plugin.version}</version>
<configuration>
<appName>${functionAppName}</appName>
<resourceGroup>java-functions-group</resourceGroup>
<appServicePlanName>java-functions-app-service-plan</appServicePlanName>
<region>westus</region>
<runtime>
<os>windows</os>
<javaVersion>11</javaVersion>
</runtime>
<appSettings>
<property>
<name>FUNCTIONS_EXTENSION_VERSION</name>
<value>~4</value>
</property>
</appSettings>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>package-functions</id>
<goals>
<goal>package</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
Add the required JSON files
Add a host.json file to your project directory. It should look similar to the following example:
{
"version": "2.0",
"logging": {
"logLevel": {
"DurableTask.AzureStorage": "Warning",
"DurableTask.Core": "Warning"
}
},
"extensions": {
"durableTask": {
"hubName": "JavaTestHub"
}
},
"extensionBundle": {
"id": "Microsoft.Azure.Functions.ExtensionBundle",
"version": "[4.*, 5.0.0)"
}
}
Note
It's important to note that only the Azure Functions v4 extension bundle currently has the necessary support for Durable Functions for Java. Durable Functions for Java is not supported in v3 and early extension bundles. For more information on extension bundles, see the extension bundles documentation.
Durable Functions needs a storage provider to store runtime state. Add a local.settings.json file to your project directory to configure the storage provider. To use Azure Storage as the provider, set the value of AzureWebJobsStorage to the connection string of your Azure Storage account:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "<your storage account connection string>",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "java"
}
}
Create your functions
The following sample code shows a basic example of each type of function:
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.annotation.*;
import com.microsoft.azure.functions.*;
import java.util.*;
import com.microsoft.durabletask.*;
import com.microsoft.durabletask.azurefunctions.DurableActivityTrigger;
import com.microsoft.durabletask.azurefunctions.DurableClientContext;
import com.microsoft.durabletask.azurefunctions.DurableClientInput;
import com.microsoft.durabletask.azurefunctions.DurableOrchestrationTrigger;
public class DurableFunctionsSample {
/**
* This HTTP-triggered function starts the orchestration.
*/
@FunctionName("StartOrchestration")
public HttpResponseMessage startOrchestration(
@HttpTrigger(name = "req", methods = {HttpMethod.GET, HttpMethod.POST}, authLevel = AuthorizationLevel.ANONYMOUS) HttpRequestMessage<Optional<String>> request,
@DurableClientInput(name = "durableContext") DurableClientContext durableContext,
final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Java HTTP trigger processed a request.");
DurableTaskClient client = durableContext.getClient();
String instanceId = client.scheduleNewOrchestrationInstance("Cities");
context.getLogger().info("Created new Java orchestration with instance ID = " + instanceId);
return durableContext.createCheckStatusResponse(request, instanceId);
}
/**
* This is the orchestrator function, which can schedule activity functions, create durable timers,
* or wait for external events in a way that's completely fault-tolerant.
*/
@FunctionName("Cities")
public String citiesOrchestrator(
@DurableOrchestrationTrigger(name = "taskOrchestrationContext") TaskOrchestrationContext ctx) {
String result = "";
result += ctx.callActivity("Capitalize", "Tokyo", String.class).await() + ", ";
result += ctx.callActivity("Capitalize", "London", String.class).await() + ", ";
result += ctx.callActivity("Capitalize", "Seattle", String.class).await() + ", ";
result += ctx.callActivity("Capitalize", "Austin", String.class).await();
return result;
}
/**
* This is the activity function that is invoked by the orchestrator function.
*/
@FunctionName("Capitalize")
public String capitalize(@DurableActivityTrigger(name = "name") String name, final ExecutionContext context) {
context.getLogger().info("Capitalizing: " + name);
return name.toUpperCase();
}
}
Create a local project by using the Maven command
Run the following command to generate a project that contains the basic functions of a Durable Functions app:
mvn archetype:generate -DarchetypeGroupId=com.microsoft.azure -DarchetypeArtifactId=azure-functions-archetype -DarchetypeVersion=1.62 -Dtrigger=durablefunctions
At the prompts, provide the following information:
| Prompt | Action |
|---|---|
| groupId | Enter com.function. |
| artifactId | Enter myDurableFunction. |
| version | Select 1.0-SNAPSHOT. |
| package | Enter com.function. |
| Y | Enter Y and select Enter to confirm. |
Now you have a local project that has the three functions that are in a basic Durable Functions app.
Check to ensure that com.microsoft:durabletask-azure-functions is set as a dependency in your pom.xml file.
Configure the back-end storage provider
Durable Functions needs a storage provider to store runtime state. You can set Azure Storage as the storage provider in local.settings.json. Use the connection string of your Azure storage account as the value for AzureWebJobsStorage like in this example:
{
"IsEncrypted": false,
"Values": {
"AzureWebJobsStorage": "<your storage account connection string>",
"FUNCTIONS_WORKER_RUNTIME": "java"
}
}
Create your local project
In Visual Studio Code, select F1 (or select Ctrl/Cmd+Shift+P) to open the command palette. At the prompt (
>), enter and then select Azure Functions: Create New Project.
Select Browse. In the Select Folder dialog, go to a folder to use for your project, and then choose Select.
At the prompts, provide the following information:
Prompt Action Select a language Select Java. Select a version of Java Select Java 8 or later. Select the Java version that your functions run on in Azure, and one that you verified locally. Provide a group ID Enter com.function. Provide an artifact ID Enter myDurableFunction. Provide a version Enter 1.0-SNAPSHOT. Provide a package name Enter com.function. Provide an app name Enter myDurableFunction. Select the build tool for Java project Select Maven. Select how you would like to open your project Select Open in new window.
You now have a project that has an example HTTP function. You can remove this function if you'd like to, because you add the basic functions of a Durable Functions app in the next step.
Add functions to the project
In the command palette, enter and then select Azure Functions: Create Function.
For Change template filter, select All.
At the prompts, provide the following information:
Prompt Action Select a template for your function Select DurableFunctionsOrchestration. Provide a package name Enter com.function. Provide a function name Enter DurableFunctionsOrchestrator. In the dialog, choose Select storage account to set up a storage account, and then follow the prompts.
You should now have the three basic functions generated for a Durable Functions app.
Configure pom.xml and host.json
Add the following dependency to your pom.xml file:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.microsoft</groupId>
<artifactId>durabletask-azure-functions</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
</dependency>
Add the extensions property to your host.json file:
"extensions": { "durableTask": { "hubName": "JavaTestHub" }}
Test the function locally
Azure Functions Core Tools gives you the capability to run an Azure Functions project on your local development computer.
Note
Durable Functions for Java requires Azure Functions Core Tools version 4.0.4915 or later. You can see which version is installed by running the func --version command in the terminal.
If you're using Visual Studio Code, open a new terminal window and run the following commands to build the project:
mvn clean packageThen, run the durable function:
mvn azure-functions:runIn the terminal panel, copy the URL endpoint of your HTTP-triggered function.
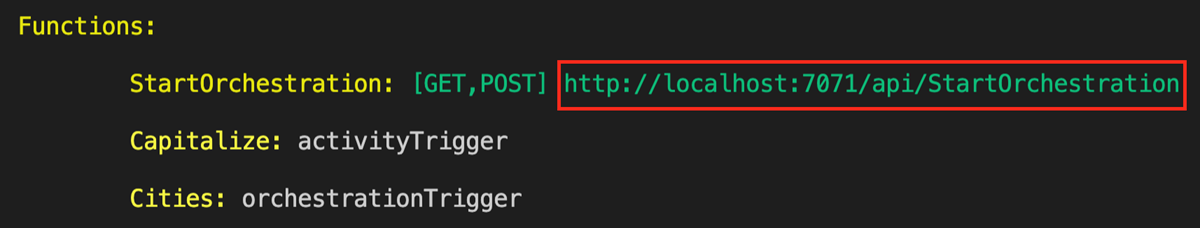
Use an HTTP test tool to send an HTTP POST request to the URL endpoint.
The response should look similar to the following example:
{ "id": "d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9", "purgeHistoryDeleteUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9?code=ACCupah_QfGKo...", "sendEventPostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9/raiseEvent/{eventName}?code=ACCupah_QfGKo...", "statusQueryGetUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9?code=ACCupah_QfGKo...", "terminatePostUri": "http://localhost:7071/runtime/webhooks/durabletask/instances/d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9/terminate?reason={text}&code=ACCupah_QfGKo..." }The response is the HTTP function's initial result. It lets you know that the durable orchestration started successfully. It doesn't yet display the end result of the orchestration. The response includes a few useful URLs. For now, query the status of the orchestration.
Copy the URL value for
statusQueryGetUri, paste it in your browser's address bar, and execute the request. Alternatively, you can continue to use the HTTP test tool to issue the GET request.The request queries the orchestration instance for the status. You should see that the instance finished and that it includes the outputs or results of the durable function, like in this example:
{ "name": "Cities", "instanceId": "d1b33a60-333f-4d6e-9ade-17a7020562a9", "runtimeStatus": "Completed", "input": null, "customStatus": "", "output":"TOKYO, LONDON, SEATTLE, AUSTIN", "createdTime": "2022-12-12T05:00:02Z", "lastUpdatedTime": "2022-12-12T05:00:06Z" }