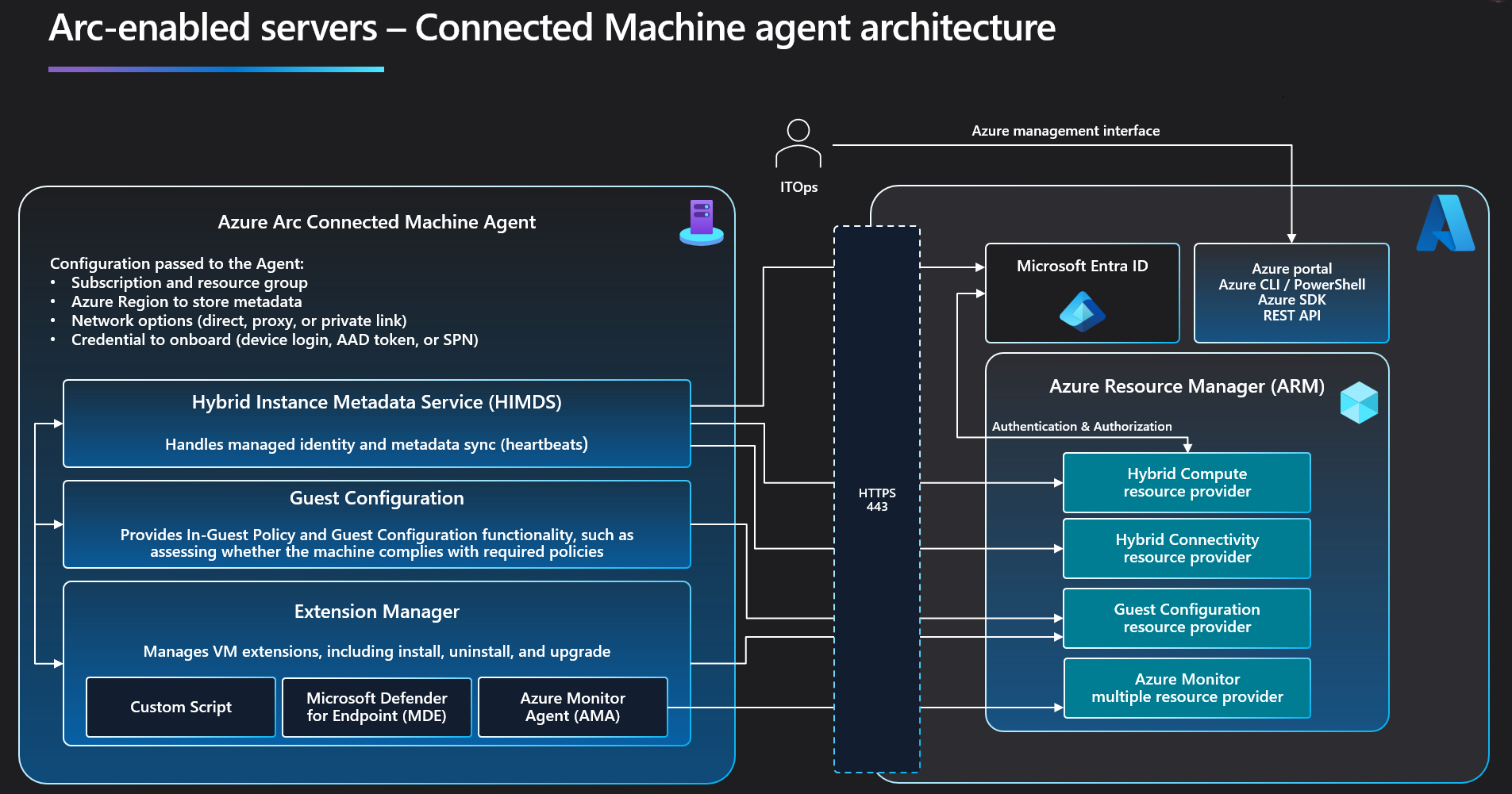
Overview of Azure Connected Machine agent
The Azure Connected Machine agent enables you to manage your Windows and Linux machines hosted outside of Azure on your corporate network or other cloud providers.
Warning
Only Connected Machine agent versions within the last one year are officially supported by the product group. Customers should update to an agent version within this window.
Agent components
The Azure Connected Machine agent package contains several logical components bundled together:
The Hybrid Instance Metadata service (HIMDS) manages the connection to Azure and the connected machine's Azure identity.
The machine configuration agent provides functionality such as assessing whether the machine complies with required policies and enforcing compliance.
Note the following behavior with Azure Policy machine configuration for a disconnected machine:
- An Azure Policy assignment that targets disconnected machines is unaffected.
- Guest assignment is stored locally for 14 days. Within the 14-day period, if the Connected Machine agent reconnects to the service, policy assignments are reapplied.
- Assignments are deleted after 14 days, and aren't reassigned to the machine after the 14-day period.
The Extension agent manages VM extensions, including install, uninstall, and upgrade. Azure downloads extensions and copies them to the
%SystemDrive%\%ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\ExtensionService\downloadsfolder on Windows, and to/opt/GC_Ext/downloadson Linux. On Windows, the extension installs to the following path%SystemDrive%\Packages\Plugins\<extension>, and on Linux the extension installs to/var/lib/waagent/<extension>.
Note
The Azure Monitor agent (AMA) is a separate agent that collects monitoring data. It doesn't replace the Connected Machine agent. The AMA only replaces the Log Analytics agent, Diagnostics extension, and Telegraf agent for both Windows and Linux machines.
Azure Arc Proxy
The Azure Arc Proxy service is responsible for aggregating network traffic from the Azure Connected Machine agent services and any extensions and deciding where to route that data. If you’re using the Azure Arc gateway (Limited preview) to simplify your network endpoints, the Azure Arc Proxy service is the local component that forwards network requests via the Azure Arc gateway instead of the default route. The Azure Arc Proxy runs as a Network Service on Windows and a standard user account (arcproxy) on Linux. It's disabled by default until you configure the agent to use the Azure Arc gateway (Limited preview).
Agent resources
The following information describes the directories and user accounts used by the Azure Connected Machine agent.
Windows agent installation details
The Windows agent is distributed as a Windows Installer package (MSI). Download the Windows agent from the Microsoft Download Center. Installing the Connected Machine agent for Window applies the following system-wide configuration changes:
The installation process creates the following folders during setup.
Directory Description %ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent azcmagent CLI and instance metadata service executables. %ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\ExtensionService2\GC Extension service executables. %ProgramFiles%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\GCArcService2\GC Machine configuration (policy) service executables. %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent Configuration, log, and identity token files for azcmagent CLI and instance metadata service. %ProgramData%\GuestConfig Extension package downloads, machine configuration (policy) definition downloads, and logs for the extension and machine configuration services. %SYSTEMDRIVE%\packages Extension package executables Installing the agent creates the following Windows services on the target machine.
Service name Display name Process name Description himds Azure Hybrid Instance Metadata Service himds.exeSynchronizes metadata with Azure and hosts a local REST API for extensions and applications to access the metadata and request Microsoft Entra managed identity tokens GCArcService Machine configuration Arc Service gc_arc_service.exe(gc_service.exe earlier than version 1.36)Audits and enforces Azure machine configuration policies on the machine. ExtensionService Machine configuration Extension Service gc_extension_service.exe(gc_service.exe earlier than version 1.36)Installs, updates, and manages extensions on the machine. Agent installation creates the following virtual service account.
Virtual Account Description NT SERVICE\himds Unprivileged account used to run the Hybrid Instance Metadata Service. Tip
This account requires the "Log on as a service" right. This right is automatically granted during agent installation. However, if your organization configures user rights assignments with Group Policy, you might need to adjust your Group Policy Object to grant the right to "NT SERVICE\himds" or "NT SERVICE\ALL SERVICES" to allow the agent to function.
Agent installation creates the following local security group.
Security group name Description Hybrid agent extension applications Members of this security group can request Microsoft Entra tokens for the system-assigned managed identity Agent installation creates the following environmental variables
Name Default value Description IDENTITY_ENDPOINT http://localhost:40342/metadata/identity/oauth2/tokenIMDS_ENDPOINT http://localhost:40342There are several log files available for troubleshooting, described in the following table.
Log Description %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Log\himds.log Records details of the heartbeat and identity agent component. %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Log\azcmagent.log Contains the output of the azcmagent tool commands. %ProgramData%\GuestConfig\arc_policy_logs\gc_agent.log Records details about the machine configuration (policy) agent component. %ProgramData%\GuestConfig\ext_mgr_logs\gc_ext.log Records details about extension manager activity (extension install, uninstall, and upgrade events). %ProgramData%\GuestConfig\extension_logs Directory containing logs for individual extensions. The process creates the local security group Hybrid agent extension applications.
After uninstalling the agent, the following artifacts remain.
- %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent\Log
- %ProgramData%\AzureConnectedMachineAgent
- %ProgramData%\GuestConfig
- %SystemDrive%\packages
Note
Before installation, temporarily exclude the installation files' location from your antivirus/antimalware scan. This prevents potential interference and file corruption during installation.
Linux agent installation details
The preferred package format for the distribution (.rpm or .deb) that is hosted in the Microsoft package repository provides the Connected Machine agent for Linux. The shell script bundle Install_linux_azcmagent.sh installs and configures the agent.
Installing, upgrading, and removing the Connected Machine agent isn't required after server restart.
Installing the Connected Machine agent for Linux applies the following system-wide configuration changes.
Setup creates the following installation folders.
Directory Description /opt/azcmagent/ azcmagent CLI and instance metadata service executables. /opt/GC_Ext/ Extension service executables. /opt/GC_Service/ Machine configuration (policy) service executables. /var/opt/azcmagent/ Configuration, log, and identity token files for azcmagent CLI and instance metadata service. /var/lib/GuestConfig/ Extension package downloads, machine configuration (policy) definition downloads, and logs for the extension and machine configuration services. Installing the agent creates the following daemons.
Service name Display name Process name Description himdsd.service Azure Connected Machine Agent Service himds This service implements the Hybrid Instance Metadata service (IMDS) to manage the connection to Azure and the connected machine's Azure identity. gcad.service GC Arc Service gc_linux_service Audits and enforces Azure machine configuration policies on the machine. extd.service Extension Service gc_linux_service Installs, updates, and manages extensions on the machine. There are several log files available for troubleshooting, described in the following table.
Log Description /var/opt/azcmagent/log/himds.log Records details of the heartbeat and identity agent component. /var/opt/azcmagent/log/azcmagent.log Contains the output of the azcmagent tool commands. /var/lib/GuestConfig/arc_policy_logs Records details about the machine configuration (policy) agent component. /var/lib/GuestConfig/ext_mgr_logs Records details about extension manager activity (extension install, uninstall, and upgrade events). /var/lib/GuestConfig/extension_logs Directory containing logs for individual extensions. Agent installation creates the following environment variables, set in
/lib/systemd/system.conf.d/azcmagent.conf.Name Default value Description IDENTITY_ENDPOINT http://localhost:40342/metadata/identity/oauth2/tokenIMDS_ENDPOINT http://localhost:40342After the agent is uninstalled, the following artifacts remain.
- /var/opt/azcmagent
- /var/lib/GuestConfig
Agent resource governance
The Azure Connected Machine agent is designed to manage agent and system resource consumption. The agent approaches resource governance under the following conditions:
The Machine Configuration (formerly Guest Configuration) service can use up to 5% of the CPU to evaluate policies.
The Extension service can use up to 5% of the CPU on Windows machines and 30% of the CPU on Linux machines to install, upgrade, run, and delete extensions. Some extensions might apply more restrictive CPU limits once installed. The following exceptions apply:
Extension type Operating system CPU limit AzureMonitorLinuxAgent Linux 60% AzureMonitorWindowsAgent Windows 100% LinuxOsUpdateExtension Linux 60% MDE.Linux Linux 60% MicrosoftDnsAgent Windows 100% MicrosoftMonitoringAgent Windows 60% OmsAgentForLinux Linux 60%
During normal operations, defined as the Azure Connected Machine agent being connected to Azure and not actively modifying an extension or evaluating a policy, you can expect the agent to consume the following system resources:
| Windows | Linux | |
|---|---|---|
| CPU usage (normalized to 1 core) | 0.07% | 0.02% |
| Memory usage | 57 MB | 42 MB |
The performance data above was gathered in April 2023 on virtual machines running Windows Server 2022 and Ubuntu 20.04. Actual agent performance and resource consumption vary based on the hardware and software configuration of your servers.
Custom resource limits
The default resource governance limits are the best choice for most servers. However, small virtual machines and servers with limited CPU resources might encounter time-outs when managing extensions or evaluating policies because there aren't enough CPU resources to complete the tasks. Starting with agent version 1.39, you can customize the CPU limits applied to the extension manager and Machine Configuration services to help the agent complete these tasks faster.
To see the current resource limits for the extension manager and Machine Configuration services, run the following command.
azcmagent config list
In the output, you'll see two fields, guestconfiguration.agent.cpulimit and extensions.agent.cpulimit with the current resource limit specified as a percentage. On a fresh install of the agent, both will show 5 because the default limit is 5% of the CPU.
To change the resource limit for the extension manager to 80%, run the following command:
azcmagent config set extensions.agent.cpulimit 80
Instance metadata
Metadata information about a connected machine is collected after the Connected Machine agent registers with Azure Arc-enabled servers. Specifically:
- Operating system name, edition, type, and version
- Computer name
- Computer manufacturer and model
- Computer fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- Domain name (if joined to an Active Directory domain)
- Active Directory and DNS fully qualified domain name (FQDN)
- UUID (BIOS ID)
- Connected Machine agent heartbeat
- Connected Machine agent version
- Public key for managed identity
- Policy compliance status and details (if using machine configuration policies)
- SQL Server installed (Boolean value)
- PostgreSQL installed (Boolean value)
- MySQL installed (Boolean value)
- Cluster resource ID (for Azure Local machines)
- Hardware manufacturer
- Hardware model
- CPU family, socket, physical core and logical core counts
- Total physical memory
- Serial number
- SMBIOS asset tag
- Network interface information
- IP address
- Subnet
- Windows licensing information
- OS license status
- OS license channel
- Extended Security Updates eligibility
- Extended Security Updates license status
- Extended Security Updates license channel
- Cloud provider
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) metadata, when running in AWS:
- Account ID
- Instance ID
- Region
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP) metadata, when running in GCP:
- Instance ID
- Image
- Machine type
- Project ID
- Project number
- Service accounts
- Zone
- Oracle Cloud Infrastructure metadata, when running in OCI:
- Display name
The agent requests the following metadata information from Azure:
- Resource location (region)
- Virtual machine ID
- Tags
- Microsoft Entra managed identity certificate
- Machine configuration policy assignments
- Extension requests - install, update, and delete.
Note
Azure Arc-enabled servers do not store/process customer data outside the region the customer deploys the service instance in.
Deployment options and requirements
Agent deployment and machine connection require certain prerequisites. There are also networking requirements to be aware of.
We provide several options for deploying the agent. For more information, see Plan for deployment and Deployment options.
Cloning guidelines
You can safely install the azcmagent package into a golden image, but once you connect a machine using the azcmagent connect command, that machine receives specific resource information. If you're building machines by cloning them from a golden image, you must first specialize each machine before connecting it to Azure with the azcmagent connect command. Don't connect the original golden image machine to Azure until you've created and specialized each machine.
If your connected server is receiving 429 error messages, it's likely that you connected the server to Azure and then used that server as the golden image for cloning. Since the resource information was recorded into the image, cloned machines created from that image try to send heartbeat messages to the same resource.
To resolve 429 error messages for existing machines, run azcmagent disconnect --force-local-only on each cloned machine, then rerun azcmagent connect using an appropriate credential to connect the machines to the cloud using a unique resource name.
Disaster Recovery
There are no customer-enabled disaster recovery options for Arc-enabled servers. In the event of an outage in an Azure region, the system will fail over to another region in the same Azure geography (if one exists). While this failover procedure is automatic, it does take some time. The Connected Machine agent is disconnected during this period and shows a status of Disconnected until the failover is complete. The system will fail back to its original region once the outage has been resolved.
An outage of Azure Arc will not affect the customer workload itself; only management of the applicable servers via Arc will be impaired.
Next steps
- To begin evaluating Azure Arc-enabled servers, see Quickstart: Connect hybrid machines with Azure Arc-enabled servers.
- Before you deploy the Azure Connected Machine agent and integrate with other Azure management and monitoring services, review the Planning and deployment guide.
- Review troubleshooting information in the agent connection issues troubleshooting guide.