Label your utterances in Language Studio
Once you have built a schema for your project, you should add training utterances to your project. The utterances should be similar to what your users use when interacting with the project. When you add an utterance, you have to assign which intent it belongs to. After the utterance is added, label the words within your utterance that you want to extract as entities.
Data labeling is a crucial step in development lifecycle; this data are used in the next step when training your model so that your model can learn from the labeled data. If you already have labeled utterances, you can directly import it into your project, but you need to make sure that your data follows the accepted data format. See create project to learn more about importing labeled data into your project. Labeled data informs the model how to interpret text, and is used for training and evaluation.
Prerequisites
Before you can label your data, you need:
- A successfully created project.
See the project development lifecycle for more information.
Data labeling guidelines
After building your schema and creating your project, you need to label your data. Labeling your data is important so your model knows which words and sentences are associated with the intents and entities in your project. Spend time labeling your utterances - introducing and refining the data that is used in training your models.
As you add utterances and label them, keep in mind:
The machine learning models generalize based on the labeled examples you provide it; the more examples you provide, the more data points the model has to make better generalizations.
The precision, consistency and completeness of your labeled data are key factors to determining model performance.
- Label precisely: Label each intent and entity to its right type always. Only include what you want classified and extracted, avoid unnecessary data in your labels.
- Label consistently: The same entity should have the same label across all the utterances.
- Label completely: Provide varied utterances for every intent. Label all the instances of the entity in all your utterances.
Clearly label utterances
Ensure that the concepts that your entities refer to are well defined and separable. Check if you can easily determine the differences reliably. If you can't, this lack of distinction might indicate that the learned component will also have difficulty.
If there's a similarity between entities, ensure that there's some aspect of your data that provides a signal for the difference between them.
For example, if you built a model to book flights, a user might use an utterance like "I want a flight from Boston to Seattle." The origin city and destination city for such utterances would be expected to be similar. A signal to differentiate origin city might be that the word from often precedes it.
Ensure that you label all instances of each entity in both your training and testing data. One approach is to use the search function to find all instances of a word or phrase in your data to check if they're correctly labeled.
Label test data for entities that have no learned component and also for the entities that do. This practice helps to ensure that your evaluation metrics are accurate.
For Multilingual projects, adding utterances in other languages increases the model's performance in these languages, but avoid duplicating your data across all the languages you would like to support. For example, to improve a calender bot's performance with users, a developer might add examples mostly in English, and a few in Spanish or French as well. They might add utterances such as:
- "Set a meeting with Matt and Kevin tomorrow at 12 PM." (English)
- "Reply as tentative to the weekly update meeting." (English)
- "Cancelar mi próxima reunión." (Spanish)
How to label your utterances
Use the following steps to label your utterances:
Go to your project page in Language Studio.
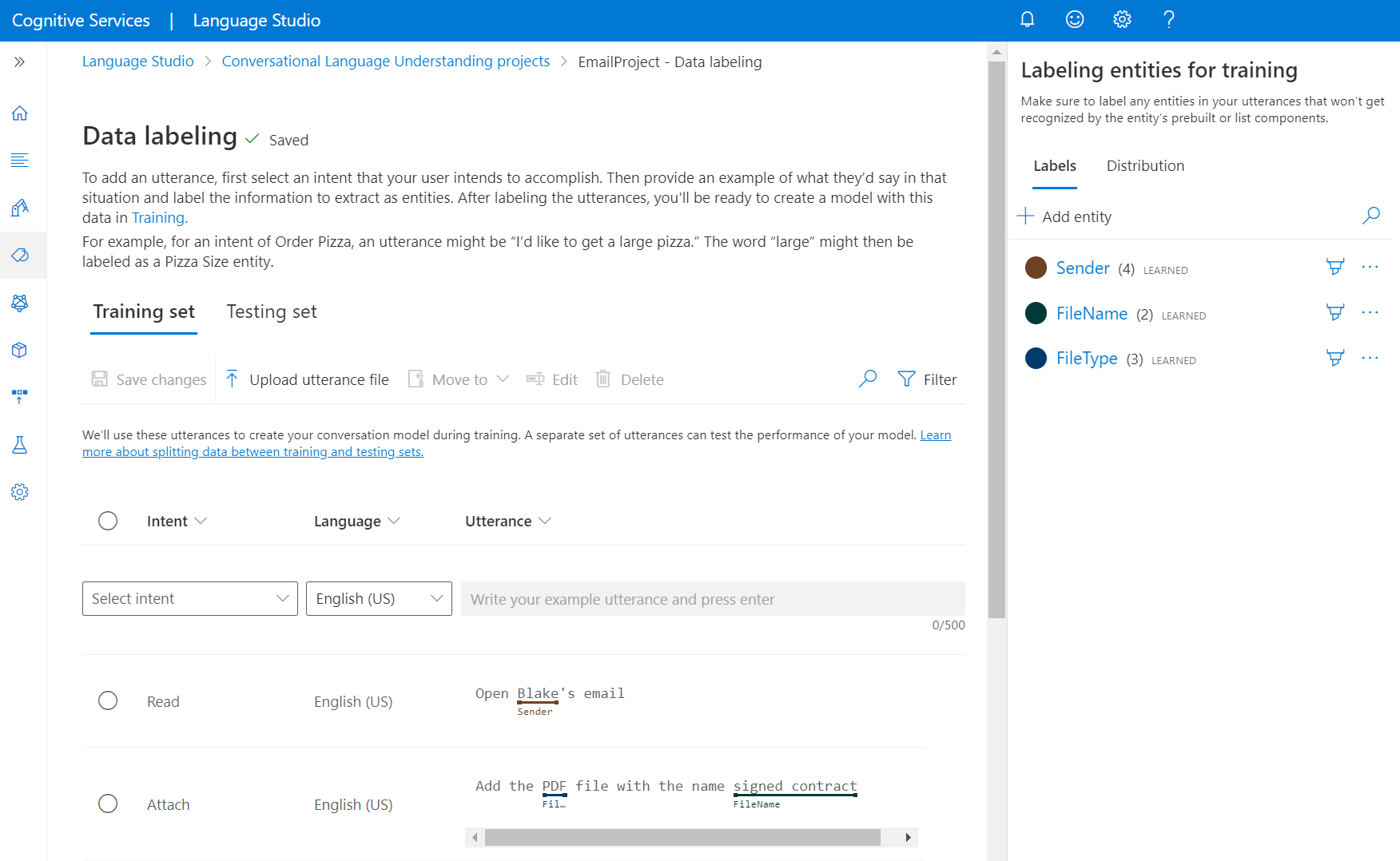
From the left side menu, select Data labeling. In this page, you can start adding your utterance and labeling them. You can also upload your utterance directly by clicking on Upload utterance file from the top menu, make sure it follows the accepted format.
From the top pivots, you can change the view to be training set or testing set. Learn more about training and testing sets and how they're used for model training and evaluation.
Tip
If you are planning on using Automatically split the testing set from training data splitting, add all your utterances to the training set.
From the Select intent dropdown menu, select one of the intents, the language of the utterance (for multilingual projects), and the utterance itself. Press the enter key in the utterance's text box to add the utterance.
You have two options to label entities in an utterance:
Option Description Label using a brush Select the brush icon next to an entity in the right pane, then highlight the text in the utterance you want to label. Label using inline menu Highlight the word you want to label as an entity, and a menu appears. Select the entity you want to label these words with. In the right side pane, under the Labels pivot, you can find all the entity types in your project and the count of labeled instances per each.
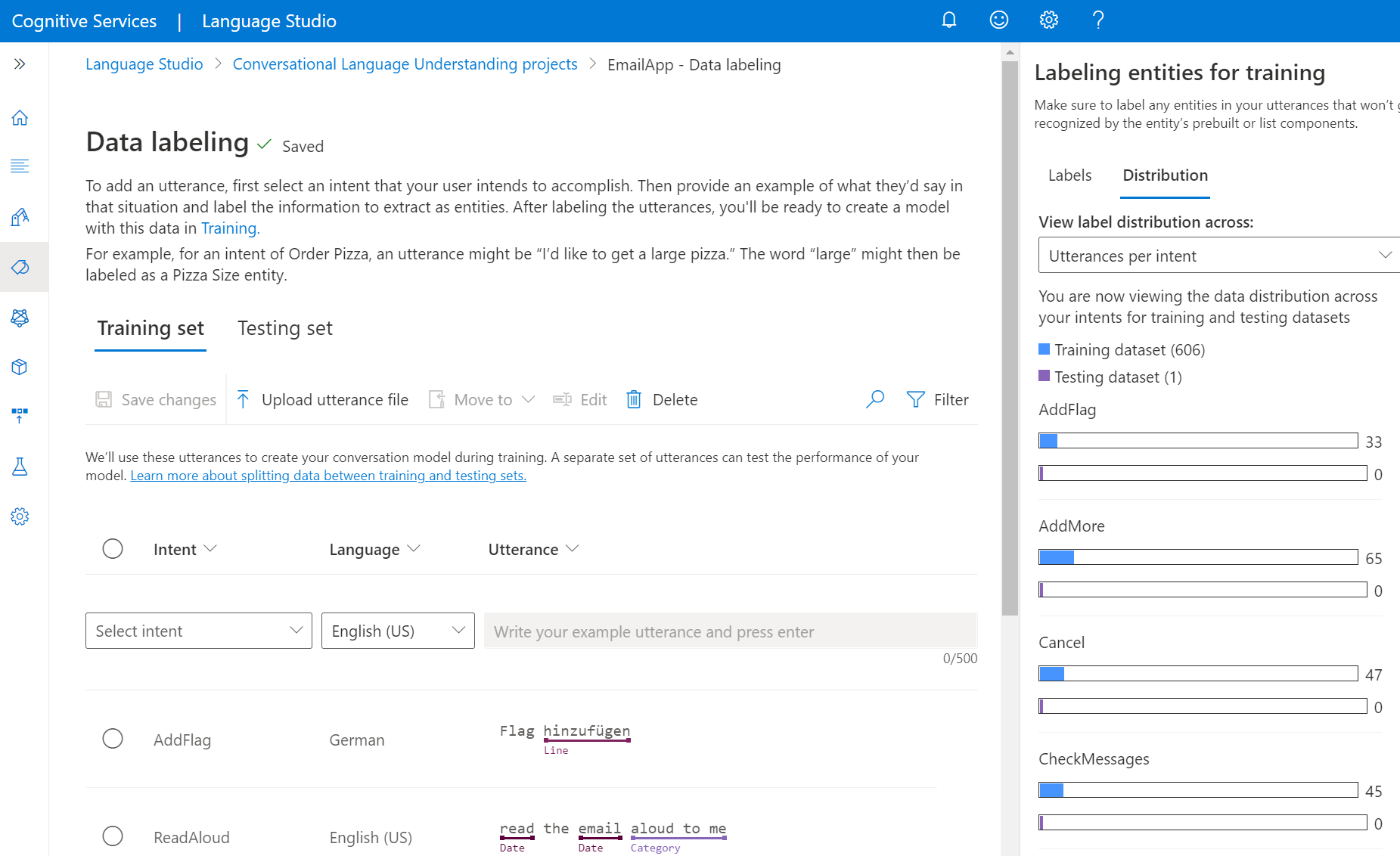
Under the Distribution pivot you can view the distribution across training and testing sets. You have two options for viewing:
- Total instances per labeled entity where you can view count of all labeled instances of a specific entity.
- Unique utterances per labeled entity where each utterance is counted if it contains at least one labeled instance of this entity.
- Utterances per intent where you can view count of utterances per intent.
Note
List and prebuilt components are not shown in the data labeling page, and all labels here only apply to the learned component.
To remove a label:
- From within your utterance, select the entity you want to remove a label from.
- Scroll through the menu that appears, and select Remove label.
To delete an entity:
- Select the entity you want to edit in the right side pane.
- Select the three dots next to the entity, and select the option you want from the drop-down menu.
Suggest utterances with Azure OpenAI
In CLU, use Azure OpenAI to suggest utterances to add to your project using GPT models. You first need to get access and create a resource in Azure OpenAI. You'll then need to create a deployment for the GPT models. Follow the pre-requisite steps here.
Before you get started, the suggest utterances feature is only available if your Language resource is in the following regions:
- East US
- South Central US
- West Europe
In the Data Labeling page:
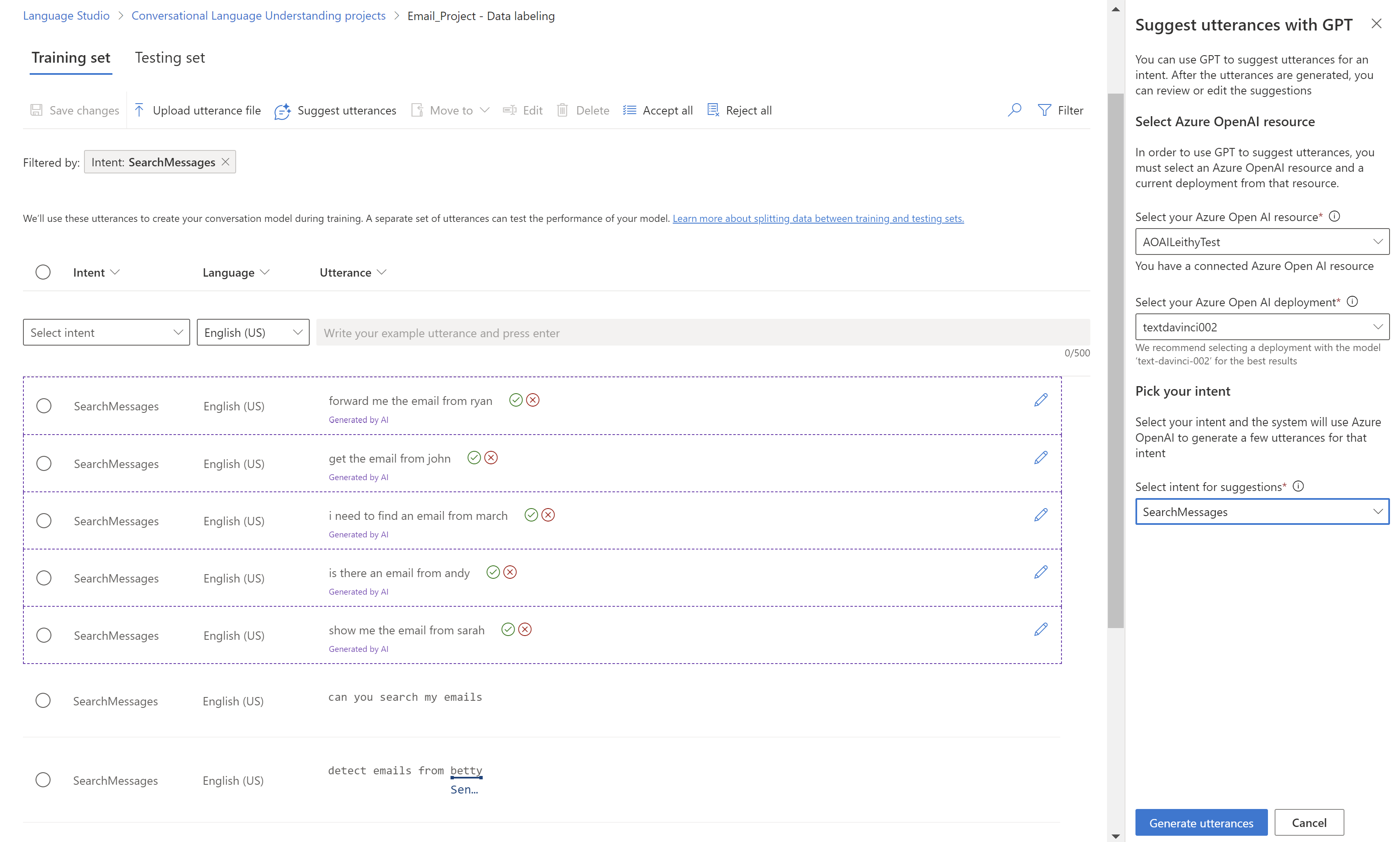
- Select the Suggest utterances button. A pane opens up on the right side prompting you to select your Azure OpenAI resource and deployment.
- On selection of an Azure OpenAI resource, select Connect, which allows your Language resource to have direct access to your Azure OpenAI resource. It assigns your Language resource the role of
Cognitive Services Userto your Azure OpenAI resource, which allows your current Language resource to have access to Azure OpenAI's service. If the connection fails, follow these steps below to add the right role to your Azure OpenAI resource manually. - Once the resource is connected, select the deployment. The recommended model for the Azure OpenAI deployment is
gpt-35-turbo-instruct. - Select the intent you'd like to get suggestions for. Make sure the intent you have selected has at least 5 saved utterances to be enabled for utterance suggestions. The suggestions provided by Azure OpenAI are based on the most recent utterances you've added for that intent.
- Select Generate utterances. Once complete, the suggested utterances show up with a dotted line around it, with the note Generated by AI. Those suggestions need to be accepted or rejected. Accepting a suggestion simply adds it to your project, as if you had added it yourself. Rejecting it deletes the suggestion entirely. Only accepted utterances are part of your project and used for training or testing. You can accept or reject by clicking on the green check or red cancel buttons beside each utterance. You can also use the
Accept allandReject allbuttons in the toolbar.
Using this feature entails a charge to your Azure OpenAI resource for a similar number of tokens to the suggested utterances generated. Details for Azure OpenAI's pricing can be found here.
Add required configurations to Azure OpenAI resource
If connecting your Language resource to an Azure OpenAI resource fails, follow these steps:
Enable identity management for your Language resource using the following options:
Your Language resource must have identity management, to enable it using the Azure portal:
- Go to your Language resource
- From left hand menu, under Resource Management section, select Identity
- From System assigned tab, make sure to set Status to On
After enabling managed identity, assign the role Cognitive Services User to your Azure OpenAI resource using the managed identity of your Language resource.
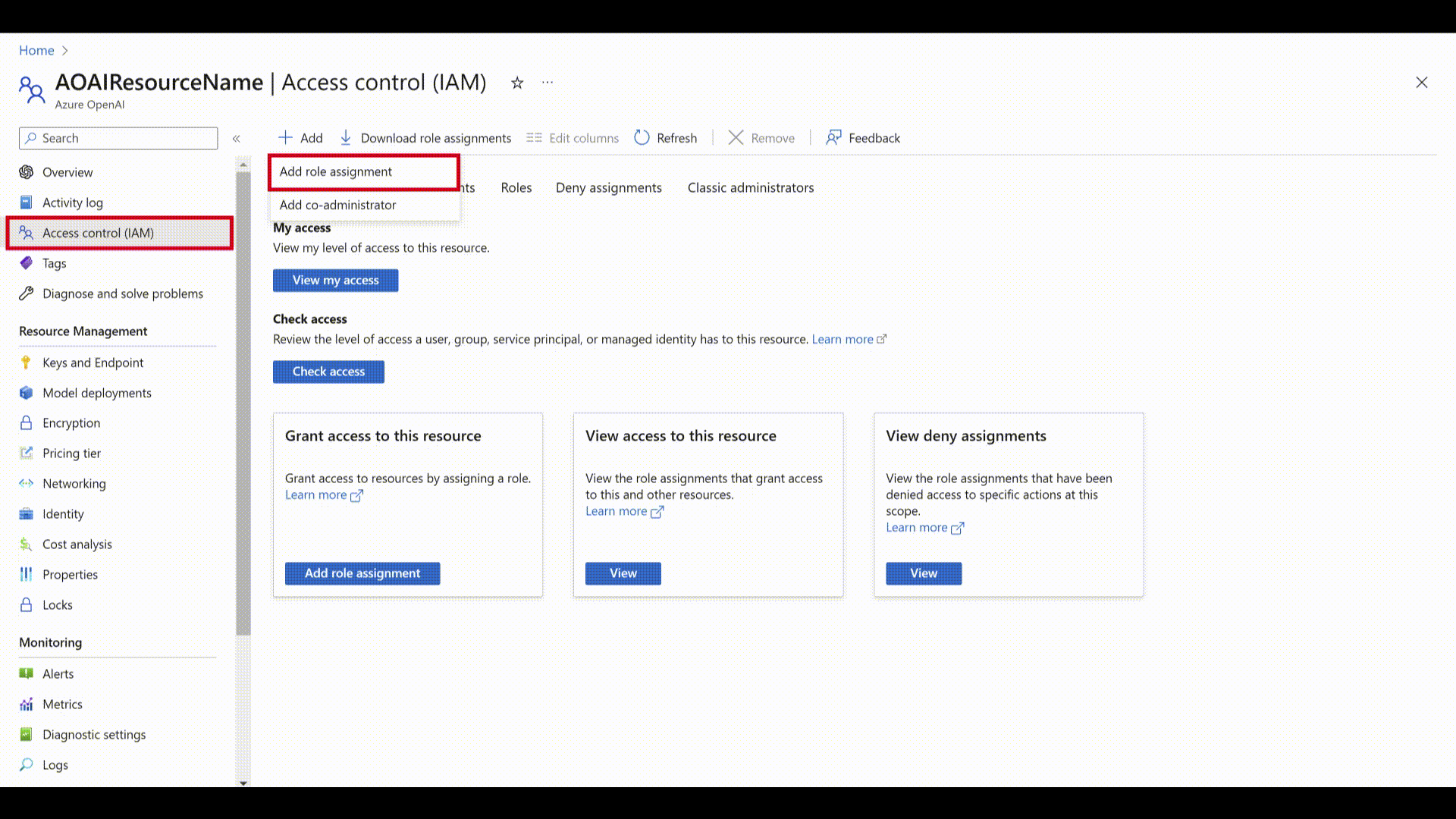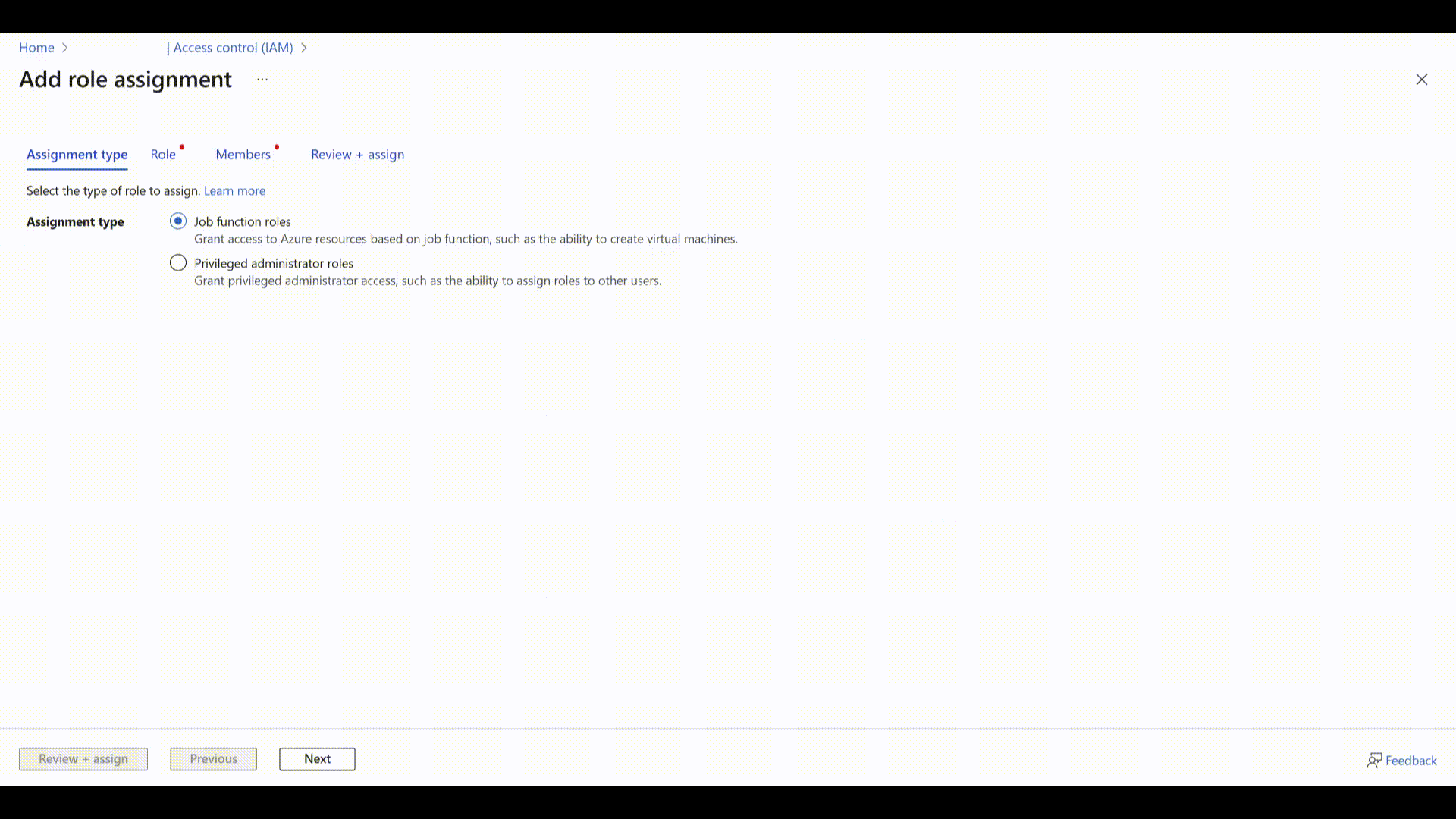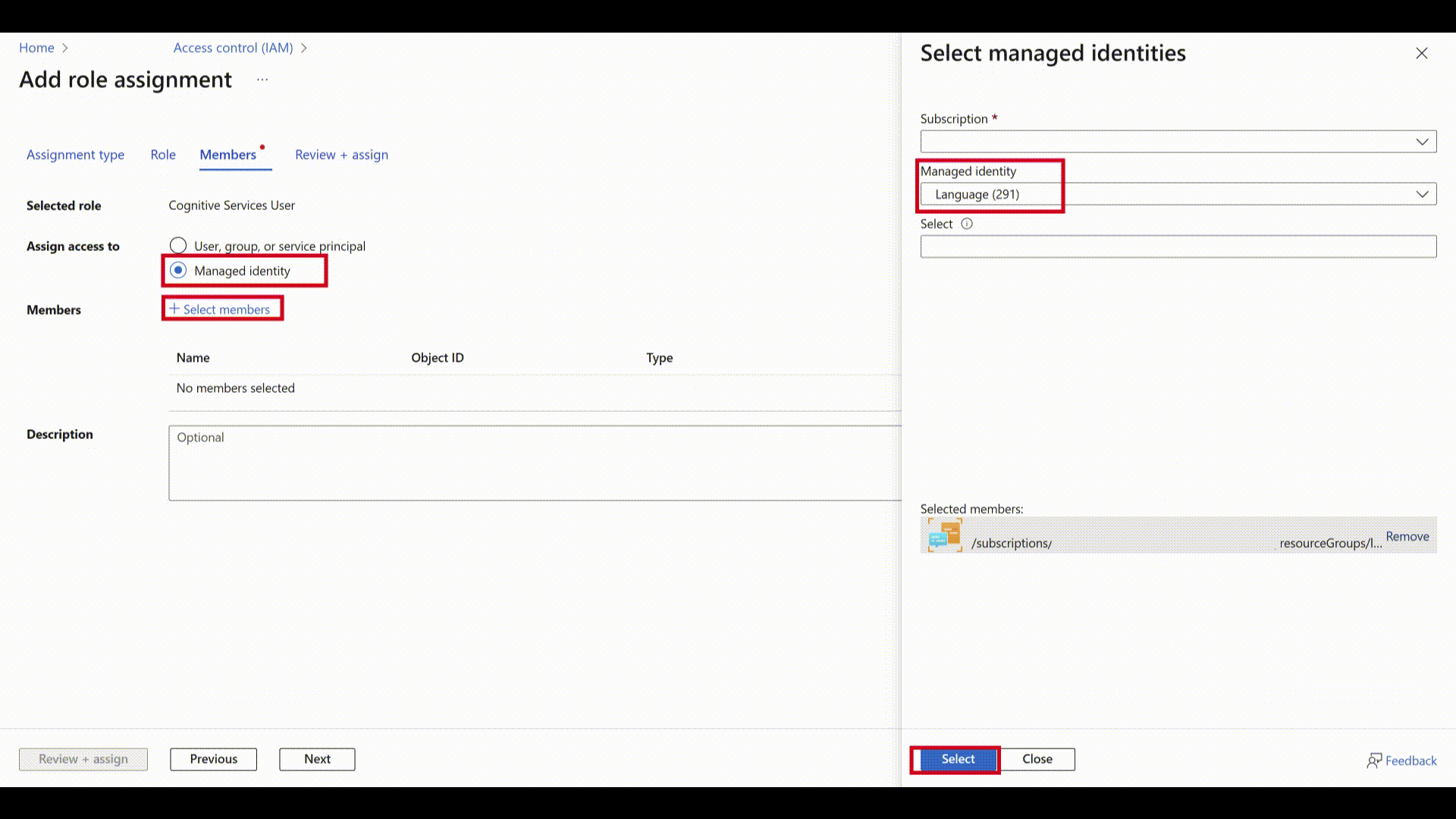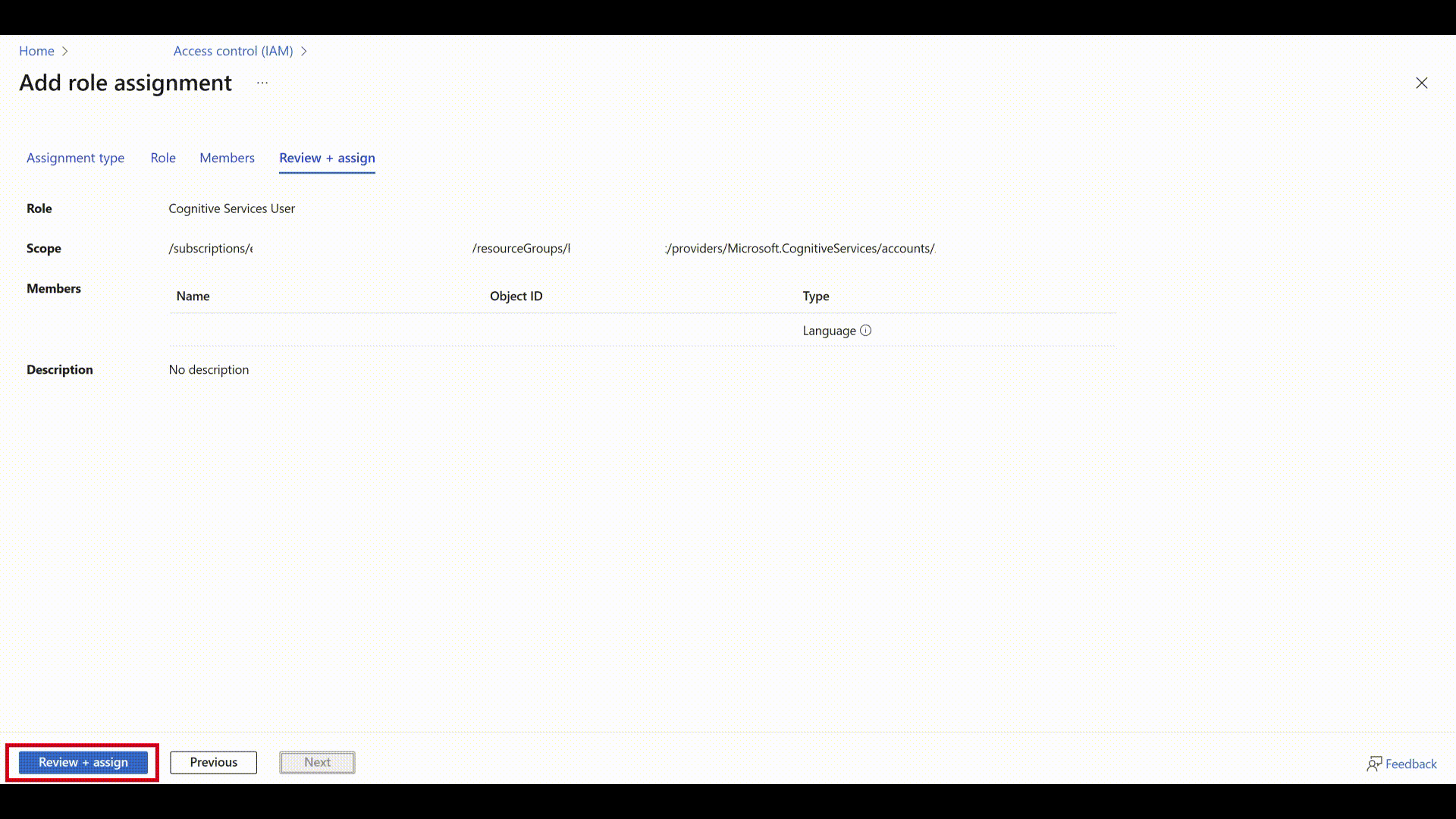
- Sign in to the Azure portal and navigate to your Azure OpenAI resource.
- Select the Access Control (IAM) tab on the left.
- Select Add > Add role assignment.
- Select "Job function roles" and click Next.
- Select
Cognitive Services Userfrom the list of roles and click Next. - Select Assign access to "Managed identity" and select "Select members".
- Under "Managed identity" select "Language".
- Search for your resource and select it. Then select the Select button below and next to complete the process.
- Review the details and select Review + Assign.
After a few minutes, refresh the Language Studio and you are able to successfully connect to Azure OpenAI.