Retrieval-Augmented Generation with Azure AI Document Intelligence
This content applies to: ![]() v4.0 (GA)
v4.0 (GA)
Introduction
Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a design pattern that combines a pretrained Large Language Model (LLM) like ChatGPT with an external data retrieval system to generate an enhanced response incorporating new data outside of the original training data. Adding an information retrieval system to your applications enables you to chat with your documents, generate captivating content, and access the power of Azure OpenAI models for your data. You also have more control over the data used by the LLM as it formulates a response.
The Document Intelligence Layout model is an advanced machine-learning based document analysis API. The Layout model offers a comprehensive solution for advanced content extraction and document structure analysis capabilities. With the Layout model, you can easily extract text and structural elements to divide large bodies of text into smaller, meaningful chunks based on semantic content rather than arbitrary splits. The extracted information can be conveniently outputted to Markdown format, enabling you to define your semantic chunking strategy based on provided building blocks.
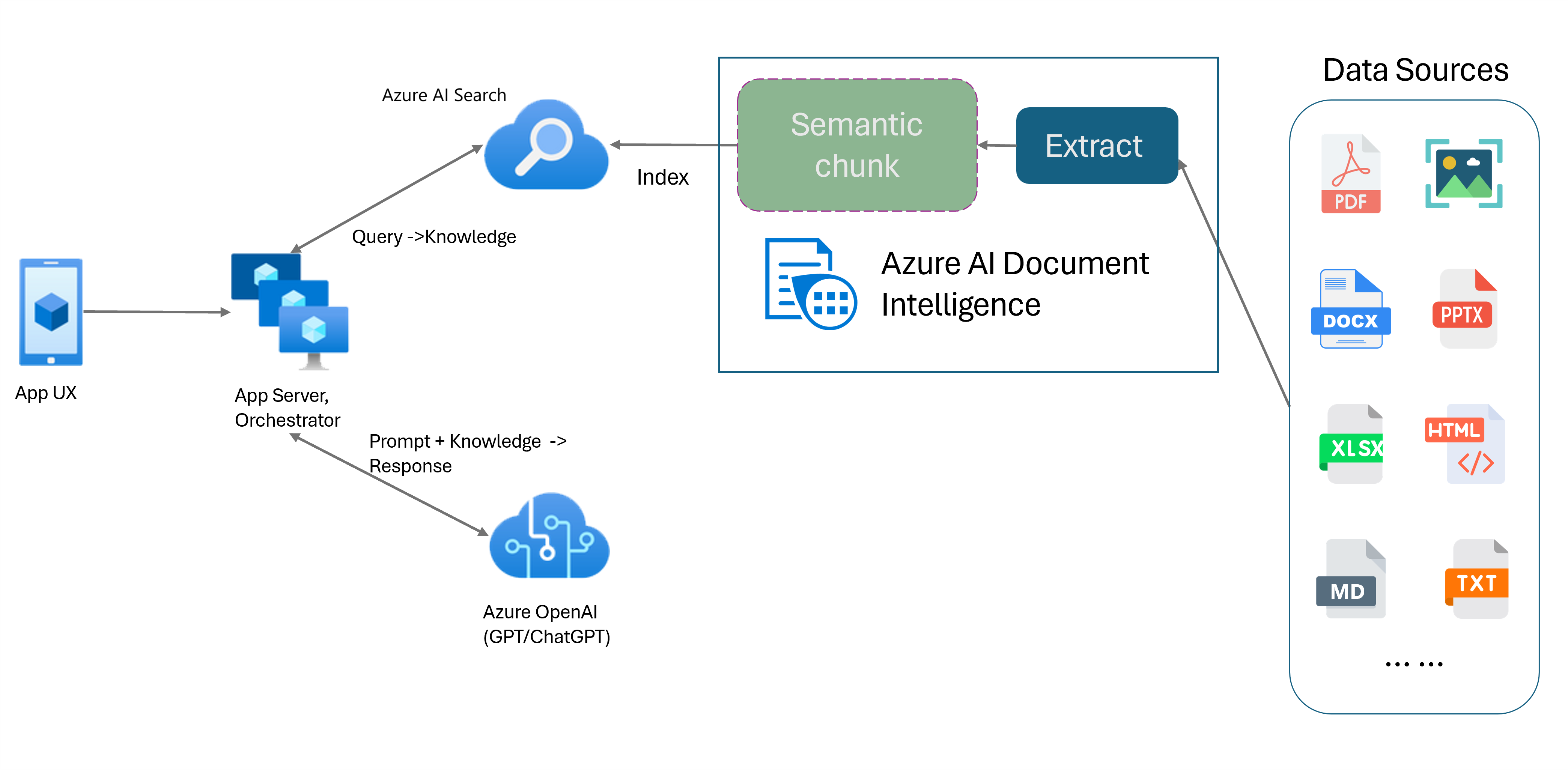
Semantic chunking
Long sentences are challenging for natural language processing (NLP) applications. Especially when they're composed of multiple clauses, complex noun or verb phrases, relative clauses, and parenthetical groupings. Just like the human beholder, an NLP system also needs to successfully keep track of all the presented dependencies. The goal of semantic chunking is to find semantically coherent fragments of a sentence representation. These fragments can then be processed independently and recombined as semantic representations without loss of information, interpretation, or semantic relevance. The inherent meaning of the text is used as a guide for the chunking process.
Text data chunking strategies play a key role in optimizing the RAG response and performance. Fixed-sized and semantic are two distinct chunking methods:
Fixed-sized chunking. Most chunking strategies used in RAG today are based on fix-sized text segments known as chunks. Fixed-sized chunking is quick, easy, and effective with text that doesn't have a strong semantic structure such as logs and data. However it isn't recommended for text that requires semantic understanding and precise context. The fixed-size nature of the window can result in severing words, sentences, or paragraphs impeding comprehension and disrupting the flow of information and understanding.
Semantic chunking. This method divides the text into chunks based on semantic understanding. Division boundaries are focused on sentence subject and use significant computational algorithmically complex resources. However, it has the distinct advantage of maintaining semantic consistency within each chunk. It's useful for text summarization, sentiment analysis, and document classification tasks.
Semantic chunking with Document Intelligence Layout model
Markdown is a structured and formatted markup language and a popular input for enabling semantic chunking in RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation). You can use the Markdown content from the Layout model to split documents based on paragraph boundaries, create specific chunks for tables, and fine-tune your chunking strategy to improve the quality of the generated responses.
Benefits of using the Layout model
Simplified processing. You can parse different document types, such as digital and scanned PDFs, images, office files (docx, xlsx, pptx), and HTML, with just a single API call.
Scalability and AI quality. The Layout model is highly scalable in Optical Character Recognition (OCR), table extraction, and document structure analysis. It supports 309 printed and 12 handwritten languages, further ensuring high-quality results driven by AI capabilities.
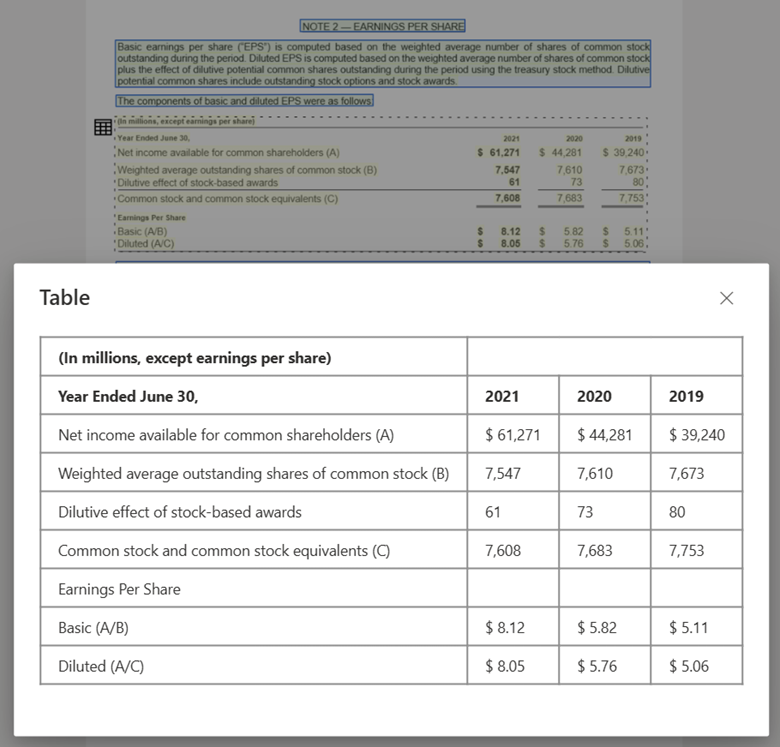
Large language model (LLM) compatibility. The Layout model Markdown formatted output is LLM friendly and facilitates seamless integration into your workflows. You can turn any table in a document into Markdown format and avoid extensive effort parsing the documents for greater LLM understanding.
Text image processed with Document Intelligence Studio and output to MarkDown using Layout model

Table image processed with Document Intelligence Studio using Layout model
Get started
The Document Intelligence Layout model 2024-11-30 (GA) supports the following development options:
Ready to begin?
Document Intelligence Studio
You can follow the Document Intelligence Studio quickstart to get started. Next, you can integrate Document Intelligence features with your own application using the sample code provided.
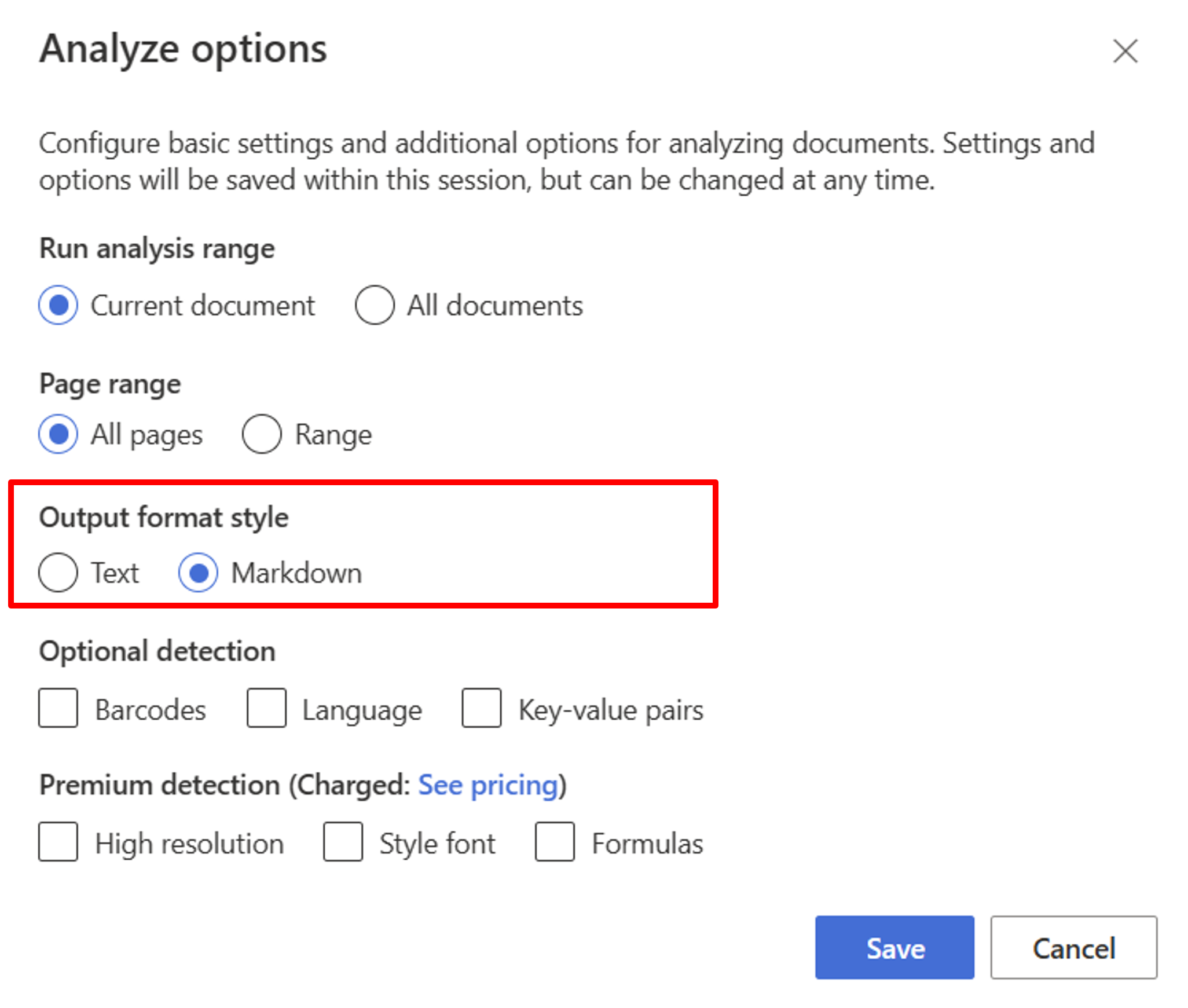
Start with the Layout model. You need to select the following Analyze options to use RAG in the studio:
**Required**- Run analysis range → Current document.
- Page range → All pages.
- Output format style → Markdown.
**Optional**- You can also select relevant optional detection parameters.
Select Save.
Select the Run analysis button to view the output.
SDK or REST API
You can follow the Document Intelligence quickstart for your preferred programming language SDK or REST API. Use the Layout model to extract content and structure from your documents.
You can also check out GitHub repos for code samples and tips for analyzing a document in markdown output format.
Build document chat with semantic chunking
Azure OpenAI on your data enables you to run supported chat on your documents. Azure OpenAI on your data applies the Document Intelligence Layout model to extract and parse document data by chunking long text based on tables and paragraphs. You can also customize your chunking strategy using Azure OpenAI sample scripts located in our GitHub repo.
Azure AI Document Intelligence is now integrated with LangChain as one of its document loaders. You can use it to easily load the data and output to Markdown format. For more information, see our sample code that shows a simple demo for RAG pattern with Azure AI Document Intelligence as document loader and Azure Search as retriever in LangChain.
The chat with your data solution accelerator code sample demonstrates an end-to-end baseline RAG pattern sample. It uses Azure AI Search as a retriever and Azure AI Document Intelligence for document loading and semantic chunking.
Use case
If you're looking for a specific section in a document, you can use semantic chunking to divide the document into smaller chunks based on the section headers helping you to find the section you're looking for quickly and easily:
# Using SDK targeting 2024-11-30 (GA), make sure your resource is in one of these regions: East US, West US2, West Europe
# pip install azure-ai-documentintelligence==1.0.0b1
# pip install langchain langchain-community azure-ai-documentintelligence
from azure.ai.documentintelligence import DocumentIntelligenceClient
endpoint = "https://<my-custom-subdomain>.cognitiveservices.azure.com/"
key = "<api_key>"
from langchain_community.document_loaders import AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader
from langchain.text_splitter import MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter
# Initiate Azure AI Document Intelligence to load the document. You can either specify file_path or url_path to load the document.
loader = AzureAIDocumentIntelligenceLoader(file_path="<path to your file>", api_key = key, api_endpoint = endpoint, api_model="prebuilt-layout")
docs = loader.load()
# Split the document into chunks base on markdown headers.
headers_to_split_on = [
("#", "Header 1"),
("##", "Header 2"),
("###", "Header 3"),
]
text_splitter = MarkdownHeaderTextSplitter(headers_to_split_on=headers_to_split_on)
docs_string = docs[0].page_content
splits = text_splitter.split_text(docs_string)
splits
Next steps
Learn more about Azure AI Document Intelligence.
Learn how to process your own forms and documents with the Document Intelligence Studio.
Complete a Document Intelligence quickstart and get started creating a document processing app in the development language of your choice.