Tutorial: Create a VM using a community template
As an Azure Stack Hub operator or user, you can create a virtual machine (VM) using custom GitHub quickstart templates rather than deploying a template manually from the Azure Stack Hub Marketplace.
In this tutorial, you learn how to:
- Use Azure Stack Hub quickstart templates
- Create a VM using a custom GitHub template
- Start Minikube and install an application
Azure Stack Hub quickstart templates
Azure Stack Hub quickstart templates are stored in the GitHub global Azure Stack Hub quickstart templates repository. This repo contains Azure Resource Manager deployment templates that have been tested with the Microsoft Azure Stack Development Kit (ASDK). You can use them to make it easier for you to evaluate Azure Stack Hub and use the ASDK environment.
Over time, many GitHub users have contributed to the repo, resulting in a collection of more than 400 deployment templates. This repo is a good starting point for understanding how you can deploy various kinds of environments to Azure Stack Hub.
Important
Some of these templates are created by members of the community and not by Microsoft. Each template is licensed under a license agreement by its owner, not Microsoft. Microsoft is not responsible for these templates and does not screen for security, compatibility, or performance. Community templates are not supported under any Microsoft support program or service, and are made available "AS IS," without warranty of any kind.
If you want to contribute Azure Resource Manager templates to GitHub, make your contribution to the AzureStack-QuickStart-Templates repo. To learn more about this repo and how to contribute to it, see the readme file.
Create a VM using a custom GitHub template
In this example tutorial, the 101-vm-linux-minikube Azure Stack Hub quickstart template is used to deploy an Ubuntu 16.04 VM on Azure Stack Hub running Minikube to manage a Kubernetes cluster.
Minikube is a tool that makes it easy to run Kubernetes locally. Minikube runs a single-node Kubernetes cluster inside a VM, enabling you to try out Kubernetes or develop with it day-to-day. It supports a simple, one-node Kubernetes cluster running on a Linux VM. Minikube is the fastest and most straightforward way to get a fully functional Kubernetes cluster running. It enables developers to develop and test their Kubernetes-based application deployments on their local machines. Architecturally, the Minikube VM runs both master and agent node components locally:
- Master node components such as API Server, Scheduler, and etcd Server are run in a single Linux process called LocalKube.
- Agent node components are run inside docker containers exactly as they would run on a normal agent node. From an application deployment standpoint, there's no difference between deploying the application on a Minikube or in a regular Kubernetes cluster.
This template installs the following components:
Important
The Ubuntu VM image (Ubuntu Server 16.04 LTS, in this example) must already have been added to the Azure Stack Hub Marketplace before performing these steps.
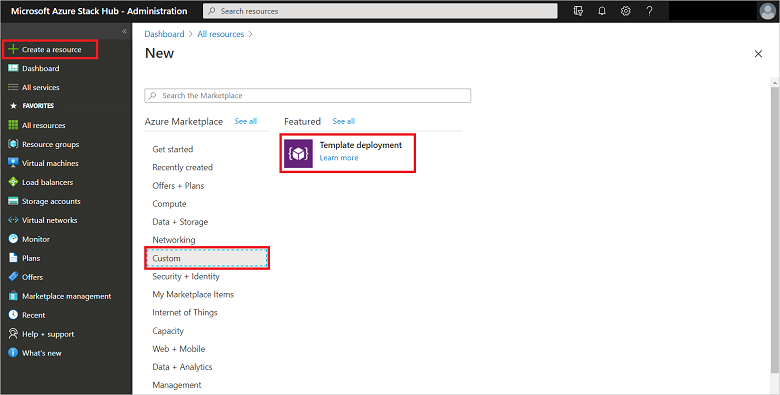
Select + Create a resource, then Custom, then Template deployment.
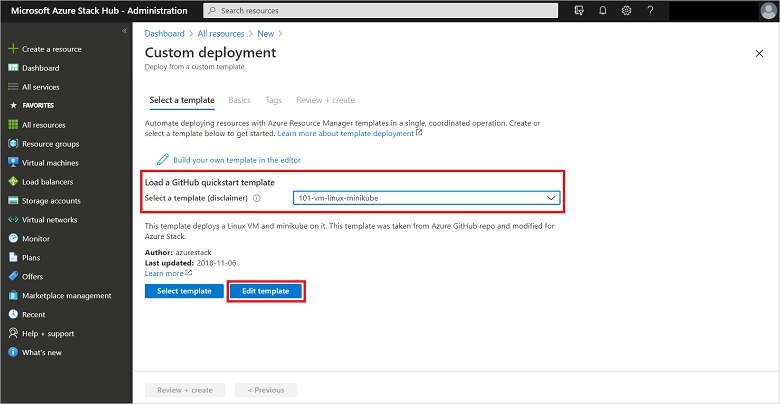
Type the name of the template to load; in this example it's 101-vm-linux-minikube. Then select Edit template.
Select Quickstart template. Then select 101-vm-linux-minikube from the available templates using the Select a template dropdown list, and then click OK.
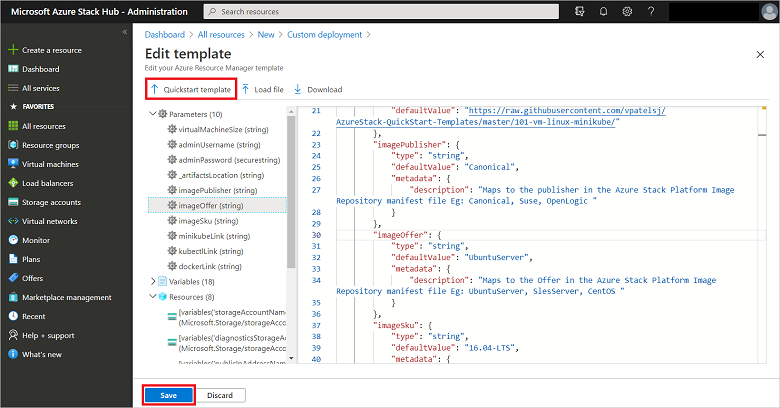
If you want to make modifications to the template JSON, you can do so. If not, or when complete, select Save to close the Edit template dialog.
Select Parameters, fill in or modify the available fields as necessary, and then click OK.
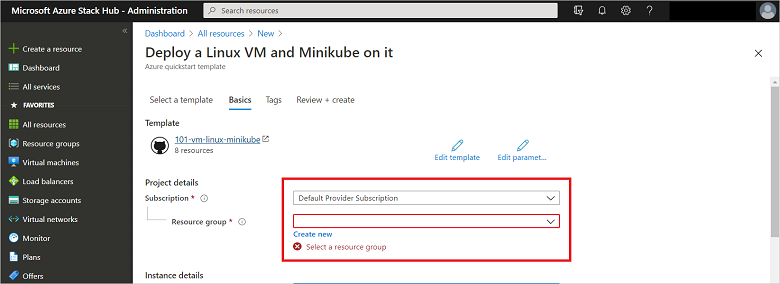
Choose the subscription to use and then create or choose an existing resource group name. Then, select Create to start the template deployment.
The resource group deployment takes several minutes to create the custom template-based VM. You can monitor the installation status through notifications and from the resource group properties.
Note
The VM will be running when the deployment completes.
Start Minikube and install an application
Now that the Linux VM has been successfully created, you can sign in to start Minikube and install an application.
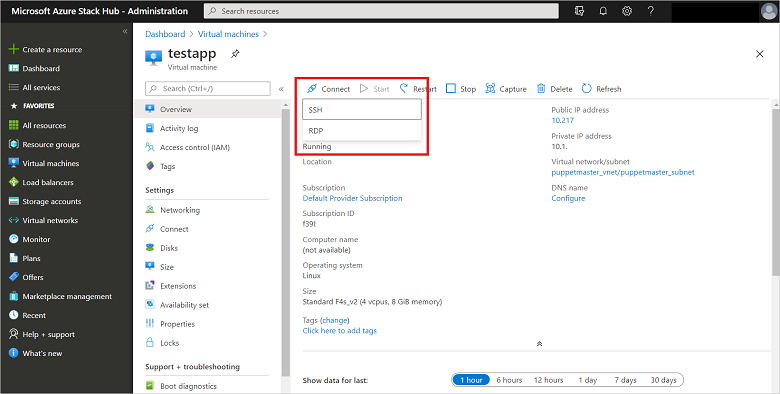
After the deployment completes, select Connect to view the public IP address that will be used to connect to the Linux VM.
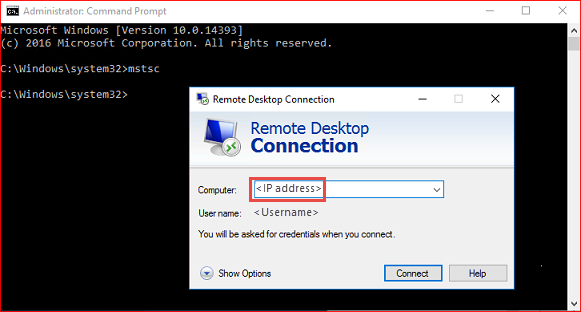
From an elevated command prompt, run mstsc.exe to open Remote Desktop Connection and connect to the Linux VM public IP address discovered in the previous step. When prompted to sign in to xRDP, use the credentials you specified when creating the VM.
Open Terminal Emulator and enter the following commands to start Minikube:
sudo minikube start --vm-driver=none sudo minikube addons enable dashboard sudo minikube dashboard --url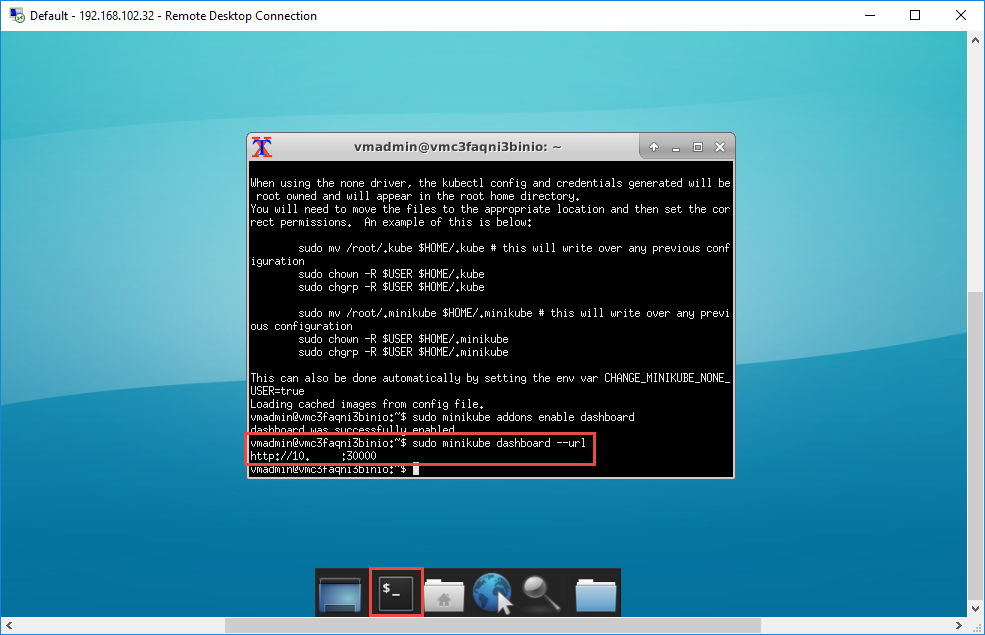
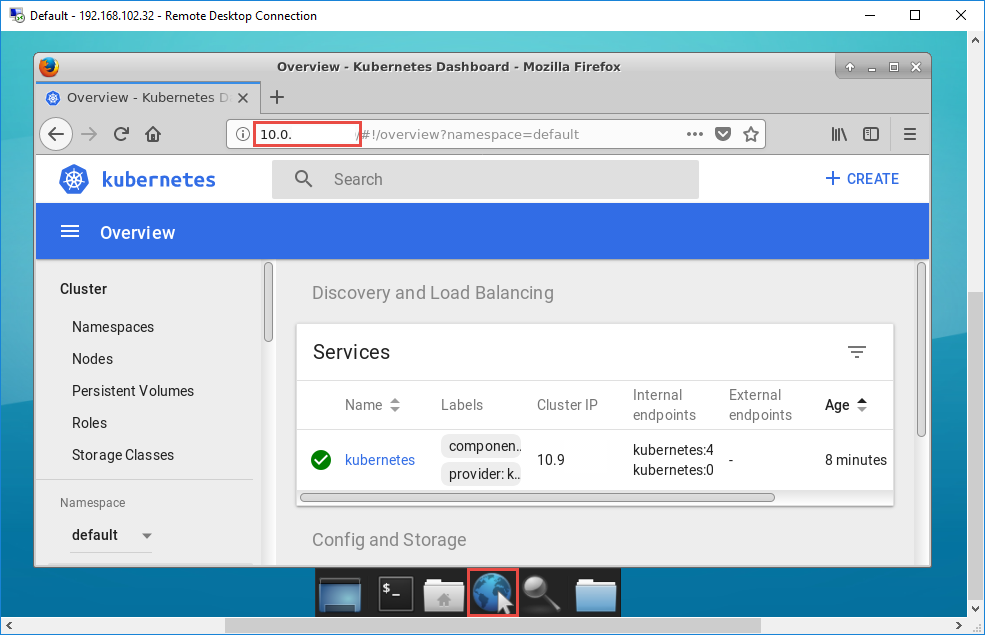
Open a browser and go to the Kubernetes dashboard address. Congratulations, you now have a fully working Kubernetes installation using Minikube!
To deploy a sample application, visit the official Kubernetes documentation page, and skip the "Create Minikube Cluster" section as you've already created one. Go to the section Create your Node.js application.
Next steps
In this tutorial, you learned how to:
- Learn about Azure Stack Hub quickstart templates
- Create a VM using a custom GitHub template
- Start minikube and install an application