Exchange Server TLS configuration best practices
This documentation outlines the necessary steps to correctly configure specific TLS versions on Microsoft Exchange Server. It also details how to optimize the cipher suites and hashing algorithms used by TLS. Incorrect TLS configuration can lead to various issues when interacting with Microsoft 365 or other systems that require a certain minimum TLS standard.
You can find more information about the TLS protocols in the Transport Layer Security protocol documentation.
Tip
You can use the Exchange HealthChecker script to check the current TLS configuration of your Exchange server.
Read carefully, as some steps can only be performed on specific operating systems or Exchange Server versions. Each section starts with a matrix showing whether a setting is supported and if it has been pre-configured from a certain Exchange Server version, followed by steps to enable or disable the specific TLS protocol or feature.
Things to consider before disabling a TLS version
Please make sure that every application supports the TLS versions, which remain enabled. Considerations such as (but not limited to):
- Do your Domain Controllers and Global Catalog servers support, for example, a TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 only configuration?
- Do partner applications support, for example, a TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 only configuration?
- Do the Operating System (OS) support the latest TLS protocol version TLS 1.2 over WinHTTP?
- Do your load balancers support TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 being used?
- Do your desktop, mobile, and browser applications support TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3?
- Do devices such as multi-function printers support TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3?
- Do your third-party or custom in-house applications that integrate with Exchange Server or Microsoft 356 support a strong TLS implementation?
As such we strongly recommend any steps you take to transition to TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 and away from older security protocols are first performed in labs which simulate your production environments before you slowly start rolling them out in production.
The steps used to disable a specific TLS version as outlined below apply to the following Exchange Server functionalities:
- Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP)
- Outlook Client Connectivity (Outlook Anywhere / MAPI/HTTP)
- Exchange Active Sync (EAS)
- Outlook on the Web (OWA)
- Exchange Admin Center (EAC) and Exchange Control Panel (ECP)
- AutoDiscover
- Exchange Web Services (EWS)
- REST (Exchange Server 2016/2019)
- Use of PowerShell by Exchange over HTTPS
- POP and IMAP
Prerequisites
TLS 1.3 support was introduced with Exchange Server 2019 Cumulative Update (CU) 15 on Windows Server 2022 and Windows Server 2025, except for the SMTP protocol. Support for this protocol will be added with a future update. TLS 1.2 support was introduced with Exchange Server 2013 CU19 and Exchange Server 2016 CU8. Exchange Server 2019 supports TLS 1.2 by default.
Exchange Server cannot run without Windows Server and therefore it is important to have the latest operating system updates installed to run a stable and secure TLS implementation.
It's also required to have the latest version of .NET Framework and associated patches supported by your CU in place.
Based on your operating system, make sure that the following updates are also in place (they should be installed if your server is current on Windows Updates):
If your operating system is Windows Server 2012 or Windows Server 2012 R2, KB3161949 and KB2973337 must be installed before TLS 1.2 can be enabled.
Warning
Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 extended support has ended on October 10, 2023. These servers no longer receive Windows Security Updates without an ESU. We strongly recommend migrating to a supported version as soon as possible!
Make sure to reboot the Exchange Server after the TLS configuration has been applied. It becomes active after the server was restarted.
Preparing .NET Framework to inherit defaults from Schannel
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations with the default .NET Framework Schannel inheritance configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 CU14 or later | Any | Yes | Yes (new installations only) |
| Exchange Server 2019 CU13 or older | Any | Yes | Partially (SchUseStrongCrypto must be configured manually) |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | Yes | No (OS defaults are used) |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | Yes | No (OS defaults are used) |
The SystemDefaultTlsVersions registry value defines which security protocol version defaults are used by .NET Framework 4.x. If the value is set to 1, then .NET Framework 4.x inherits its defaults from the Windows Secure Channel (Schannel) DisabledByDefault registry values. If the value is undefined, it behaves as if the value is set to 0.
The strong cryptography (configured by the SchUseStrongCrypto registry value) uses more secure network protocols (TLS 1.3, TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.1) and blocks protocols that are not secure. SchUseStrongCrypto affects only client (outgoing) connections in your application. By configuring .NET Framework 4.x to inherit its values from Schannel we gain the ability to use the latest versions of TLS supported by the OS, including TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3.
Enable .NET Framework 4.x Schannel inheritance
Run the following commands from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the .NET Framework 4.x Schannel inheritance:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319" -Name "SystemDefaultTlsVersions" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319" -Name "SchUseStrongCrypto" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319" -Name "SystemDefaultTlsVersions" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v4.0.30319" -Name "SchUseStrongCrypto" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Enable .NET Framework 3.5 Schannel inheritance
Exchange Server 2013 and later do not need this setting. However, we recommend configuring it identically to the .NET 4.x settings to ensure a consistent configuration.
Run the following commands from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the .NET Framework 3.5 Schannel inheritance:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727" -Name "SystemDefaultTlsVersions" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727" -Name "SchUseStrongCrypto" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727" -Name "SystemDefaultTlsVersions" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Microsoft\.NETFramework\v2.0.50727" -Name "SchUseStrongCrypto" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Steps to configure TLS 1.3
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations on which TLS 1.3 is supported. The table also shows the default configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 CU15 | Windows Server 2022/2025 | Yes | Yes (enabled) |
| Exchange Server 2019 CU15 | Windows Server 2019 | No | N/A |
| Exchange Server 2019 CU14 or older | Any | No | N/A |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | No | N/A |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | No | N/A |
Enable TLS 1.3
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to enable TLS 1.3 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.3" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
As per RFC 8446 TLS 1.3 uses the same cipher suite space as previous versions of TLS. However, TLS 1.3 cipher suites are defined differently, only specifying the symmetric ciphers, and cannot be used for TLS 1.2. Similarly, cipher suites for TLS 1.2 and lower cannot be used with TLS 1.3.
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the TLS 1.3 cipher suites:
Enable-TlsCipherSuite -Name TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 -Position 0
Enable-TlsCipherSuite -Name TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 -Position 1
Disable TLS 1.3
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable TLS 1.3 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.3" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.3\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to remove the TLS 1.3 cipher suites:
Remove-TlsCipherSuite -Name TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Remove-TlsCipherSuite -Name TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Steps to configure TLS 1.2
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations on which TLS 1.2 is supported. The table also shows the default configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 | Any | Yes | Yes (enabled) |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | Yes | No |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | Yes | No |
Enable TLS 1.2
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to enable TLS 1.2 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.2" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Disable TLS 1.2
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable TLS 1.2 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.2" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.2\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Steps to configure TLS 1.1
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations on which TLS 1.1 is supported. The table also shows the default configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 | Any | Yes | Yes (disabled) |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | Yes | No |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | Yes | No |
Enable TLS 1.1
Note
The Microsoft TLS 1.1 implementation has no known security vulnerabilities. But because of the potential for future protocol downgrade attacks and other TLS vulnerabilities, it is recommended to carefully plan and disable TLS 1.1. Failure to plan carefully may cause clients to lose connectivity.
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to enable TLS 1.1 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.1" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Disable TLS 1.1
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable TLS 1.1 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.1" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.1\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Steps to configure TLS 1.0
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations on which TLS 1.0 is supported. The table also shows the default configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 | Any | Yes | Yes (disabled) |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | Yes | No |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | Yes | No |
Enable TLS 1.0
Note
The Microsoft TLS 1.0 implementation has no known security vulnerabilities. But because of the potential for future protocol downgrade attacks and other TLS vulnerabilities, it is recommended to carefully plan and disable TLS 1.0. Failure to plan carefully may cause clients to lose connectivity.
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to enable TLS 1.0 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.0" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Disable TLS 1.0
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable TLS 1.0 for client and server connections:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols" -Name "TLS 1.0" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0" -Name "Client" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0" -Name "Server" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Client" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server" -Name "DisabledByDefault" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Protocols\TLS 1.0\Server" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Steps to configure TLS renegotiation strict mode
TLS strict mode is a security feature that ensures only clients with the necessary security updates can establish and renegotiate TLS sessions with the server.
The following table shows the Exchange Server/Windows Server combinations with the default TLS renegotiation strict mode configuration:
| Exchange Server | Windows Server | Supported | Configured by default |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exchange Server 2019 | Any | Yes | Yes (enabled) |
| Exchange Server 2016 | Any | Yes | No |
| Exchange Server 2013 | Any | No | N/A |
Enable TLS renegotiation strict mode
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to enable renegotiation strict mode:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "AllowInsecureRenegoClients" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "AllowInsecureRenegoServers" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Disable TLS renegotiation strict mode
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable renegotiation strict mode:
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "AllowInsecureRenegoClients" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "AllowInsecureRenegoServers" -Value 1 -Type DWord
Validate TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 usage
Once TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 has been enabled, it can be helpful to validate your work was successful and the system is able to negotiate TLS 1.2 or TLS 1.3 for inbound (server) connections and outbound (client) connections. There are a few methods available for validating TLS usage, some of them are discussed in the following sections.
Many protocols used in Exchange Server are HTTP based, and therefore traverse the IIS processes on the Exchange server. MAPI/HTTP, Outlook Anywhere, Exchange Web Services, Exchange ActiveSync, REST, OWA & EAC, Offline Address Book downloads, and AutoDiscover are examples of HTTP based protocols used by Exchange Server.
IIS logging
The Internet Information Services (IIS) team has added capabilities to Windows Server 2012 R2 or later to log custom fields related to encryption protocol versions and ciphers. We recommend reviewing the blog for documentation on how to enable these custom fields and begin parsing logs for information on incoming connections in your environment related to HTTP based protocols.
These IIS custom fields do not exist for Windows Server version prior Windows Server 2012 R2. Your load balancer or firewall logs may be able to provide this information. Please request guidance from your vendors to determine if their logs may provide this information.
Microsoft Edge Developer Tools
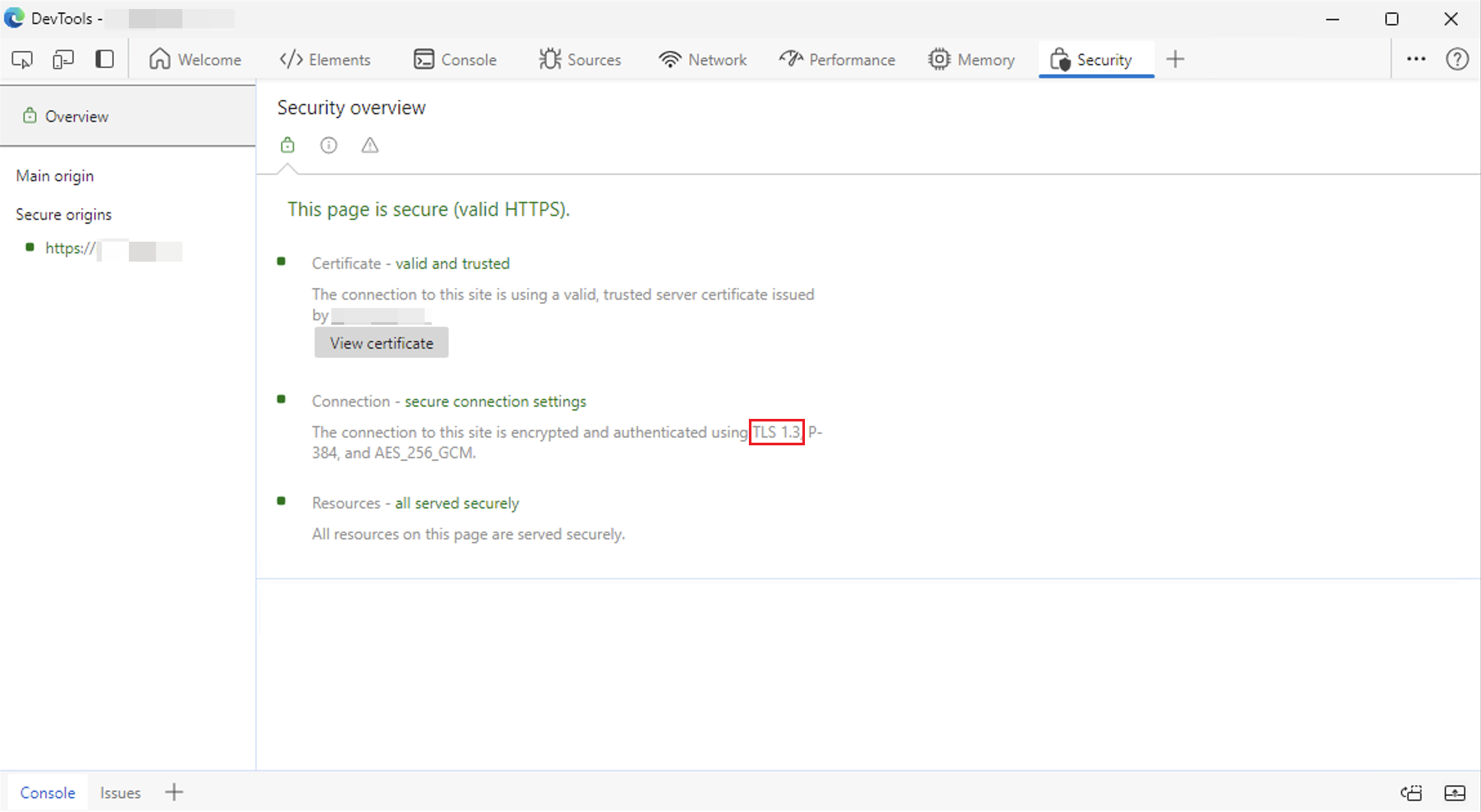
You can utilize the Developer Tools, which are available with Microsoft Edge, to check the TLS version that was used to establish a secure connection, when connecting to Outlook on the Web (OWA) or the Exchange Admin Center (ECP). To do this, follow these steps:
Open the Microsoft Edge browser and establish an HTTPS connection to OWA or ECP.
Press
CTRL + SHIFT + Ito open theDeveloper Tools.Click on the
+symbol in the upper right corner.Click on
Securityin the dropdown menu.Check the TLS version in the
Connection - secure connection settingssection.
Message headers
Message header data in Exchange Server 2016 or later provides the protocol negotiated and used when the sending and receiving host exchanged a piece of mail. You can use the Message Header Analyzer to get a clear overview of each hop.
There is a known exception to the message headers example. When a client sends a message by connecting to a server using authenticated SMTP (also known as the SMTP client submission protocol), the TLS version in the messages headers does not show the correct TLS version used by the client. Microsoft is investigating the possibility of adding this information in a future update.
SMTP logging
SMTP logs in Exchange Server contain the encryption protocol and other encryption related information used during the exchange of email between two systems.
When the server is the SMTP receiving system, search for the Server value in the log depending on the version of TLS used. If the server is the SMTP sending system, search for the Client value in the log depending on the version of TLS used.
| TLS version | Server value | Client value |
|---|---|---|
| TLS 1.0 | SP_PROT_TLS1_0_SERVER | SP_PROT-TLS1_0_CLIENT |
| TLS 1.1 | SP_PROT_TLS1_1_SERVER | SP_PROT-TLS1_1_CLIENT |
| TLS 1.2 | SP_PROT_TLS1_2_SERVER | SP_PROT-TLS1_2_CLIENT |
Note
Support for SMTP TLS 1.3 will be included in an upcoming Exchange 2019 CU15 update.
The following example searches the log files on an Exchange server, which runs the mailbox role, for connections that were made using the TLS 1.0 protocol:
Select-String -Path (((Get-TransportService -Identity $env:COMPUTERNAME).ReceiveProtocolLogPath).PathName.Replace("Hub","FrontEnd")+"\*.log") "SP_PROT_TLS1_0"
Example of searching log files on an Exchange server, which runs the Edge Transport role, for connections that were made using the TLS 1.1 protocol:
Select-String -Path (((Get-TransportService -Identity $env:COMPUTERNAME).ReceiveProtocolLogPath).PathName+"\*.log") "SP_PROT_TLS1_1"
POP and IMAP
No logging exists that exposes the encryption protocol version used for POP and IMAP clients. To capture this information, you may need to capture a Netmon trace from your server or inspect traffic as it flows through your load balancer or firewall where HTTPS bridging is taking place.
Cipher and hashing algorithms best practices
The steps in this section can be used to configure Exchange Server 2016 with the same set of cipher and hashing algorithms as Exchange Server 2019. These steps are not necessary for Exchange Server 2019, as it already comes with a preconfigured cipher and hashing algorithm setup.
As a prerequisite, you must first configure TLS 1.2 and then disable TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1. Consider applying the following settings separately from disabling TLS 1.0 and TLS 1.1 to isolate configuration issues with problematic clients.
Enable recommended cipher suites
Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2
Run the following commands from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the recommended cipher suites:
New-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Cryptography\Configuration\Local\SSL\00010002" -Name "Functions" -PropertyType MultiString -Value "TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256_P256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P256,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P384,TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA_P256,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P384,TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA_P256,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256" -Force
Windows Server 2016
Run the following commands from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the recommended cipher suites.
Note
It is possible to configure the cipher suites by utilizing a Group Policy Object (GPO). You can't configure them manually by using the Enable-TlsCipherSuite or Disable-TLSCipherSuite cmdlets if they were already configured via GPO or if the Functions registry entry already exists under the HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Cryptography\Configuration\SSL\00010002 path.
First, disable all cipher suites:
foreach ($suite in (Get-TLSCipherSuite).Name) {
if (-not([string]::IsNullOrWhiteSpace($suite))) {
Disable-TlsCipherSuite -Name $suite -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
}
}
Next, re-enable only the recommended TLS 1.2 cipher suites:
$cipherSuites = @('TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384',
'TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256',
'TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384',
'TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256',
'TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384',
'TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256',
'TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384',
'TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256')
$suiteCount = 0
foreach ($suite in $cipherSuites) {
Enable-TlsCipherSuite -Name $suite -Position $suiteCount
$suiteCount++
}
Disable outdated ciphers and hashes
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to explicitly disable outdated ciphers and hashes:
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "Hashes" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL" -Name "Ciphers" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("DES 56/56")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("NULL")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC2 40/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC2 56/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC2 56/56")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC4 40/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC4 56/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC4 64/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("RC4 128/128")
(Get-Item HKLM:).OpenSubKey("SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers", $true).CreateSubKey("Triple DES 168")
New-Item -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Hashes" -Name "MD5" -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\DES 56/56" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\NULL" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC2 40/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC2 56/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC2 56/56" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 40/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 56/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 64/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\RC4 128/128" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Ciphers\Triple DES 168" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Set-ItemProperty -Path "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL\Hashes\MD5" -Name "Enabled" -Value 0 -Type DWord
Configure the elliptic curve preference
It's recommended to disable the curve25519 elliptic curve as it's not available in FIPS mode.
More information can be found in the TLS Elliptic Curves in Windows 10 version 1607 and later documentation.
Run the following command from an elevated PowerShell window to configure the elliptic curve preference:
Disable-TlsEccCurve -Name "curve25519"
Enable-TlsEccCurve -Name "NistP384" -Position 0
Enable-TlsEccCurve -Name "NistP256" -Position 1