Transport Layer Security (TLS) support in IoT Hub
IoT Hub uses Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure connections from IoT devices and services.
Note
Azure IoT Hub will end support for TLS 1.0 and 1.1 in alignment with the Azure wide service announcement for TLS 1.0 and 1.1 retirement on August 31, 2025.
It's therefore essential that you properly test and validate that all your IoT devices and services are compatible with TLS 1.2 and the recommended ciphers in advance. It's highly recommended to use the minimum TLS enforcement feature as the mechanism for testing and compliance
To find out the version of TLS your IoT Hub devices are running, please refer to TLS 1.0 and 1.1 end of support guide.
Mutual TLS support
Mutual TLS authentication ensures that the client authenticates the server (IoT Hub) certificate and the server (IoT Hub) authenticates the client using X.509 client certificate or X.509 thumbprint. IoT Hub performs authorization after authentication is complete.
For Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) and Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) protocols, IoT Hub requests a client certificate in the initial TLS handshake. If one is provided, IoT Hub authenticates the client certificate, and the client authenticates the IoT Hub certificate. This process is called mutual TLS authentication. When IoT Hub receives an MQTT connect packet or an AMQP link opens, IoT Hub performs authorization for the requesting client and determines if the client requires X.509 authentication. If mutual TLS authentication was completed and the client is authorized to connect as the device, It's allowed. However, if the client requires X.509 authentication and client authentication wasn't completed during the TLS handshake, then IoT Hub rejects the connection.
For HTTP protocol, when the client makes its first request, IoT Hub checks if the client requires X.509 authentication and if client authentication was complete then IoT Hub performs authorization. If client authentication wasn't complete, then IoT Hub rejects the connection
After a successful TLS handshake, IoT Hub can authenticate a device using a symmetric key or an X.509 certificate. For certificate-based authentication, IoT Hub validates the certificate against the thumbprint or certificate authority (CA) you provide. To learn more, see Supported X.509 certificates.
IoT Hub's server TLS certificate
During a TLS handshake, IoT Hub presents RSA-keyed server certificates to connecting clients. All IoT hubs in the global Azure cloud use the TLS certificate issued by the DigiCert Global Root G2.
We strongly recommend that all devices trust the following three root CAs:
- DigiCert Global G2 root CA
- Microsoft RSA root CA 2017
For links to download these certificates, see Azure Certificate Authority details.
Root CA migrations are rare. You should always prepare your IoT solution for the unlikely event that a root CA is compromised and an emergency root CA migration is necessary.
Cipher Suites
To comply with Azure security policy for a secure connection, IoT Hub supports the following RSA and ECDSA cipher suites for TLS 1.2:
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256
- TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
The following cipher suites are currently allowed in IoT Hub. However, these cipher suites are no longer recommended by the Azure security guidelines.
| Cipher Suites | TLS Version support |
|---|---|
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_DHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA256 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256 | TLS 1.2 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_ECDHE_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_3DES_EDE_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
| TLS_RSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA | TLS 1.0/1.1/1.2 |
A client can suggest a list of higher cipher suites to use during ClientHello. However, some of them might not be supported by IoT Hub (for example, ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384). In this case, IoT Hub tries to follow the preference of the client, but eventually negotiate down the cipher suite with ServerHello.
Enforce IoT Hub to use TLS 1.2 and strong cipher suites
To ensure your IoT devices are TLS 1.2 and strong cipher suites compliance, you can enforce compliance using minimum TLS enforcement feature in Azure IoT Hub.
Currently this feature is only available in the following regions and during IoT Hub creation (other Azure regions will be supported in 2025):
- East US
- South Central US
- West US 2
- US Gov Arizona
- US Gov Virginia (TLS 1.0/1.1 support isn't available in this region - TLS 1.2 enforcement must be enabled or IoT hub creation fails)
To enable TLS 1.2 and strong cipher suites enforcement in Azure portal:
Staring with the IoT Hub create wizard in Azure portal
Choose a Region from one in the list above.
Under Management -> Advanced -> Transport Layer Security (TLS) -> Minimum TLS version, select 1.2. This setting only appears for IoT hub created in supported region.
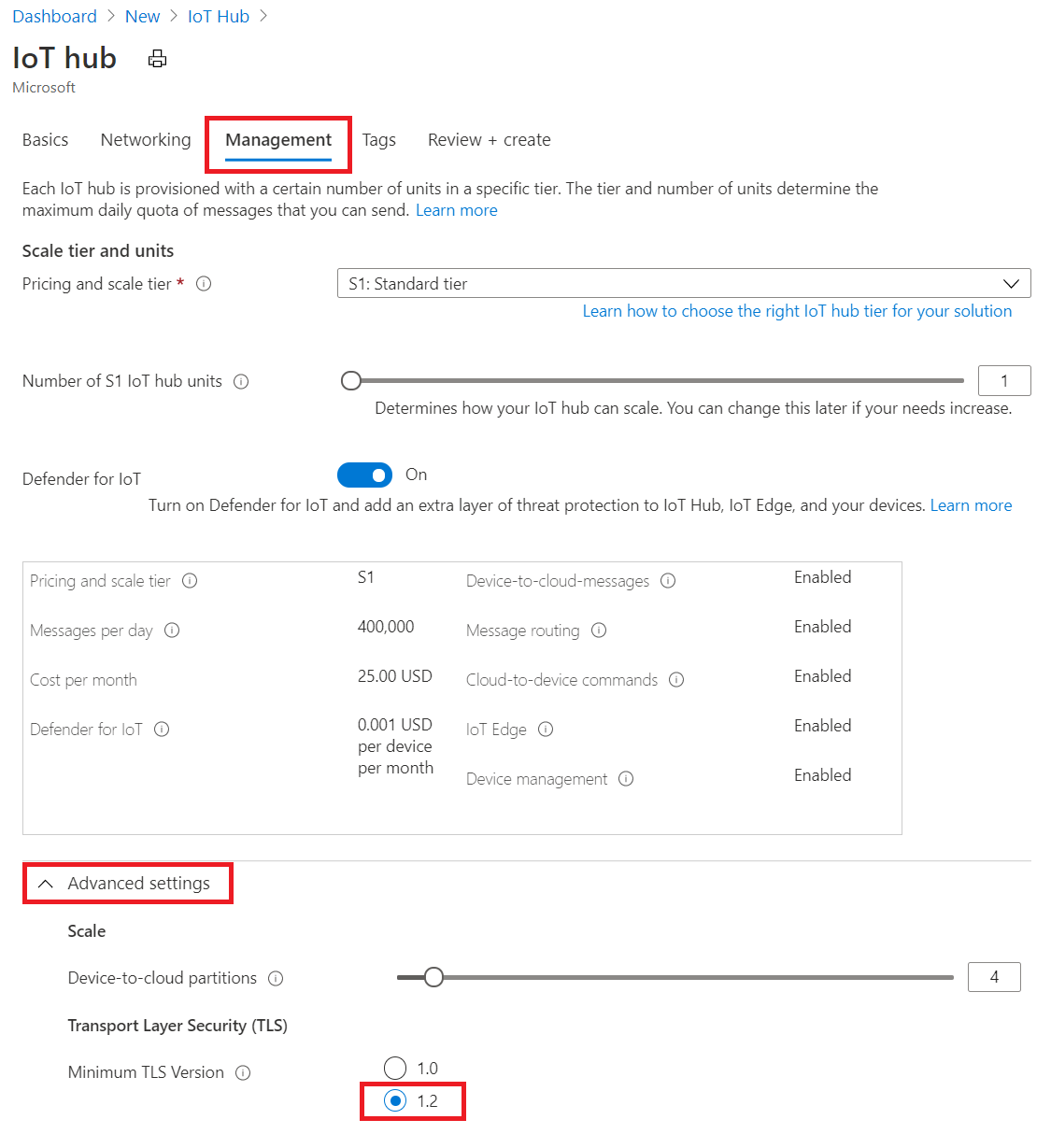
Click Create
Connect your IoT devices to this IoT Hub
To use ARM template for creation, provision a new IoT Hub in any of the supported regions and set the minTlsVersion property to 1.2 in the resource specification:
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"resources": [
{
"type": "Microsoft.Devices/IotHubs",
"apiVersion": "2020-01-01",
"name": "<provide-a-valid-resource-name>",
"location": "<any-of-supported-regions-below>",
"properties": {
"minTlsVersion": "1.2"
},
"sku": {
"name": "<your-hubs-SKU-name>",
"tier": "<your-hubs-SKU-tier>",
"capacity": 1
}
}
]
}
The created IoT Hub resource using this configuration refuses device and service clients that attempt to connect using TLS versions 1.0 and 1.1. Similarly, the TLS handshake is refused if the ClientHello message doesn't list any of the recommended ciphers.
Note
The minTlsVersion property is read-only and can't be changed once your IoT Hub resource is created. It's therefore essential that you properly test and validate that all your IoT devices and services are compatible with TLS 1.2 and the recommended ciphers in advance.
Upon failovers, the minTlsVersion property of your IoT Hub remains effective in the geo-paired region post-failover.
Checking TLS versions for IoT Hub devices
Azure IoT Hub can provide diagnostic logs for several categories that can be analyzed using Azure Monitor Logs. In the connections log you can find the TLS Version for your IoT Hub devices.
To view these logs, follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, go to your IoT hub.
- In the resource menu under Monitoring, select Diagnostic settings. Ensure diagnostic settings have "Connections" checkmarked.
- In the resource menu under Monitoring, select Logs.
- Enter the following query:
AzureDiagnostics
| where ResourceProvider == "MICROSOFT.DEVICES" and ResourceType == "IOTHUBS"
| where Category == "Connections"
| where OperationName == "deviceConnect"
| extend props_json = parse_json(properties_s)
| project DeviceId = props_json.deviceId, TLSVersion = props_json.tlsVersion
- An example of the query results looks like:
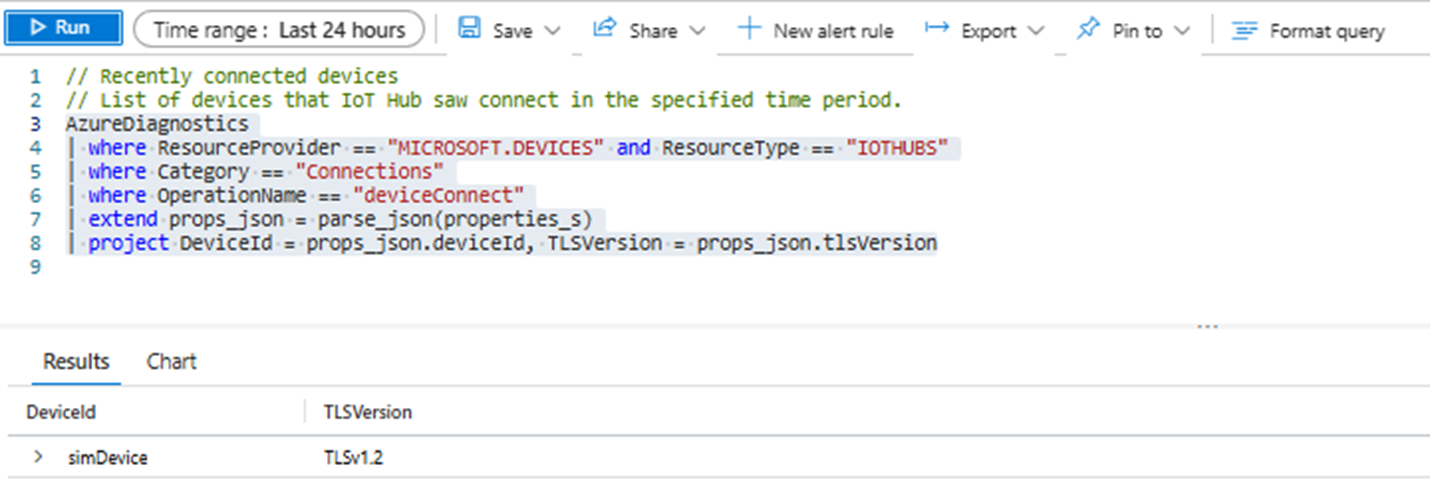
- Note: TLS version query is not available for devices using HTTPS connections.
TLS configuration for SDK and IoT Edge
Use the following links to configure TLS 1.2 and allowed ciphers in IoT Hub client SDKs.
| Language | Versions supporting TLS 1.2 | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| C | Tag 2019-12-11 or newer | Link |
| Python | Version 2.0.0 or newer | Link |
| C# | Version 1.21.4 or newer | Link |
| Java | Version 1.19.0 or newer | Link |
| NodeJS | Version 1.12.2 or newer | Link |
IoT Edge devices can be configured to use TLS 1.2 when communicating with IoT Hub. For this purpose, use the IoT Edge documentation page.
Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) server TLS certificate
While offering similar security to RSA certificates, ECC certificate validation (with ECC-only cipher suites) uses up to 40% less compute, memory, and bandwidth. These savings are important for IoT devices because of their smaller profiles and memory, and to support use cases in network bandwidth limited environments.
To use IoT Hub's ECC server certificate:
- Ensure all devices trust the following root CAs:
- DigiCert Global G2 root CA
- Microsoft RSA root CA 2017
- Configure your client to include only ECDSA cipher suites and exclude any RSA ones. These are the supported cipher suites for the ECC certificate:
TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_GCM_SHA256TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_GCM_SHA384TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_128_CBC_SHA256TLS_ECDHE_ECDSA_WITH_AES_256_CBC_SHA384
- Connect your client to the IoT hub.
TLS maximum fragment length negotiation
IoT Hub also supports TLS maximum fragment length negotiation, which is sometimes known as TLS frame size negotiation. This feature is in public preview.
Use this feature to specify the maximum plaintext fragment length to a value smaller than the default 2^14 bytes. Once negotiated, IoT Hub and the client begin fragmenting messages to ensure all fragments are smaller than the negotiated length. This behavior is helpful to compute or memory constrained devices. To learn more, see the official TLS extension spec.
Official SDK support for this public preview feature isn't yet available. To get started
- Create an IoT Hub.
- When using OpenSSL, call SSL_CTX_set_tlsext_max_fragment_length to specify the fragment size.
- Connect your client to the IoT Hub.
Certificate pinning
Certificate pinning and filtering of the TLS server certificates and intermediate certificates associated with IoT Hub endpoints is strongly discouraged as Microsoft frequently rolls these certificates with little or no notice. If you must, only pin the root certificates as described in this Azure IoT blog post.
Next steps
- To learn more about IoT Hub security and access control, see Control access to IoT Hub.
- To learn more about using X509 certificate for device authentication, see Device Authentication using X.509 CA Certificates