EBLC — Embedded Bitmap Location Table (OpenType 1.8.1)
The EBLC provides embedded bitmap locators. It is used together with the EDBTtable, which provides embedded, monochrome or grayscale bitmap glyph data, and the EBSC table, which provided embedded bitmap scaling information.
OpenType embedded bitmaps are called 'sbits' (for “scaler bitmaps”). A set of bitmaps for a face at a given size is called a strike.
The 'EBLC' table identifies the sizes and glyph ranges of the sbits, and keeps offsets to glyph bitmap data in indexSubTables. The 'EBDT' table then stores the glyph bitmap data, also in a number of different possible formats. Glyph metrics information may be stored in either the 'EBLC' or 'EBDT' table, depending upon the indexSubTable and glyph bitmap formats. The 'EBSC' table identifies sizes that will be handled by scaling up or scaling down other sbit sizes.
The 'EBLC' table uses the same format as the Apple Apple Advanced Typography (AAT) 'bloc' table.
The 'EBLC' table begins with a header containing the table version and number of strikes. An OpenType font may have one or more strikes embedded in the 'EBDT' table.
eblcHeader
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uint16 | majorVersion | Major version of the EBLC table, = 2. |
| uint16 | minorVersion | Minor version of the EBLC table, = 0. |
| uint32 | numSizes | Number of bitmapSizeTables |
Note that the first version of the EBLC table is 2.0.
The eblcHeader is followed immediately by the bitmapSizeTable array(s). The numSizes in the eblcHeader indicates the number of bitmapSizeTables in the array. Each strike is defined by one bitmapSizeTable.
bitmapSizeTable
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Offset32 | indexSubTableArrayOffset | offset to index subtable from beginning of EBLC. |
| uint32 | indexTablesSize | number of bytes in corresponding index subtables and array |
| uint32 | numberOfIndexSubTables | an index subtable for each range or format change |
| uint32 | colorRef | not used; set to 0. |
| sbitLineMetrics | hori | line metrics for text rendered horizontally |
| sbitLineMetrics | vert | line metrics for text rendered vertically |
| uint16 | startGlyphIndex | lowest glyph index for this size |
| uint16 | endGlyphIndex | highest glyph index for this size |
| uint8 | ppemX | horizontal pixels per Em |
| uint8 | ppemY | vertical pixels per Em |
| uint8 | bitDepth | the Microsoft rasterizer v.1.7 or greater supports the following bitDepth values, as described below: 1, 2, 4, and 8. |
| int8 | flags | vertical or horizontal (see bitmapFlags) |
The indexSubTableArrayOffset is the offset from the beginning of the 'EBLC' table to the indexSubTableArray. Each strike has one of these arrays to support various formats and discontiguous ranges of bitmaps. The indexTablesSize is the total number of bytes in the indexSubTableArray and the associated indexSubTables. The numberOfIndexSubTables is a count of the indexSubTables for this strike.
The horizontal and vertical line metrics contain the ascender, descender, linegap, and advance information for the strike. The line metrics format is described in the following table:
sbitLineMetrics
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| int8 | ascender |
| int8 | descender |
| uint8 | widthMax |
| int8 | caretSlopeNumerator |
| int8 | caretSlopeDenominator |
| int8 | caretOffset |
| int8 | minOriginSB |
| int8 | minAdvanceSB |
| int8 | maxBeforeBL |
| int8 | minAfterBL |
| int8 | pad1 |
| int8 | pad2 |
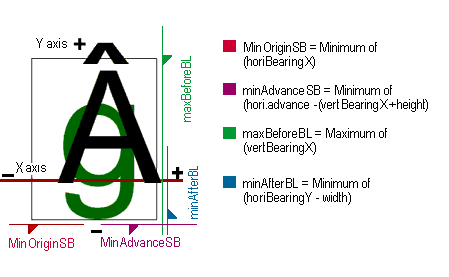
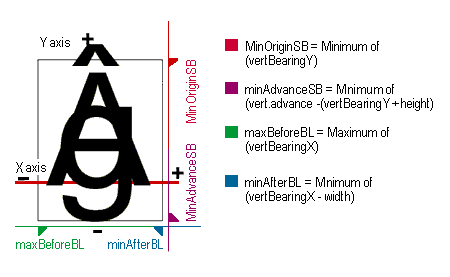
The caret slope determines the angle at which the caret is drawn, and the offset is the number of pixels (+ or -) to move the caret. This is a signed integer since we are dealing with integer metrics. The minOriginSB, minAdvanceSB , maxBeforeBL, and minAfterBL are described in the diagrams below. The main need for these numbers is for scalers that may need to pre-allocate memory and/or need more metric information to position glyphs. All of the line metrics are one byte in length. The line metrics are not used directly by the rasterizer, but are available to clients who want to parse the 'EBLC' table.
The startGlyphIndex and endGlyphIndex describe the minimum and maximum glyph codes in the strike, but a strike does not necessarily contain bitmaps for all glyph codes in this range. The indexSubTables determine which glyphs are actually present in the 'EBDT' table.
The ppemX and ppemY fields describe the size of the strike in pixels per Em. The ppem measurement is equivalent to point size on a 72 dots per inch device. Typically, ppemX will be equal to ppemY for devices with ‘square pixels’. To accommodate devices with rectangular pixels, and to allow for bitmaps with other aspect ratios, ppemX and ppemY may differ.
The bitDepth field is used to specify the number of levels of gray used in the embedded bitmaps. The Microsoft rasterizer v.1.7 or greater support the following values.
bitDepth
| Value | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | black/white |
| 2 | 4 levels of gray |
| 4 | 16 levels of gray |
| 8 | 256 levels of gray |
The ‘flags’ byte contains two bits to indicate the direction of small glyph metrics: horizontal or vertical. The remaining bits are reserved.
Bitmap Flags
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| int8 | 0x01 | Horizontal |
| int8 | 0x02 | Vertical |
The colorRef and bitDepth fields are reserved for future enhancements. For monochrome bitmaps they should have the values colorRef=0 and bitDepth=1.
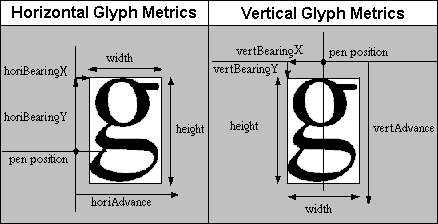
Associated with the image data for every glyph in a strike is a set of glyph metrics. These glyph metrics describe bounding box height and width, as well as side bearing and advance width information. The glyph metrics can be found in one of two places. For ranges of glyphs (not necessarily the whole strike) whose metrics may be different for each glyph, the glyph metrics are stored along with the glyph image data in the 'EBDT' table. Details of how this is done is described in the 'EBDT' section of this document. For ranges of glyphs whose metrics are identical for every glyph, we save significant space by storing a single copy of the glyph metrics in the indexSubTable in the 'EBLC'.
There are also two different formats for glyph metrics: big glyph metrics and small glyph metrics. Big glyph metrics define metrics information for both horizontal and vertical layouts. This is important in fonts (such as Kanji) where both types of layout may be used. Small glyph metrics define metrics information for one layout direction only. Which direction applies, horizontal or vertical, is determined by the ‘flags’ field in the bitmapSizeTable.
bigGlyphMetrics
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| uint8 | height |
| uint8 | width |
| int8 | horiBearingX |
| int8 | horiBearingY |
| uint8 | horiAdvance |
| int8 | vertBearingX |
| int8 | vertBearingY |
| uint8 | vertAdvance |
smallGlyphMetrics
| Type | Name |
|---|---|
| uint8 | height |
| uint8 | width |
| int8 | BearingX |
| int8 | BearingY |
| uint8 | Advance |
The following diagram illustrates the meaning of the glyph metrics.
The bitmapSizeTable for each strike contains the offset to an array of indexSubTableArray elements. Each element describes a glyph code range and an offset to the indexSubTable for that range. This allows a strike to contain multiple glyph code ranges and to be represented in multiple index formats if desirable.
indexSubTableArray
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uint16 | firstGlyphIndex | first glyph code of this range |
| uint16 | lastGlyphIndex | last glyph code of this range (inclusive) |
| Offset32 | additionalOffset ToIndexSubtable |
add to indexSubTableArrayOffset to get offset from beginning of 'EBLC' |
After determining the strike, the rasterizer searches this array for the range containing the given glyph code. When the range is found, the additionalOffsetToIndexSubtable is added to the indexSubTableArrayOffset to get the offset of the indexSubTable in the 'EBLC'.
The first indexSubTableArray is located after the last bitmapSizeSubTable entry. Then the indexSubTables for the strike follow. Another indexSubTableArray (if more than one strike) and its indexSubTables are next. The 'EBLC' continues with an array and indexSubTables for each strike.
We now have the offset to the indexSubTable. All indexSubTable formats begin with an indexSubHeader which identifies the indexSubTable format, the format of the 'EBDT' image data, and the offset from the beginning of the 'EBDT' table to the beginning of the image data for this range.
indexSubHeader
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uint16 | indexFormat | format of this indexSubTable |
| uint16 | imageFormat | format of 'EBDT' image data |
| Offset32 | imageDataOffset | offset to image data in 'EBDT' table |
There are currently five different formats used for the indexSubTable, depending upon the size and type of bitmap data in the glyph code range. Apple 'bloc' tables support only formats 1 through 3.
The choice of which indexSubTable format to use is up to the font manufacturer, but should be made with the aim of minimizing the size of the font file. Ranges of glyphs with variable metrics - that is, where glyphs may differ from each other in bounding box height, width, side bearings or advance - must use format 1, 3 or 4. Ranges of glyphs with constant metrics can save space by using format 2 or 5, which keep a single copy of the metrics information in the indexSubTable rather than a copy per glyph in the 'EBDT' table. In some monospaced fonts it makes sense to store extra white space around some of the glyphs to keep all metrics identical, thus permitting the use of format 2 or 5.
Structures for each indexSubTable format are listed below.
indexSubTable1: variable metrics glyphs with 4-byte offsets
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| indexSubHeader | header | header info |
| Offset32 | offsetArray[] | offsetArray[glyphIndex]+ imageDataOffset=glyphData sizeOfArray= (lastGlyph-firstGlyph+1)+1+1 pad if needed |
indexSubTable2: all glyphs have identical metrics
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| indexSubHeader | header | header info |
| uint32 | imageSize | all the glyphs are of the same size |
| bigGlyphMetrics | bigMetrics | all glyphs have the same metrics; glyph data may be compressed, byte-aligned, or bit-aligned |
indexSubTable3: variable metrics glyphs with 2-byte offsets
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| indexSubHeader | header | header info |
| Offset16 | offsetArray[] | offsetArray[glyphIndex] +imageDataOffset= glyphData sizeOfArray= (lastGlyph-firstGlyph+1)+1+1 pad if needed |
indexSubTable4: variable metrics glyphs with sparse glyph codes
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| indexSubHeader | header | header info |
| uint32 | numGlyphs | array length |
| codeOffsetPair | glyphArray[] | one per glyph; sizeOfArray=numGlyphs+1 |
used by indexSubTable4
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| uint16 | glyphCode | code of glyph present |
| Offset16 | offset | location in EBDT |
indexSubTable5: constant metrics glyphs with sparse glyph codes
| Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| indexSubHeader | header | header info |
| uint32 | imageSize | all glyphs have the same data size |
| bigGlyphMetrics | bigMetrics | all glyphs have the same metrics |
| uint32 | numGlyphs | array length |
| uint16 | glyphCodeArray[] | one per glyph, sorted by glyph code; sizeOfArray=numGlyphs |
The size of the 'EBDT' image data can be calculated from the indexSubTable information. For the constant metrics formats (2 and 5) the image data size is constant, and is given in the imageSize field. For the variable metrics formats (1, 3, and 4) image data must be stored contiguously and in glyph code order, so the image data size may be calculated by subtracting the offset for the current glyph from the offset of the next glyph. Because of this, it is necessary to store one extra element in the offsetArray pointing just past the end of the range’s image data. This will allow the correct calculation of the image data size for the last glyph in the range.
Contiguous, or nearly contiguous, ranges of glyph codes are handled best by formats 1, 2, and 3 which store an offset for every glyph code in the range. Very sparse ranges of glyph codes should use format 4 or 5 which explicitly call out the glyph codes represented in the range. A small number of missing glyphs can be efficiently represented in formats 1 or 3 by having the offset for the missing glyph be followed by the same offset for the next glyph, thus indicating a data size of zero.
The only difference between formats 1 and 3 is the size of the offsetArray elements: format 1 uses uint32s while format 3 uses uint16s. Therefore format 1 can cover a greater range (> 64k bytes) while format 3 saves more space in the 'EBLC' table. Since the offsetArray elements are added to the imageDataOffset base address in the indexSubHeader, a very large set of glyph bitmap data could be addressed by splitting it into multiple ranges, each less than 64k bytes in size, allowing the use of the more efficient format 3.
The 'EBLC' table specification requires 16-bit alignment for all subtables. This occurs naturally for indexSubTable formats 1, 2, and 4, but may not for formats 3 and 5, since they include arrays of type uint16. When there is an odd number of elements in these arrays it is necessary to add an extra padding element to maintain proper alignment.
OpenType specification