자습서: R에서 SQL 기계 학습을 사용하여 예측 모델 만들기
적용 대상: SQL Server 2016(13.x) 이상
Azure SQL Managed Instance
4부로 구성된 이 자습서 시리즈의 3부에서는 R에서 예측 모델을 학습시킵니다. 이 시리즈의 다음 부분에서는 Machine Learning Services를 사용하여 SQL Server 데이터베이스 또는 빅 데이터 클러스터에 이 모델을 배포합니다.
4부로 구성된 이 자습서 시리즈의 3부에서는 R에서 예측 모델을 학습시킵니다. 이 시리즈의 다음 부분에서는 Machine Learning Services를 사용하여 SQL Server 데이터베이스에 이 모델을 배포합니다.
4부로 구성된 이 자습서 시리즈의 3부에서는 R에서 예측 모델을 학습시킵니다. 이 시리즈의 다음 부분에서는 SQL Server R Services를 사용하여 데이터베이스에 이 모델을 배포합니다.
4부로 구성된 이 자습서 시리즈의 3부에서는 R에서 예측 모델을 학습시킵니다. 이 시리즈의 다음 부분에서는 Machine Learning Services를 사용하여 Azure SQL Managed Instance 데이터베이스에 이 모델을 배포합니다.
이 문서에서는 다음을 수행하는 방법을 알아봅니다.
- 두 가지 기계 학습 모델 학습
- 두 모델에서 예측 수행
- 결과를 비교하여 가장 정확한 모델 선택
1부에서는 샘플 데이터베이스를 복원하는 방법을 알아보았습니다.
2부에서는 데이터베이스의 데이터를 Python 데이터 프레임에 로드하고, R에서 데이터를 준비하는 방법을 배웠습니다.
4부에서는 모델을 데이터베이스에 저장한 다음, 2부와 3부에서 개발한 Python 스크립트에서 저장 프로시저를 만드는 방법을 알아봅니다. 저장 프로시저는 서버에서 실행되어 새 데이터를 기반으로 예측을 만듭니다.
필수 조건
이 자습서의 3부에서는 1부의 사전 요구 사항을 이행하고, 2부의 단계를 완료했다고 가정합니다.
두 가지 모델 학습
스키 대여 데이터에 가장 적합한 모델을 찾으려면 두 가지 모델(선형 회귀 및 의사 결정 트리)을 만들고 어떤 모델이 더 정확하게 예측되는지 확인합니다. 이 시리즈 1부에서 만든 데이터 프레임 rentaldata를 사용합니다.
#First, split the dataset into two different sets:
# one for training the model and the other for validating it
train_data = rentaldata[rentaldata$Year < 2015,];
test_data = rentaldata[rentaldata$Year == 2015,];
#Use the RentalCount column to check the quality of the prediction against actual values
actual_counts <- test_data$RentalCount;
#Model 1: Use lm to create a linear regression model, trained with the training data set
model_lm <- lm(RentalCount ~ Month + Day + WeekDay + Snow + Holiday, data = train_data);
#Model 2: Use rpart to create a decision tree model, trained with the training data set
library(rpart);
model_rpart <- rpart(RentalCount ~ Month + Day + WeekDay + Snow + Holiday, data = train_data);
두 모델에서 예측 수행
예측 함수를 사용하여 학습된 각 모델을 사용하여 임대 수를 예측합니다.
#Use both models to make predictions using the test data set.
predict_lm <- predict(model_lm, test_data)
predict_lm <- data.frame(RentalCount_Pred = predict_lm, RentalCount = test_data$RentalCount,
Year = test_data$Year, Month = test_data$Month,
Day = test_data$Day, Weekday = test_data$WeekDay,
Snow = test_data$Snow, Holiday = test_data$Holiday)
predict_rpart <- predict(model_rpart, test_data)
predict_rpart <- data.frame(RentalCount_Pred = predict_rpart, RentalCount = test_data$RentalCount,
Year = test_data$Year, Month = test_data$Month,
Day = test_data$Day, Weekday = test_data$WeekDay,
Snow = test_data$Snow, Holiday = test_data$Holiday)
#To verify it worked, look at the top rows of the two prediction data sets.
head(predict_lm);
head(predict_rpart);
RentalCount_Pred RentalCount Month Day WeekDay Snow Holiday
1 27.45858 42 2 11 4 0 0
2 387.29344 360 3 29 1 0 0
3 16.37349 20 4 22 4 0 0
4 31.07058 42 3 6 6 0 0
5 463.97263 405 2 28 7 1 0
6 102.21695 38 1 12 2 1 0
RentalCount_Pred RentalCount Month Day WeekDay Snow Holiday
1 40.0000 42 2 11 4 0 0
2 332.5714 360 3 29 1 0 0
3 27.7500 20 4 22 4 0 0
4 34.2500 42 3 6 6 0 0
5 645.7059 405 2 28 7 1 0
6 40.0000 38 1 12 2 1 0
결과 비교
이제 최상의 예측을 제공하는 모델을 확인하려고 합니다. 이 작업을 빠르고 쉽게 수행할 수 있는 방법은 기본 그리기 함수를 사용하여 학습 데이터의 실제 값과 예측 값 간의 차이를 보는 것입니다.
#Use the plotting functionality in R to visualize the results from the predictions
par(mfrow = c(1, 1));
plot(predict_lm$RentalCount_Pred - predict_lm$RentalCount, main = "Difference between actual and predicted. lm")
plot(predict_rpart$RentalCount_Pred - predict_rpart$RentalCount, main = "Difference between actual and predicted. rpart")
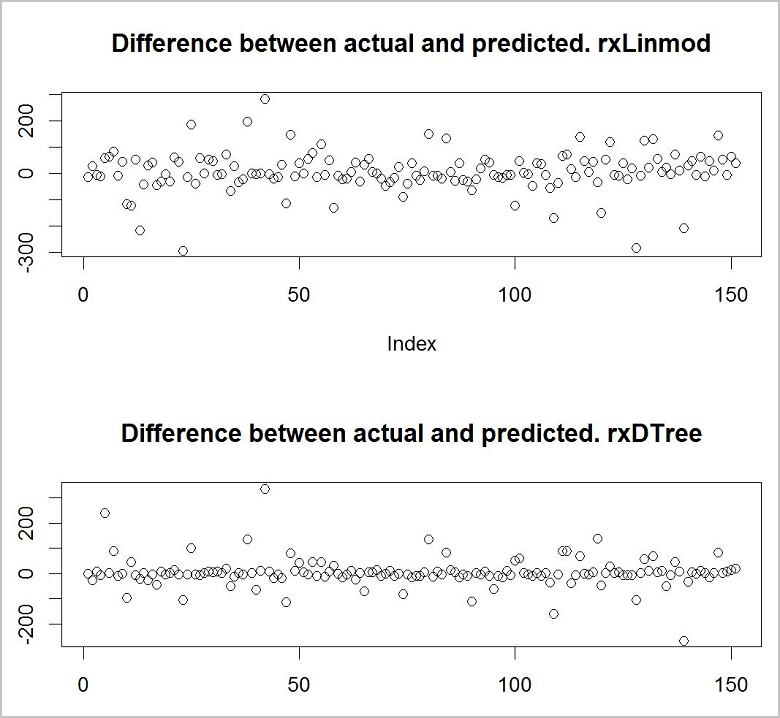
의사 결정 트리 모델이 두 모델 중에서 좀 더 정확한 것 같습니다.
리소스 정리
이 자습서를 계속 진행하지 않으려면 TutorialDB 데이터베이스를 삭제합니다.
다음 단계
이 자습서 시리즈의 3부에서는 다음 작업을 수행하는 방법을 알아보았습니다.
- 두 가지 기계 학습 모델 학습
- 두 모델에서 예측 수행
- 결과를 비교하여 가장 정확한 모델 선택
만든 기계 학습 모델을 배포하려면 다음 자습서 시리즈의 4부를 따르세요.