Differences between Office Scripts and Office Add-ins
Understand the differences between Office Scripts and Office Add-ins to know when to use each one. Office Scripts are designed to be quickly made by anyone looking to improve their workflow. Office Add-ins integrate with the Office UI for a more interactive experience through ribbon buttons and task panes. Office Add-ins can also expand built-in Excel functions by providing custom functions.
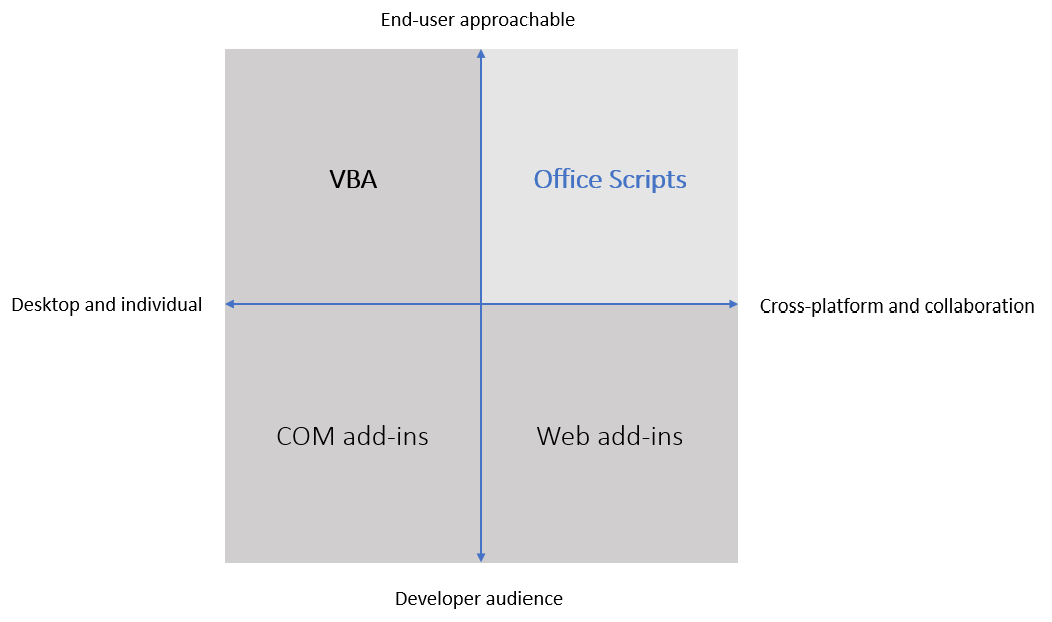
Office Scripts run to completion with a manual button selection or as a step in Power Automate, whereas Office Add-ins continue running depending on how they are configured. For example, you can configure an Office Add-in to continue running even when its task pane is closed. This means that Office Add-ins maintain state during a session, whereas Office Scripts don't maintain an internal state between runs. If the solution you're building requires a maintained state, you should visit the Office Add-ins documentation to learn more about Office Add-ins.
The rest of this article describes on the main differences between Office Add-ins and Office Scripts.
Platform support
The following table shows which features are supported by which platforms and products.
| Excel on the web | Excel for Windows | Excel for Mac | Excel for iOS | Other Office products | Power Automate | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Office Scripts | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| Office Scripts Action Recorder | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | No |
| VBA macros | No | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Office Add-ins | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| COM Add-ins | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
APIs
While the Office JavaScript APIs for Office Add-ins and the Office Scripts APIs share some functionality, they are different platforms. The Office Scripts APIs are an optimized, synchronous subset of the Excel JavaScript API model. The major difference is usage of the load/sync paradigm with add-ins. Additionally, add-ins offer APIs for events and a broader set of functionality outside of Excel, known as the Common APIs.
Office Add-ins offer greater connectivity to external web services and libraries. Office Scripts are limited to specific external calls.
Events
Office Scripts do not support workbook-level events. Scripts are either triggered by users selecting the Run button for a script or through Power Automate. Every script runs the code in a single main function, then ends.
UX and UI controls
Office Scripts can only interact with the workbook, not the task pane. If you need authentication, dialog windows, or additional UX and UI controls, you'll need to create an Office Add-in instead of an Office Script.
See also
Office Scripts