Deploy Teams app to container service
You can deploy a Teams bot or tab app to an Azure Container Apps, Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), or on-premises Kubernetes Cluster.
Prerequisites
Download the sample Teams bot or the sample Teams tab app, which offers a ready-to-use experience for Azure Container Apps development. You can make a few configuration changes and deploy it to AKS or an on-premises Kubernetes Cluster.
Before you get started, ensure that you have the following tools:
Azure account.
Azure Command Line Interfaces (CLI) for Azure Container Apps or AKS deployment.
Note
The commands in the article are based on Git Bash. If you're using any other interface, update the commands as required.
Deploy to Azure Container Apps
Azure Container Apps is a fully managed service that enables you to run containerized applications in the cloud. It's an ideal choice if you don't need direct access to all native Kubernetes APIs and cluster management and you prefer a fully managed experience grounded on best practices.
With the help of sample applications, you can run the provision and deploy commands in Teams Toolkit. Teams Toolkit creates an Azure Container Registry and Azure Container Apps for you and constructs your app into a container image and deploys it to Azure Container Apps.
The provision command creates and configures the following resources:
- A Teams app with tab or bot capability.
- An Azure Container Registry to host your container image.
- An Azure Container App environment and an Azure Container Apps to host your app.
- A Microsoft Entra App for authentication.
In the sample Teams bot, the provision command also creates an Azure Bot Service to channel Teams client and Azure Container Apps.
The deploy command executes the following actions:
- Builds the app into a container image.
- Pushes the container image to Azure Container Registry.
- Deploys the image to Azure Container Apps.
Deploy Teams bot to Azure Kubernetes Service
AKS is a managed container orchestration service provided by Azure. With AKS, you can fully manage Kubernetes experience within Azure.
Architecture
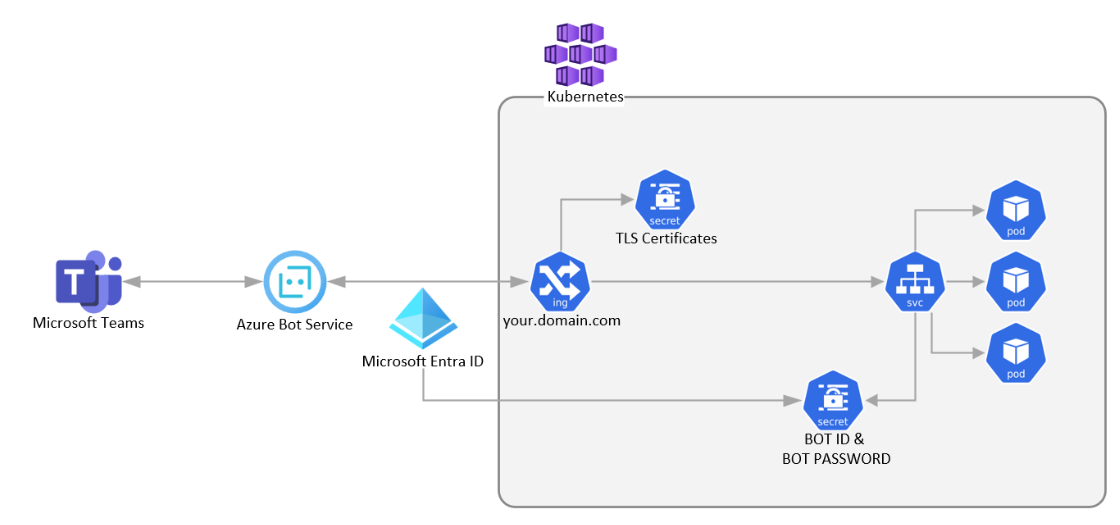
The Teams backend server interacts with your bot through the Azure Bot Service. This service requires your bot to be reachable through a public HTTPS endpoint. To set up, deploy an ingress controller on your Kubernetes cluster and secure it with a TLS certificate.
You can use Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate your bot with Azure Bot Service. Create a Kubernetes secret that includes the app ID and password and integrate the secret into your container's runtime configuration.
Setup ingress with HTTPS on AKS
Ensure that your AKS is connected to your Azure Container Registry, which hosts your container images. For more information, see use the Azure CLI.
Run the following command to install the ingress controller and certificate manager:
NAMESPACE=teams-bot helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx helm repo update helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --create-namespace --namespace $NAMESPACE \ --set controller.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \ --set defaultBackend.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \ --set controller.healthStatus=true \ --set controller.service.externalTrafficPolicy=Local \ --set controller.service.annotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/azure-load-balancer-health-probe-request-path"=/healthz helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io helm repo update helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --namespace $NAMESPACE --set installCRDs=true --set nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linuxNote
You can also follow the instructions available in create an unmanaged ingress controller and use TLS with Let's encrypt certificates to set up ingress and TLS certificates on your Kubernetes cluster.
Run the following command to update the DNS for the ingress public IP and get the ingress endpoint:
> kubectl get services --namespace $NAMESPACE -w ingress-nginx-controller NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer $CLUSTER_IP $EXTERNAL_IP 80:32514/TCP,443:32226/TCP > PUBLICIPID=$(az network public-ip list --query "[?ipAddress!=null]|[?contains(ipAddress, '$EXTERNAL_IP')].[id]" --output tsv) > az network public-ip update --ids $PUBLICIPID --dns-name $DNSLABEL > az network public-ip show --ids $PUBLICIPID --query "[dnsSettings.fqdn]" --output tsv $DNSLABEL.$REGION.cloudapp.azure.com
Provision resources with Teams Toolkit
You can use the provision command in Teams Toolkit to create a Teams app with bot capability, incorporate the Azure Bot Service, and add the Microsoft Entra ID for authentication.
To provision resources with Teams Toolkit, follow these steps:
Open the sample app that you've downloaded earlier.
Go to the
env/.env.${envName}file and update theBOT_DOMAINvalue with your FQDN.Go to the
teamsapp.ymlfile and update the followingarm/deployaction to ensure that Teams Toolkit provisions an Azure Bot Service during the execution of theprovisioncommand:- uses: arm/deploy with: subscriptionId: ${{AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}} resourceGroupName: ${{AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME}} templates: - path: ./infra/botRegistration/azurebot.bicep parameters: ./infra/botRegistration/azurebot.parameters.json deploymentName: Create-resources-for-bot bicepCliVersion: v0.9.1Run the
provisioncommand in Teams Toolkit.After provisioning, locate the
BOT_IDinenv/.env.${envName}file and the encryptedSECRET_BOT_PASSWORDinenv/.env.${envName}.userfile. To obtain the actual value ofBOT_PASSWORD. Select the Decrypt secret annotation.To create a Kubernetes secret that contains
BOT_IDandBOT_PASSWORD, save the key value pair in the./deploy/.env.dev-secretsfile and execute the following command to provision the secret:kubectl create secret generic dev-secrets --from-env-file ./deploy/.env.dev-secrets -n $NAMESPACE
Apply the deployment
The sample includes a deployment file, deploy/sso-bot.yaml, for your reference.
Update the following placeholders:
<image>: Update your image. For example,myacr.azurecr.io/sso-bot:latest.<hostname>: Update your ingress FQDN.
To apply
deploy/tab.yaml, run the following command:kubectl apply -f deploy/sso-bot.yaml -n $NAMESPACEGo to Visual Studio Code.
In the Run and Debug panel, select the Launch Remote configuration.
To preview the Teams bot application deployed on AKS, select Start Debugging (F5).
Deploy Teams bot to an on-premises Kubernetes Cluster
You can deploy a Teams bot to your personal Kubernetes cluster or a Kubernetes service from different cloud services by following similar steps that are used to deploy Teams bot on AKS.
Architecture
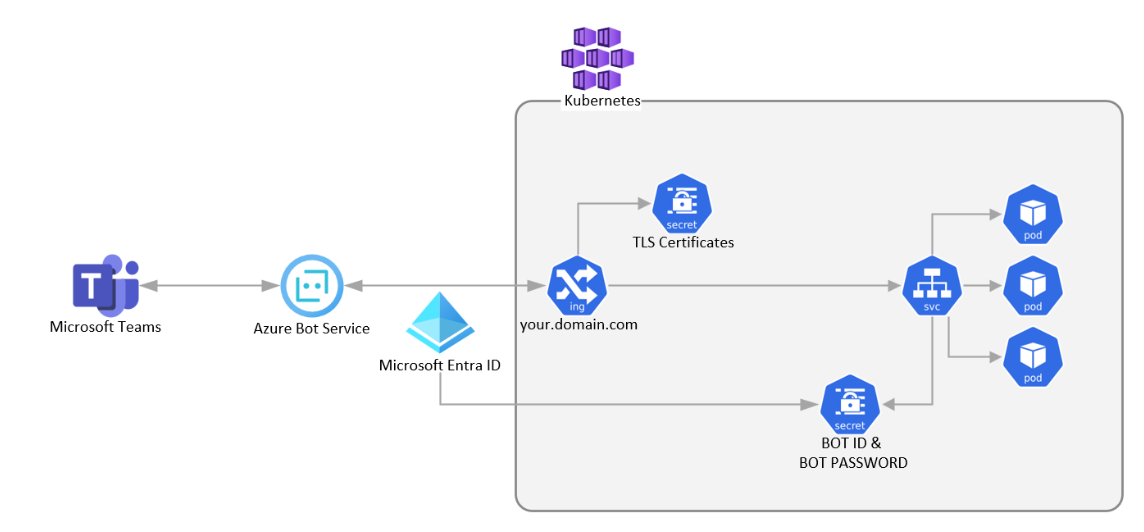
The Teams backend server interacts with your bot through the Azure Bot Service. This service requires your bot to be reachable through a public HTTPS endpoint. To set up, deploy an ingress controller on your Kubernetes cluster and secure it with a TLS certificate.
You can use Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate your bot with Azure Bot Service. Create a Kubernetes secret that includes the app ID and password and integrate the secret into your container's runtime configuration.
Provision resources with Teams Toolkit
You can use the provision command in Teams Toolkit to create a Teams app with bot capability, incorporate the Azure Bot Service, and add the Microsoft Entra ID for authentication.
To provision resources with Teams Toolkit, follow these steps:
Open the sample app that you've downloaded earlier.
Go to the
env/.env.${envName}file and update theBOT_DOMAINvalue with your FQDN.Go to the
teamsapp.ymlfile and update the followingarm/deployaction to ensure that Teams Toolkit provisions an Azure Bot Service during the execution of theprovisioncommand:- uses: arm/deploy with: subscriptionId: ${{AZURE_SUBSCRIPTION_ID}} resourceGroupName: ${{AZURE_RESOURCE_GROUP_NAME}} templates: - path: ./infra/botRegistration/azurebot.bicep parameters: ./infra/botRegistration/azurebot.parameters.json deploymentName: Create-resources-for-bot bicepCliVersion: v0.9.1In the
teamsapp.ymlfile, update thebotFramework/createaction during the provision stage. This action enables Teams Toolkit to create a bot registration with the appropriate messaging endpoint.Note
We recommend you use Azure Bot Service for channeling. If you don't have an Azure account and can't create Azure Bot Service, you can create a bot registration.
- uses: botFramework/create with: botId: ${{BOT_ID}} name: <Bot display name> messagingEndpoint: https://${{BOT_DOMAIN}}/api/messages description: "" channels: - name: msteamsYou can remove the
arm/deployaction inteamsapp.ymlfile, as we don't need any Azure resources.Run the
provisioncommand in Teams Toolkit.After provisioning, locate the
BOT_IDin theenv/.env.${envName}file and the encryptedSECRET_BOT_PASSWORDin theenv/.env.${envName}.userfile. To obtain the actual value ofBOT_PASSWORD. Select the Decrypt secret annotation.To create a Kubernetes secret that contains
BOT_IDandBOT_PASSWORD, save the key value pair in the./deploy/.env.dev-secretsfile and execute the following command to provision the secret:kubectl create secret generic dev-secrets --from-env-file ./deploy/.env.dev-secrets -n $NAMESPACE
Apply the deployment
The sample includes a deployment file, deploy/sso-bot.yaml, for your guidance.
Update the following placeholders:
<image>: Update your image. For example,myacr.azurecr.io/sso-bot:latest.<hostname>: Update your ingress FQDN.
To apply
deploy/tab.yaml, run the following command:kubectl apply -f deploy/sso-bot.yaml -n $NAMESPACEGo to Visual Studio Code.
In the Run and Debug panel, select the Launch Remote configuration.
To preview the Teams bot application deployed on AKS, select Start Debugging (F5).
Deploy Teams tab app to Kubernetes
AKS serves as a managed container orchestration service offered by Azure. With AKS, you can fully manage Kubernetes experience within Azure.
Deploy a Teams tab app to AKS is similar to deploying a web app to AKS. However, since a Teams tab app requires an HTTPS connection, you need to own a domain and setup TLS ingress in your AKS.
You can also deploy a Teams tab app to your personal Kubernetes cluster or a Kubernetes service on different cloud platforms. This involves steps similar to those used when deploying on Azure Kubernetes Service.
Setup ingress with HTTPS on AKS
Ensure that your AKS is already connected to your Azure Container Registry, which hosts your container images. For more information, see Azure CLI.
Run the following command to install the ingress controller and certificate manager:
NAMESPACE=teams-tab helm repo add ingress-nginx https://kubernetes.github.io/ingress-nginx helm repo update helm install ingress-nginx ingress-nginx/ingress-nginx --create-namespace --namespace $NAMESPACE \ --set controller.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \ --set defaultBackend.nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linux \ --set controller.healthStatus=true \ --set controller.service.externalTrafficPolicy=Local \ --set controller.service.annotations."service\.beta\.kubernetes\.io/azure-load-balancer-health-probe-request-path"=/healthz helm repo add jetstack https://charts.jetstack.io helm repo update helm install cert-manager jetstack/cert-manager --namespace $NAMESPACE --set installCRDs=true --set nodeSelector."kubernetes\.io/os"=linuxNote
You can also follow the instructions available in create an unmanaged ingress controller and use TLS with Let's encrypt certificates to set up ingress and TLS certificates on your Kubernetes cluster.
Run the following command to update the DNS for the ingress public IP and get the ingress endpoint:
> kubectl get services --namespace $NAMESPACE -w ingress-nginx-controller NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer $CLUSTER_IP $EXTERNAL_IP 80:32514/TCP,443:32226/TCP > PUBLICIPID=$(az network public-ip list --query "[?ipAddress!=null]|[?contains(ipAddress, '$EXTERNAL_IP')].[id]" --output tsv) > az network public-ip update --ids $PUBLICIPID --dns-name $DNSLABEL > az network public-ip show --ids $PUBLICIPID --query "[dnsSettings.fqdn]" --output tsv $DNSLABEL.$REGION.cloudapp.azure.com
Provision resources with Teams Toolkit
You can use the provision command in Teams Toolkit to create a Teams app with tab capability, incorporate the Azure Bot Service, and add the Microsoft Entra ID for authentication.
To provision resources with Teams Toolkit, follow these steps:
Open the sample app that you've downloaded earlier.
Go to the
env/.env.${envName}file and update theTAB_DOMAINvalue with your FQDN.Go to the
teamsapp.ymlfile and remove thearm/deployaction, as no additional Azure resources are required.Run the
provisioncommand in Teams Toolkit.Use the Teams Toolkit to create a Microsoft Entra ID, which you might want to set as your apps environment variables.
After provisioning, locate the
AAD_APP_CLIENT_IDin theenv/.env.${envName}file and the encryptedSECRET_AAD_APP_CLIENT_SECRETin theenv/.env.${envName}.userfile.To obtain the actual value of
SECRET_AAD_APP_CLIENT_SECRET. Select the Decrypt secret annotation.
Apply the deployment
The sample includes a deployment file, deploy/tab.yaml, for your reference.
Update the following placeholders:
<tab-image>: Update your image. For example,myacr.azurecr.io/tab:latest.<api-image>: Update your API image. If you don't have an API, remove thehello-world-apiservice and deploy from the yaml file.<hostname>: Update your ingress FQDN.
To apply
deploy/tab.yaml, run the following command:kubectl apply -f deploy/tab.yaml -n $NAMESPACEGo to Visual Studio Code.
In the Run and Debug panel, select the Launch Remote configuration.
To preview the Teams bot application deployed on AKS, select Start Debugging (F5).
Platform Docs