Your extensibility options for Microsoft 365 Copilot
Microsoft 365 Copilot is an AI-powered productivity tool that keeps users in the flow of their work across Microsoft 365 applications like Outlook, Teams, and Word, grounded in data from Microsoft Graph. Although Copilot offers powerful capabilities, users might need to integrate additional knowledge, data sources, or applications into Copilot to meet specific business needs.
Agents for Microsoft 365 Copilot are specialized assistants focused on a specific subject, powered by organizational knowledge and actions to automate business processes. You can build two types of agents for Copilot: declarative agents and custom engine agents. This article describes the two types of agents how to choose the right one for your scenario.
Microsoft Graph connectors enable organizations to bring in external data, allowing Copilot and agents to access and reason over a broader range of enterprise content.
Types of agents you can build
You can choose to extend Copilot by building one of the following types of agents:
- Declarative agents allow you to configure Copilot for specific scenarios with custom instructions, additional knowledge, and actions to automate business processes.
- Custom engine agents are ideal for advanced scenarios that require complex workflows, advanced orchestration, or specialized language models.
Declarative agents
Declarative agents enable you to configure Copilot for specific scenarios by adding custom instructions, additional knowledge, and actions to automate business processes. Because declarative agents use Copilot's AI infrastructure, model, and orchestrator, they adhere to the security, compliance, and responsible AI (RAI) requirements for Microsoft 365.
To configure a declarative agent, you provide:
- Custom instructions to shape Copilot's responses to your organization's specific needs or workflow.
- Custom knowledge to connect Microsoft 365 data sources (such as SharePoint and OneDrive) or external data via Microsoft Graph connectors.
- Custom actions to integrate with APIs to interact with external systems in real time.
Declarative agents have the following characteristics:
- Hosting: Use Copilot's orchestrator and foundation model. No additional hosting is required.
- Tooling: Can be created using low-code tools such as Copilot Studio and pro-code tools like Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, and Teams Toolkit.
- Publishing channels: Can be used in Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 apps like Teams, Word, Excel, and Outlook.
Custom engine agents
Custom engine agents are fully customized AI assistants. They're useful for scenarios that require complex workflows, orchestration, or specific language models. Building a custom engine agent might require you to provide additional hosting for models and orchestrators and to ensure that your custom agent is compliant, secure, and adheres to responsible AI (RAI) policies.
To develop a custom engine agent, you need:
- Custom orchestration to take full control of workflows and integrate additional knowledge and external API calls. You can incorporate one or more language models to enhance functionality.
- Custom models to choose the most suitable model for your use case, whether foundation large language, small language, fine-tuned, or industry-specific models.
- Proactive agentic support to programmatically initiate workflows and actions.
Custom engine agents have the following characteristics:
- Hosting: Requires additional hosting outside of Microsoft 365, typically with cloud services such as Azure or Copilot Studio, at an additional cost.
- Tooling: Orchestration can be built using low-code Copilot Studio or pro-code tools like Visual Studio, Visual Studio Code, and Teams Toolkit, using languages such as .NET, Python, and JavaScript, and frameworks like Semantic Kernel or LangChain.
- Publishing channels: Can be used in Microsoft 365 Copilot and Microsoft 365 apps like Teams, Word, Excel, and Outlook, as well as external apps and websites.
Agent feature comparison
The following table summarizes the key differences between declarative agents and custom engine agents to help you choose the right option for your use case.
| Feature | Declarative agents | Custom engine agents |
|---|---|---|
| Use case | Use Microsoft 365 Copilot for task-specific scenarios. | Use complex workflows or custom AI systems. |
| Customization | Limited to Copilot's models and actions. | Fully customizable, including choice of AI models and orchestration. |
| Proactive interactions | Not supported; rely on user-initiated interactions. | Enable agents to trigger actions automatically, even without direct user input. |
| Channels | Integrated into Microsoft 365 apps. | Available for Microsoft 365 and external apps. |
| Setup complexity | Can be developed with low-code tools (Copilot Studio) and pro-code tools (Visual Studio Code/Teams Toolkit) | Varies from simple setups in Copilot Studio to advanced pro-code implementations using Visual Studio and Visual Studio Code. |
| Engine hosting | Hosted in Microsoft 365. | Hosted in Microsoft 365 with Copilot Studio or externally with custom solutions such as Azure AI. |
Choose what type of agent to build
This section describes the features and scenarios for declarative and custom engine agents to help you decide which type of agent to build.
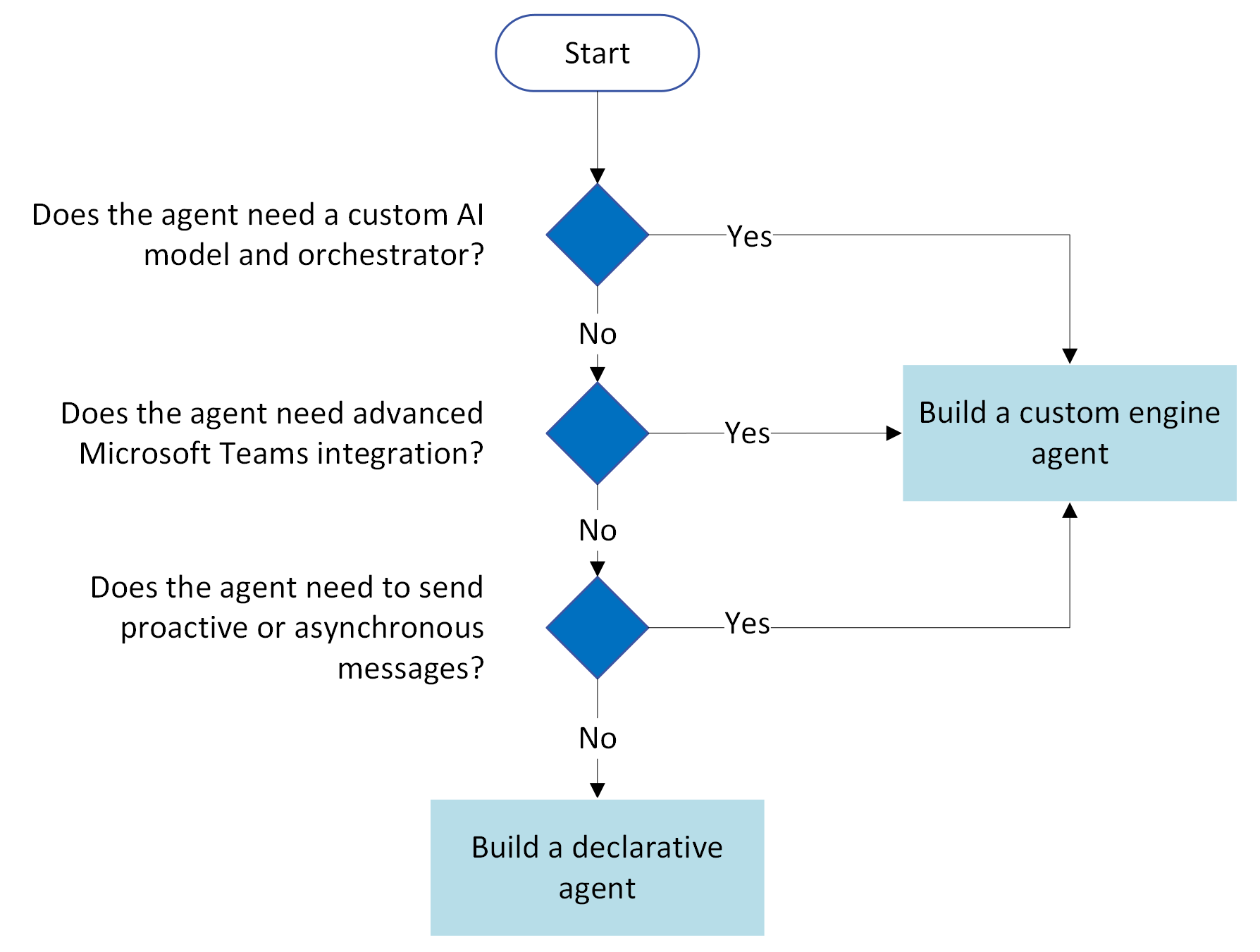
The following flow chart summarizes the decision process for choosing what type of agent to build.
Build a declarative agent when:
- You want your agent to work within Copilot's orchestration and language models to ensure consistency with security and compliance.
- You want a faster implementation or want to develop an agent with no or low-code.
- Your user's workflow is within Microsoft 365 apps (SharePoint, OneDrive, Teams) and they want to work within the context of these applications (via @mentions or in Teams business chats).
Build a custom engine agent when:
- You've built an existing conversational assistant outside of Copilot and want to integrate it with Microsoft 365 and Copilot.
- You want to use your own AI models or your agent might benefit from domain-specific models with specialized knowledge or multimodal models.
- You want advanced Teams integrations (such as with meetings and channels).
- You want to make your agent available outside of Microsoft 365 and Copilot.
- You want to support proactive messaging, which enables developers to define workflows and trigger agent behavior without the need for user interaction.
- You need multiple system integration, such as managing logistics by integrating data from GPS, warehouse systems, and customer databases.
- You need to implement custom business logic (such as specific rules for patient triage in a healthcare setting based on symptoms and medical history).
- You have complex decision-making (for example, evaluating loan applications based on multiple factors like credit score, income, and employment history).