박싱과 언박싱 (C# 프로그래밍 가이드)
Boxing은 값 형식 형식 object 또는 이 값 형식으로 구현된 인터페이스 형식으로 변환하는 프로세스입니다. CLR(공용 언어 런타임)이 값 형식을 상자에 넣으면 System.Object 인스턴스 내에 값을 래핑하고 관리되는 힙에 저장합니다. Unboxing은 개체에서 값 형식을 추출합니다. Boxing은 암시적입니다. unboxing은 명시적입니다. boxing 및 unboxing의 개념은 모든 형식의 값을 개체로 처리할 수 있는 형식 시스템의 C# 통합 뷰를 기초로 합니다.
다음 예제에서 정수 변수 i가 박싱되어 객체 o에 할당됩니다.
int i = 123;
// The following line boxes i.
object o = i;
그런 다음, o 개체를 unboxed하고 i정수 변수에 할당할 수 있습니다.
o = 123;
i = (int)o; // unboxing
다음 예제에서는 C#에서 boxing을 사용하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
// String.Concat example.
// String.Concat has many versions. Rest the mouse pointer on
// Concat in the following statement to verify that the version
// that is used here takes three object arguments. Both 42 and
// true must be boxed.
Console.WriteLine(String.Concat("Answer", 42, true));
// List example.
// Create a list of objects to hold a heterogeneous collection
// of elements.
List<object> mixedList = new List<object>();
// Add a string element to the list.
mixedList.Add("First Group:");
// Add some integers to the list.
for (int j = 1; j < 5; j++)
{
// Rest the mouse pointer over j to verify that you are adding
// an int to a list of objects. Each element j is boxed when
// you add j to mixedList.
mixedList.Add(j);
}
// Add another string and more integers.
mixedList.Add("Second Group:");
for (int j = 5; j < 10; j++)
{
mixedList.Add(j);
}
// Display the elements in the list. Declare the loop variable by
// using var, so that the compiler assigns its type.
foreach (var item in mixedList)
{
// Rest the mouse pointer over item to verify that the elements
// of mixedList are objects.
Console.WriteLine(item);
}
// The following loop sums the squares of the first group of boxed
// integers in mixedList. The list elements are objects, and cannot
// be multiplied or added to the sum until they are unboxed. The
// unboxing must be done explicitly.
var sum = 0;
for (var j = 1; j < 5; j++)
{
// The following statement causes a compiler error: Operator
// '*' cannot be applied to operands of type 'object' and
// 'object'.
//sum += mixedList[j] * mixedList[j];
// After the list elements are unboxed, the computation does
// not cause a compiler error.
sum += (int)mixedList[j] * (int)mixedList[j];
}
// The sum displayed is 30, the sum of 1 + 4 + 9 + 16.
Console.WriteLine("Sum: " + sum);
// Output:
// Answer42True
// First Group:
// 1
// 2
// 3
// 4
// Second Group:
// 5
// 6
// 7
// 8
// 9
// Sum: 30
성능
단순 할당과 관련하여 "boxing" 및 "unboxing"은 계산 비용이 많이 소요되는 프로세스입니다. 값 형식이 boxed이면 새 개체를 할당하고 생성해야 합니다. 어느 정도 덜하지만, 언박싱에 필요한 캐스트도 계산 자원이 많이 소모됩니다. 자세한 내용은 성능을 참조하세요.
권투
Boxing은 가비지 수집 힙에 값 형식을 저장하는 데 사용됩니다. Boxing은 값 형식을 형식 object 또는 해당 값 형식이 구현한 인터페이스 형식으로 암시적으로 변환하는 것입니다. 값 형식을 'Boxing' 하면 힙에 개체 인스턴스가 할당되고, 값이 새로운 개체에 복사됩니다.
값 형식 변수의 다음 선언을 고려합니다.
int i = 123;
다음 문은 변수 i에 박싱 연산을 암시적으로 적용합니다.
// Boxing copies the value of i into object o.
object o = i;
이 문장은 스택에서 개체 참조 o을 생성하여, 힙에 있는 int형의 값을 참조합니다. 이 값은 변수 i할당된 값 형식 값의 복사본입니다. 두 변수(i 및 o)의 차이는 다음 boxing 변환 이미지에 설명되어 있습니다.
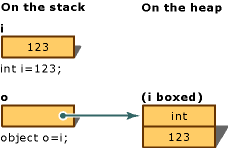
다음 예제처럼 명시적으로 박싱을 수행할 수도 있지만, 명시적으로 할 필요는 없습니다.
int i = 123;
object o = (object)i; // explicit boxing
예시
다음은 boxing을 사용하여 정수 변수 i 개체 o 변환하는 예제입니다. 그런 다음 변수 i에 저장된 값이 123에서 456로 변경됩니다. 이 예제에서는 원래 값 형식과 boxed 개체가 별도의 메모리 위치를 사용하므로 다른 값을 저장할 수 있음을 보여 있습니다.
// Create an int variable
int i = 123;
// Box the value type into an object reference
object o = i; // boxing
// Display the initial values
Console.WriteLine($"Value of i: {i}");
Console.WriteLine($"Value of boxed object o: {o}");
// Modify the original value type
i = 456;
// Display the values after modification
Console.WriteLine("\nAfter changing i to 456:");
Console.WriteLine($"Value of i: {i}");
Console.WriteLine($"Value of boxed object o: {o}");
// Output:
// Value of i: 123
// Value of boxed object o: 123
// After changing i to 456:
// Value of i: 456
// Value of boxed object o: 123
제품 개봉
Unboxing은 형식 object에서 값 형식로 또는 인터페이스 형식에서 인터페이스를 구현하는 값 형식으로의 명시적 변환입니다. unboxing 작업은 다음으로 구성됩니다.
주어진 값 형식의 boxed 값인지 확인하기 위해 개체 인스턴스를 검사합니다.
인스턴스의 값을 값 형식 변수로 복사합니다.
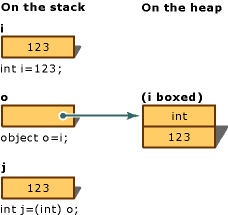
다음 문장은 박싱 및 언박싱 작업을 모두 보여 줍니다.
int i = 123; // a value type
object o = i; // boxing
int j = (int)o; // unboxing
다음 그림에서는 이전 문의 결과를 보여 줍니다.
런타임에 값 형식을 성공적으로 해제하려면, 해제되는 항목은 해당 값 형식의 인스턴스를 박싱하여 이전에 생성된 객체에 대한 참조여야 합니다.
null을(를) 언박싱을 시도하면 NullReferenceException이(가) 발생합니다. 호환되지 않는 값 형식에 대한 참조를 언박싱하려고 하면 InvalidCastException오류가 발생합니다.
예시
다음 예제에서는 잘못된 언박싱(unboxing) 및 그로 인해 발생하는 InvalidCastException결과를 보여 줍니다.
try 및 catch사용하면 오류가 발생할 때 오류 메시지가 표시됩니다.
class TestUnboxing
{
static void Main()
{
int i = 123;
object o = i; // implicit boxing
try
{
int j = (short)o; // attempt to unbox
System.Console.WriteLine("Unboxing OK.");
}
catch (System.InvalidCastException e)
{
System.Console.WriteLine($"{e.Message} Error: Incorrect unboxing.");
}
}
}
이 프로그램은 다음을 출력합니다.
Specified cast is not valid. Error: Incorrect unboxing.
문장을 변경하는 경우:
int j = (short)o;
다음과 같이 변경합니다.
int j = (int)o;
변환이 수행되고 출력이 표시됩니다.
Unboxing OK.
C# 언어 사양
자세한 내용은 C# 언어 사양참조하세요. 언어 사양은 C# 구문 및 사용의 최종 소스입니다.
참고하십시오
.NET
