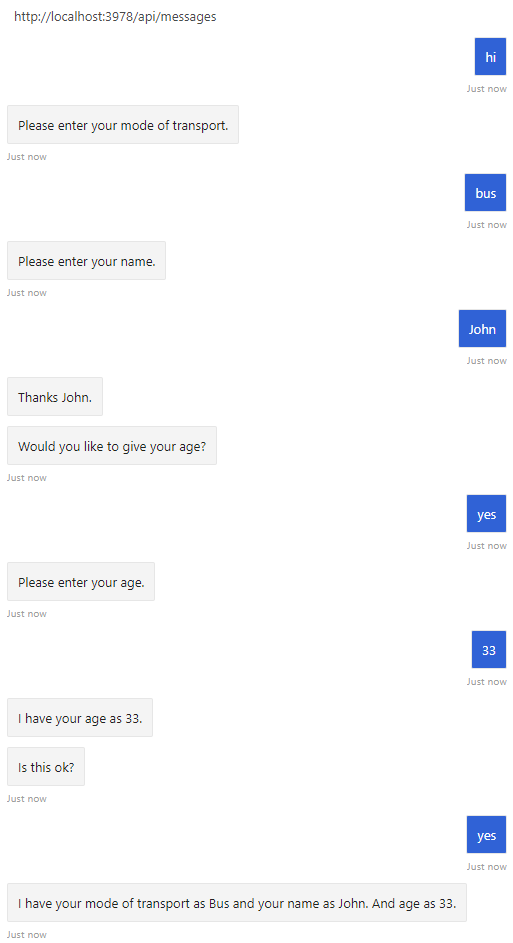
질문을 제기하여 정보를 수집하는 것은 봇이 사용자와 상호 작용하는 주요 방법 중 하나입니다. 대화 상자 라이브러리는 쉽게 질문하고 응답의 유효성을 검사하여 특정 데이터 형식과 일치하거나 사용자 지정 유효성 검사 규칙을 충족하는지 확인할 수 있는 ‘프롬프트’ 클래스 등의 유용한 기본 제공 기능을 제공합니다.
대화 상자 라이브러리를 사용하여 선형 및 더 복잡한 대화 흐름을 관리할 수 있습니다. 선형 상호 작용에서 봇은 고정된 단계 시퀀스를 통해 실행되고 대화가 완료됩니다. 대화 상자는 봇이 사용자로부터 정보를 수집해야 하는 경우에 유용합니다.
이 문서에서는 프롬프트를 만들고 폭포 대화 상자에서 호출하여 선형 대화 흐름을 구현하는 방법을 보여 줍니다.
대화 상자 라이브러리를 사용하지 않고 사용자 고유의 프롬프트를 작성하는 방법에 대한 예제는 사용자 입력 문서를 수집하기 위한 사용자 고유의 프롬프트 만들기를 참조하세요.
다중 턴 프롬프트 샘플은 폭포 대화 상자, 몇 가지 프롬프트 및 구성 요소 대화 상자를 사용하여 사용자에게 일련의 질문을 하는 선형 상호 작용을 만듭니다. 코드는 대화 상자를 사용하여 다음 단계를 순환합니다.
마지막으로, '예'라고 대답하면 수집된 정보를 표시합니다. 그렇지 않으면 사용자에게 해당 정보가 유지되지 않는다고 알릴 수 있습니다.
대화를 사용하려면 Microsoft.Bot.Builder.Dialogs NuGet 패키지를 설치합니다.
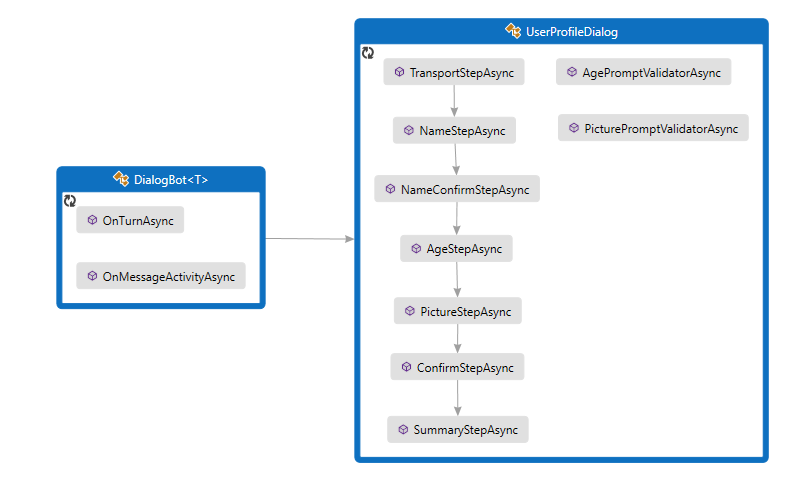
봇은 .를 통해 UserProfileDialog사용자와 상호 작용합니다. 봇의 DialogBot 클래스를 만들 때 기본 UserProfileDialog 대화 상자로 설정됩니다. 그런 다음, 봇은 Run 도우미 메서드를 사용하여 대화 상자에 액세스합니다.
Dialogs\UserProfileDialog.cs
먼저 클래스에서 파생되는 7단계를 ComponentDialog 만듭니 UserProfileDialog 다.
UserProfileDialog 생성자에서 폭포 단계, 프롬프트 및 폭포 대화 상자를 만들고 대화 집합에 추가합니다. 프롬프트는 사용되는 것과 동일한 대화 상자 집합에 있어야 합니다.
public UserProfileDialog(UserState userState)
: base(nameof(UserProfileDialog))
{
_userProfileAccessor = userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>("UserProfile");
// This array defines how the Waterfall will execute.
var waterfallSteps = new WaterfallStep[]
{
TransportStepAsync,
NameStepAsync,
NameConfirmStepAsync,
AgeStepAsync,
PictureStepAsync,
SummaryStepAsync,
ConfirmStepAsync,
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
AddDialog(new WaterfallDialog(nameof(WaterfallDialog), waterfallSteps));
AddDialog(new TextPrompt(nameof(TextPrompt)));
AddDialog(new NumberPrompt<int>(nameof(NumberPrompt<int>), AgePromptValidatorAsync));
AddDialog(new ChoicePrompt(nameof(ChoicePrompt)));
AddDialog(new ConfirmPrompt(nameof(ConfirmPrompt)));
AddDialog(new AttachmentPrompt(nameof(AttachmentPrompt), PicturePromptValidatorAsync));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
InitialDialogId = nameof(WaterfallDialog);
}
다음으로, 대화 상자에서 입력을 요청하는 데 사용하는 단계를 추가합니다. 프롬프트를 사용하려면 대화의 단계에서 호출하고 다음 단계에서 stepContext.Result를 사용하여 프롬프트 결과를 검색합니다. 백그라운드에서 프롬프트는 2단계 대화 상자입니다. 먼저 프롬프트에서 입력을 요청합니다. 그런 다음 유효한 값을 반환하거나 처음부터 다시 시작하여 유효한 입력을 받을 때까지 다시 시작합니다.
항상 폭포 단계에서 null DialogTurnResult 이 아닌 값을 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 대화 상자가 설계된 대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다. 아래는 폭포 대화 상자의 구현 NameStepAsync 입니다.
private static async Task<DialogTurnResult> NameStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
stepContext.Values["transport"] = ((FoundChoice)stepContext.Result).Value;
return await stepContext.PromptAsync(nameof(TextPrompt), new PromptOptions { Prompt = MessageFactory.Text("Please enter your name.") }, cancellationToken);
}
에서 AgeStepAsync프롬프트가 구문 분석할 수 없는 형식이거나 입력이 유효성 검사 조건에 실패하기 때문에 사용자 입력의 유효성을 검사하지 못하는 경우에 대한 재시도 프롬프트를 지정합니다. 이 경우 다시 시도 프롬프트가 제공되지 않은 경우 프롬프트는 초기 프롬프트 텍스트를 사용하여 사용자에게 입력을 다시 표시합니다.
private async Task<DialogTurnResult> AgeStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if ((bool)stepContext.Result)
{
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
var promptOptions = new PromptOptions
{
Prompt = MessageFactory.Text("Please enter your age."),
RetryPrompt = MessageFactory.Text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."),
};
return await stepContext.PromptAsync(nameof(NumberPrompt<int>), promptOptions, cancellationToken);
}
else
{
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await stepContext.NextAsync(-1, cancellationToken);
}
}
UserProfile.cs
사용자의 교통 수단, 이름 및 나이가 UserProfile 클래스의 인스턴스에 저장됩니다.
public class UserProfile
{
public string Transport { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public Attachment Picture { get; set; }
}
Dialogs\UserProfileDialog.cs
마지막 단계에서는 이전 폭포 단계에서 호출된 대화 상자에서 반환된 항목을 확인 stepContext.Result 합니다. 반환 값이 true이면 사용자 프로필 접근자가 사용자 프로필을 가져오고 업데이트합니다. 사용자 프로필을 얻으려면 호출 GetAsync 한 다음 , userProfile.NameuserProfile.Age 및 userProfile.Picture 속성의 userProfile.Transport값을 설정합니다. 마지막으로, 대화 상자를 종료하는 호출 EndDialogAsync하기 전에 사용자의 정보를 요약합니다. 대화 상자를 종료하면 대화 상자 스택에서 팝업되고 선택적 결과가 대화의 부모에 반환됩니다. 부모는 대화 또는 방금 전에 종료된 대화를 시작한 메서드입니다.
else
{
msg += $" Your profile will not be kept.";
}
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text(msg), cancellationToken);
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is the end.
return await stepContext.EndDialogAsync(cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
private async Task<DialogTurnResult> SummaryStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
stepContext.Values["picture"] = ((IList<Attachment>)stepContext.Result)?.FirstOrDefault();
// Get the current profile object from user state.
var userProfile = await _userProfileAccessor.GetAsync(stepContext.Context, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
userProfile.Transport = (string)stepContext.Values["transport"];
userProfile.Name = (string)stepContext.Values["name"];
userProfile.Age = (int)stepContext.Values["age"];
userProfile.Picture = (Attachment)stepContext.Values["picture"];
var msg = $"I have your mode of transport as {userProfile.Transport} and your name as {userProfile.Name}";
if (userProfile.Age != -1)
{
msg += $" and your age as {userProfile.Age}";
}
msg += ".";
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text(msg), cancellationToken);
if (userProfile.Picture != null)
{
try
{
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Attachment(userProfile.Picture, "This is your profile picture."), cancellationToken);
}
catch
{
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text("A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."), cancellationToken);
대화 상자를 사용하려면 프로젝트에서 botbuilder-dialogs npm 패키지를 설치해야 합니다.
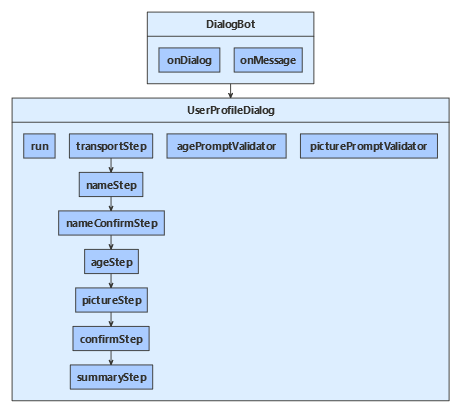
봇은 UserProfileDialog를 통해 사용자와 상호 작용합니다. 봇 DialogBot을 만들 때 기본 UserProfileDialog 대화 상자로 설정됩니다. 그런 다음, 봇은 run 도우미 메서드를 사용하여 대화 상자에 액세스합니다.
dialogs/userProfileDialog.js
먼저 클래스에서 파생되는 7단계를 ComponentDialog 만듭니 UserProfileDialog 다.
UserProfileDialog 생성자에서 폭포 단계, 프롬프트 및 폭포 대화 상자를 만들고 대화 집합에 추가합니다. 프롬프트는 사용되는 것과 동일한 대화 상자 집합에 있어야 합니다.
constructor(userState) {
super('userProfileDialog');
this.userProfile = userState.createProperty(USER_PROFILE);
this.addDialog(new TextPrompt(NAME_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new ChoicePrompt(CHOICE_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt(CONFIRM_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new NumberPrompt(NUMBER_PROMPT, this.agePromptValidator));
this.addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt(ATTACHMENT_PROMPT, this.picturePromptValidator));
this.addDialog(new WaterfallDialog(WATERFALL_DIALOG, [
this.transportStep.bind(this),
this.nameStep.bind(this),
this.nameConfirmStep.bind(this),
this.ageStep.bind(this),
this.pictureStep.bind(this),
this.summaryStep.bind(this),
this.confirmStep.bind(this)
]));
this.initialDialogId = WATERFALL_DIALOG;
}
다음으로, 대화 상자에서 입력을 요청하는 데 사용하는 단계를 추가합니다. 프롬프트를 사용하려면 대화 상자의 한 단계에서 프롬프트를 호출하고 단계 컨텍스트에서 다음 단계에서 프롬프트 결과를 검색합니다. 이 경우 step.result. 백그라운드에서 프롬프트는 2단계 대화 상자입니다. 먼저 프롬프트에서 입력을 요청합니다. 그런 다음 유효한 값을 반환하거나 처음부터 다시 시작하여 유효한 입력을 받을 때까지 다시 시작합니다.
항상 폭포 단계에서 null DialogTurnResult 이 아닌 값을 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 대화 상자가 설계된 대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다. 아래는 폭포 대화 상자의 nameStep 구현입니다.
async nameStep(step) {
step.values.transport = step.result.value;
return await step.prompt(NAME_PROMPT, 'Please enter your name.');
}
에서 ageStep프롬프트가 구문 분석할 수 없는 형식이거나 입력이 위의 생성자에 지정된 유효성 검사 조건에 실패하기 때문에 사용자의 입력 유효성 검사에 실패하는 경우에 대한 재시도 프롬프트를 지정합니다. 이 경우 다시 시도 프롬프트가 제공되지 않은 경우 프롬프트는 초기 프롬프트 텍스트를 사용하여 사용자에게 입력을 다시 표시합니다.
async ageStep(step) {
if (step.result) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
const promptOptions = { prompt: 'Please enter your age.', retryPrompt: 'The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150.' };
return await step.prompt(NUMBER_PROMPT, promptOptions);
} else {
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await step.next(-1);
}
}
userProfile.js
사용자의 교통 수단, 이름 및 나이가 UserProfile 클래스의 인스턴스에 저장됩니다.
class UserProfile {
constructor(transport, name, age, picture) {
this.transport = transport;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.picture = picture;
}
}
dialogs/userProfileDialog.js
마지막 단계에서는 이전 폭포 단계에서 호출된 대화 상자에서 반환된 항목을 확인 step.result 합니다. 반환 값이 true이면 사용자 프로필 접근자가 사용자 프로필을 가져오고 업데이트합니다. 사용자 프로필을 얻으려면 호출get한 다음 , userProfile.nameuserProfile.age 및 userProfile.picture 속성의 userProfile.transport값을 설정합니다. 마지막으로, 대화 상자를 종료하는 호출 endDialog하기 전에 사용자의 정보를 요약합니다. 대화 상자를 종료하면 대화 상자 스택에서 팝업되고 선택적 결과가 대화의 부모에 반환됩니다. 부모는 대화 또는 방금 전에 종료된 대화를 시작한 메서드입니다.
await step.context.sendActivity(msg);
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
return await step.endDialog();
}
async summaryStep(step) {
step.values.picture = step.result && step.result[0];
// Get the current profile object from user state.
const userProfile = await this.userProfile.get(step.context, new UserProfile());
userProfile.transport = step.values.transport;
userProfile.name = step.values.name;
userProfile.age = step.values.age;
userProfile.picture = step.values.picture;
let msg = `I have your mode of transport as ${ userProfile.transport } and your name as ${ userProfile.name }`;
if (userProfile.age !== -1) {
msg += ` and your age as ${ userProfile.age }`;
}
msg += '.';
await step.context.sendActivity(msg);
if (userProfile.picture) {
try {
await step.context.sendActivity(MessageFactory.attachment(userProfile.picture, 'This is your profile picture.'));
} catch {
await step.context.sendActivity('A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here.');
}
폭포 대화 상자를 실행하는 확장 메서드 만들기
run 내부에 userProfileDialog정의된 도우미 메서드는 대화 컨텍스트를 만들고 액세스하는 데 사용됩니다. 여기서 accessor는 대화 상태 속성의 상태 속성 접근자이며, this는 사용자 프로필 구성 요소 대화입니다. 구성 요소 대화 상자는 내부 대화 집합을 정의하므로 메시지 처리기 코드에 표시되고 대화 컨텍스트를 만드는 데 사용되는 외부 대화 집합을 만들어야 합니다.
대화 컨텍스트는 메서드를 createContext 호출하여 만들어지고 봇의 턴 처리기 내에서 대화 집합과 상호 작용하는 데 사용됩니다. 대화 컨텍스트는 현재 순서 컨텍스트, 부모 대화 및 대화 상태를 포함하여 대화 내에서 정보를 유지하는 메서드를 제공합니다.
대화 컨텍스트를 사용하면 문자열 ID를 사용하여 대화 상자를 시작하거나 현재 대화 상자(예: 여러 단계가 있는 폭포 대화 상자)를 계속할 수 있습니다. 대화 컨텍스트는 모든 봇의 대화 상자 및 폭포 단계로 전달됩니다.
async run(turnContext, accessor) {
const dialogSet = new DialogSet(accessor);
dialogSet.add(this);
const dialogContext = await dialogSet.createContext(turnContext);
const results = await dialogContext.continueDialog();
if (results.status === DialogTurnStatus.empty) {
await dialogContext.beginDialog(this.id);
}
}
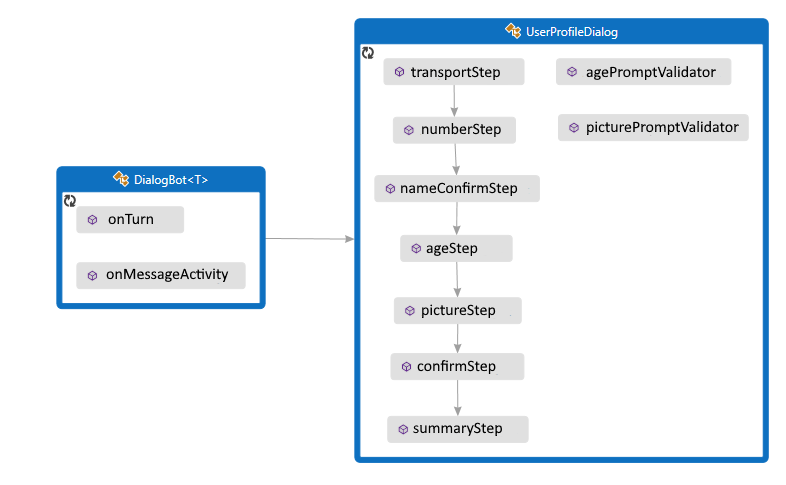
봇은 .를 통해 UserProfileDialog사용자와 상호 작용합니다. 봇의 DialogBot 클래스를 만들 때 기본 UserProfileDialog 대화 상자로 설정됩니다. 그런 다음, 봇은 Run 도우미 메서드를 사용하여 대화 상자에 액세스합니다.
UserProfileDialog.java
먼저 클래스에서 파생되는 7단계를 ComponentDialog 만듭니 UserProfileDialog 다.
UserProfileDialog 생성자에서 폭포 단계, 프롬프트 및 폭포 대화 상자를 만들고 대화 집합에 추가합니다. 프롬프트는 사용되는 것과 동일한 대화 상자 집합에 있어야 합니다.
public UserProfileDialog(UserState withUserState) {
super("UserProfileDialog");
userProfileAccessor = withUserState.createProperty("UserProfile");
WaterfallStep[] waterfallSteps = {
UserProfileDialog::transportStep,
UserProfileDialog::nameStep,
this::nameConfirmStep,
this::ageStep,
UserProfileDialog::pictureStep,
this::confirmStep,
this::summaryStep
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
addDialog(new WaterfallDialog("WaterfallDialog", Arrays.asList(waterfallSteps)));
addDialog(new TextPrompt("TextPrompt"));
addDialog(new NumberPrompt<Integer>("NumberPrompt", UserProfileDialog::agePromptValidator, Integer.class));
addDialog(new ChoicePrompt("ChoicePrompt"));
addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt("ConfirmPrompt"));
addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt("AttachmentPrompt", UserProfileDialog::picturePromptValidator));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
setInitialDialogId("WaterfallDialog");
}
다음으로, 대화 상자에서 입력을 요청하는 데 사용하는 단계를 추가합니다. 프롬프트를 사용하려면 대화의 단계에서 호출하고 다음 단계에서 stepContext.getResult()를 사용하여 프롬프트 결과를 검색합니다. 백그라운드에서 프롬프트는 2단계 대화 상자입니다. 먼저 프롬프트에서 입력을 요청합니다. 그런 다음 유효한 값을 반환하거나 처음부터 다시 시작하여 유효한 입력을 받을 때까지 다시 시작합니다.
항상 폭포 단계에서 null DialogTurnResult 이 아닌 값을 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 대화 상자가 설계된 대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다. 아래는 폭포 대화 상자의 구현 nameStep 입니다.
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("transport", ((FoundChoice) stepContext.getResult()).getValue());
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name."));
return stepContext.prompt("TextPrompt", promptOptions);
}
에서 ageStep프롬프트가 구문 분석할 수 없는 형식이거나 입력이 유효성 검사 조건에 실패하기 때문에 사용자 입력의 유효성을 검사하지 못하는 경우에 대한 재시도 프롬프트를 지정합니다. 이 경우 다시 시도 프롬프트가 제공되지 않은 경우 프롬프트는 초기 프롬프트 텍스트를 사용하여 사용자에게 입력을 다시 표시합니다.
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> ageStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."));
return stepContext.prompt("NumberPrompt", promptOptions);
}
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return stepContext.next(-1);
}
UserProfile.java
사용자의 교통 수단, 이름 및 나이가 UserProfile 클래스의 인스턴스에 저장됩니다.
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.microsoft.bot.sample.multiturnprompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.schema.Attachment;
/**
* This is our application state.
*/
public class UserProfile {
public String transport;
public String name;
public Integer age;
public Attachment picture;
}
UserProfileDialog.java
마지막 단계에서는 이전 폭포 단계에서 호출된 대화 상자에서 반환된 항목을 확인 stepContext.Result 합니다. 반환 값이 true이면 사용자 프로필 접근자가 사용자 프로필을 가져오고 업데이트합니다. 사용자 프로필을 얻으려면 호출 get 한 다음 , userProfile.NameuserProfile.Age 및 userProfile.Picture 속성의 userProfile.Transport값을 설정합니다. 마지막으로, 대화 상자를 종료하는 호출 endDialog하기 전에 사용자의 정보를 요약합니다. 대화 상자를 종료하면 대화 상자 스택에서 팝업되고 선택적 결과가 대화의 부모에 반환됩니다. 부모는 대화 또는 방금 전에 종료된 대화를 시작한 메서드입니다.
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.microsoft.bot.sample.multiturnprompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.MessageFactory;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.StatePropertyAccessor;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.UserState;
import com.microsoft.bot.connector.Channels;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.ComponentDialog;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.DialogTurnResult;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallDialog;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallStep;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallStepContext;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.choices.ChoiceFactory;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.choices.FoundChoice;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.AttachmentPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.ChoicePrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.ConfirmPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.NumberPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.PromptOptions;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.PromptValidatorContext;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.TextPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.schema.Attachment;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class UserProfileDialog extends ComponentDialog {
private final StatePropertyAccessor<UserProfile> userProfileAccessor;
public UserProfileDialog(UserState withUserState) {
super("UserProfileDialog");
userProfileAccessor = withUserState.createProperty("UserProfile");
WaterfallStep[] waterfallSteps = {
UserProfileDialog::transportStep,
UserProfileDialog::nameStep,
this::nameConfirmStep,
this::ageStep,
UserProfileDialog::pictureStep,
this::confirmStep,
this::summaryStep
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
addDialog(new WaterfallDialog("WaterfallDialog", Arrays.asList(waterfallSteps)));
addDialog(new TextPrompt("TextPrompt"));
addDialog(new NumberPrompt<Integer>("NumberPrompt", UserProfileDialog::agePromptValidator, Integer.class));
addDialog(new ChoicePrompt("ChoicePrompt"));
addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt("ConfirmPrompt"));
addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt("AttachmentPrompt", UserProfileDialog::picturePromptValidator));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
setInitialDialogId("WaterfallDialog");
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> transportStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
// Running a prompt here means the next WaterfallStep will be run when the user's response is received.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your mode of transport."));
promptOptions.setChoices(ChoiceFactory.toChoices("Car", "Bus", "Bicycle"));
return stepContext.prompt("ChoicePrompt", promptOptions);
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("transport", ((FoundChoice) stepContext.getResult()).getValue());
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name."));
return stepContext.prompt("TextPrompt", promptOptions);
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameConfirmStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("name", stepContext.getResult());
// We can send messages to the user at any point in the WaterfallStep.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(String.format("Thanks %s.", stepContext.getResult())))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> {
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Would you like to give your age?"));
return stepContext.prompt("ConfirmPrompt", promptOptions);
});
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> ageStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."));
return stepContext.prompt("NumberPrompt", promptOptions);
}
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return stepContext.next(-1);
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> pictureStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("age", (Integer) stepContext.getResult());
String msg = (Integer)stepContext.getValues().get("age") == -1
? "No age given."
: String.format("I have your age as %d.", (Integer)stepContext.getValues().get("age"));
// We can send messages to the user at any point in the WaterfallStep.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> {
if (StringUtils.equals(stepContext.getContext().getActivity().getChannelId(), Channels.MSTEAMS)) {
// This attachment prompt example is not designed to work for Teams attachments, so skip it in this case
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text("Skipping attachment prompt in Teams channel..."))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse1 -> stepContext.next(null));
}
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please attach a profile picture (or type any message to skip)."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The attachment must be a jpeg/png image file."));
return stepContext.prompt("AttachmentPrompt", promptOptions);
});
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> confirmStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
List<Attachment> attachments = (List<Attachment>)stepContext.getResult();
stepContext.getValues().put("picture", attachments == null ? null : attachments.get(0));
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Is this ok?"));
return stepContext.prompt("ConfirmPrompt", promptOptions);
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> summaryStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// Get the current profile object from user state.
return userProfileAccessor.get(stepContext.getContext(), () -> new UserProfile())
.thenCompose(userProfile -> {
userProfile.transport = (String) stepContext.getValues().get("transport");
userProfile.name = (String) stepContext.getValues().get("name");
userProfile.age = (Integer) stepContext.getValues().get("age");
userProfile.picture = (Attachment) stepContext.getValues().get("picture");
String msg = String.format(
"I have your mode of transport as %s and your name as %s",
userProfile.transport, userProfile.name
);
if (userProfile.age != -1) {
msg += String.format(" and your age as %s", userProfile.age);
}
msg += ".";
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
.thenApply(resourceResponse -> userProfile);
})
.thenCompose(userProfile -> {
if (userProfile.picture != null) {
try {
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.attachment(userProfile.picture,
"This is your profile picture."
));
} catch(Exception ex) {
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.text(
"A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."
));
}
}
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.text("A profile picture wasn't attached.")
);
})
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> stepContext.endDialog());
}
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is the end.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text("Thanks. Your profile will not be kept."))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> stepContext.endDialog());
}
private static CompletableFuture<Boolean> agePromptValidator(
PromptValidatorContext<Integer> promptContext
) {
// This condition is our validation rule. You can also change the value at this point.
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(
promptContext.getRecognized().getSucceeded()
&& promptContext.getRecognized().getValue() > 0
&& promptContext.getRecognized().getValue() < 150);
}
private static CompletableFuture<Boolean> picturePromptValidator(
PromptValidatorContext<List<Attachment>> promptContext
) {
if (promptContext.getRecognized().getSucceeded()) {
List<Attachment> attachments = promptContext.getRecognized().getValue();
List<Attachment> validImages = new ArrayList<>();
for (Attachment attachment : attachments) {
if (StringUtils.equals(
attachment.getContentType(), "image/jpeg") || StringUtils.equals(attachment.getContentType(), "image/png")
) {
validImages.add(attachment);
}
}
promptContext.getRecognized().setValue(validImages);
// If none of the attachments are valid images, the retry prompt should be sent.
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(!validImages.isEmpty());
}
else {
// We can return true from a validator function even if Recognized.Succeeded is false.
return promptContext.getContext().sendActivity("No attachments received. Proceeding without a profile picture...")
.thenApply(resourceResponse -> true);
}
}
}
대화 상자를 사용하려면 터미널에서 실행 pip install botbuilder-dialogs pip install botbuilder-ai 하여 botbuilder-dialogs 및 botbuilder-ai PyPI 패키지를 설치합니다.
봇은 .를 통해 UserProfileDialog사용자와 상호 작용합니다. 봇의 DialogBot 클래스가 만들어 UserProfileDialog 지면 기본 대화 상자로 설정됩니다. 그런 다음, 봇은 run_dialog 도우미 메서드를 사용하여 대화 상자에 액세스합니다.
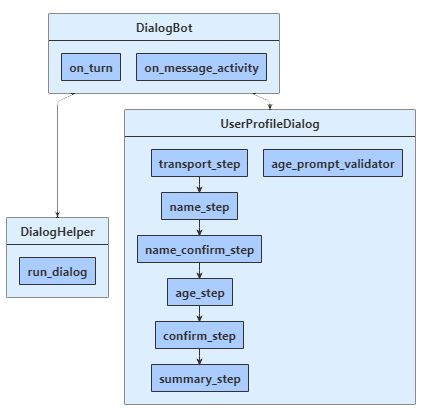
dialogs\user_profile_dialog.py
먼저 클래스에서 파생되는 7단계를 ComponentDialog 만듭니 UserProfileDialog 다.
UserProfileDialog 생성자에서 폭포 단계, 프롬프트 및 폭포 대화 상자를 만들고 대화 집합에 추가합니다. 프롬프트는 사용되는 것과 동일한 대화 상자 집합에 있어야 합니다.
def __init__(self, user_state: UserState):
super(UserProfileDialog, self).__init__(UserProfileDialog.__name__)
self.user_profile_accessor = user_state.create_property("UserProfile")
self.add_dialog(
WaterfallDialog(
WaterfallDialog.__name__,
[
self.transport_step,
self.name_step,
self.name_confirm_step,
self.age_step,
self.picture_step,
self.summary_step,
self.confirm_step,
],
)
)
self.add_dialog(TextPrompt(TextPrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(
NumberPrompt(NumberPrompt.__name__, UserProfileDialog.age_prompt_validator)
)
self.add_dialog(ChoicePrompt(ChoicePrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(ConfirmPrompt(ConfirmPrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(
AttachmentPrompt(
AttachmentPrompt.__name__, UserProfileDialog.picture_prompt_validator
)
)
self.initial_dialog_id = WaterfallDialog.__name__
다음으로, 대화 상자에서 입력을 요청하는 데 사용하는 단계를 추가합니다. 프롬프트를 사용하려면 대화의 단계에서 호출하고 다음 단계에서 step_context.result를 사용하여 프롬프트 결과를 검색합니다. 백그라운드에서 프롬프트는 2단계 대화 상자입니다. 먼저 프롬프트에서 입력을 요청합니다. 그런 다음 유효한 값을 반환하거나 처음부터 다시 시작하여 유효한 입력을 받을 때까지 다시 시작합니다.
항상 폭포 단계에서 null DialogTurnResult 이 아닌 값을 반환해야 합니다. 그렇지 않으면 대화 상자가 설계된 대로 작동하지 않을 수 있습니다. 여기서 폭포 대화 상자에서 구현을 name_step 볼 수 있습니다.
async def name_step(self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext) -> DialogTurnResult:
step_context.values["transport"] = step_context.result.value
return await step_context.prompt(
TextPrompt.__name__,
PromptOptions(prompt=MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name.")),
)
에서 age_step프롬프트가 구문 분석할 수 없는 형식이거나 입력이 위의 생성자에 지정된 유효성 검사 조건에 실패하기 때문에 사용자의 입력 유효성 검사에 실패하는 경우에 대한 재시도 프롬프트를 지정합니다. 이 경우 재시도 프롬프트가 제공되지 않은 경우 프롬프트는 초기 프롬프트 텍스트를 사용하여 사용자에게 입력을 다시 표시합니다.
async def age_step(self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext) -> DialogTurnResult:
if step_context.result:
# User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
# WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog,
# here it is a Prompt Dialog.
return await step_context.prompt(
NumberPrompt.__name__,
PromptOptions(
prompt=MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."),
retry_prompt=MessageFactory.text(
"The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."
),
),
)
# User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await step_context.next(-1)
data_models\user_profile.py
사용자의 교통 수단, 이름 및 나이가 UserProfile 클래스의 인스턴스에 저장됩니다.
class UserProfile:
"""
This is our application state. Just a regular serializable Python class.
"""
def __init__(self, name: str = None, transport: str = None, age: int = 0, picture: Attachment = None):
self.name = name
self.transport = transport
self.age = age
self.picture = picture
dialogs\user_profile_dialog.py
마지막 단계에서는 이전 폭포 단계에서 호출된 대화 상자에서 반환된 항목을 확인 step_context.result 합니다. 반환 값이 true이면 사용자 프로필 접근자가 사용자 프로필을 가져오고 업데이트합니다. 사용자 프로필을 얻으려면 호출get한 다음 , user_profile.name및 user_profile.age 속성의 user_profile.transport값을 설정합니다. 마지막으로, 대화 상자를 종료하는 호출 end_dialog하기 전에 사용자의 정보를 요약합니다. 대화 상자를 종료하면 대화 상자 스택에서 팝업되고 선택적 결과가 대화의 부모에 반환됩니다. 부모는 대화 또는 방금 전에 종료된 대화를 시작한 메서드입니다.
async def summary_step(
self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext
) -> DialogTurnResult:
step_context.values["picture"] = (
None if not step_context.result else step_context.result[0]
)
# Get the current profile object from user state. Changes to it
# will saved during Bot.on_turn.
user_profile = await self.user_profile_accessor.get(
step_context.context, UserProfile
)
user_profile.transport = step_context.values["transport"]
user_profile.name = step_context.values["name"]
user_profile.age = step_context.values["age"]
user_profile.picture = step_context.values["picture"]
msg = f"I have your mode of transport as {user_profile.transport} and your name as {user_profile.name}."
if user_profile.age != -1:
msg += f" And age as {user_profile.age}."
await step_context.context.send_activity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
if user_profile.picture:
await step_context.context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.attachment(
user_profile.picture, "This is your profile picture."
)
)
else:
await step_context.context.send_activity(
"A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."
)
# WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another
# dialog, here it is the end.
return await step_context.prompt(
ConfirmPrompt.__name__,
폭포 대화 상자를 실행하는 확장 메서드 만들기
run_dialog() 도우미 메서드는 대화 컨텍스트를 만들고 액세스하는 데 사용되는 helpers\dialog_helper.py 정의됩니다. 여기서 accessor는 대화 상태 속성의 상태 속성 접근자이며, dialog는 사용자 프로필 구성 요소 대화입니다. 구성 요소 대화 상자는 내부 대화 집합을 정의하므로 메시지 처리기 코드에 표시되는 외부 대화 집합을 만들고 이를 사용하여 대화 컨텍스트를 만들어야 합니다.
봇의 턴 처리기 내에서 대화 집합과 상호 작용하는 데 사용되는 대화 컨텍스트를 호출 create_context하여 대화 컨텍스트를 만듭니다. 대화 컨텍스트는 현재 순서 컨텍스트, 부모 대화 및 대화 상태를 포함하여 대화 내에서 정보를 유지하는 메서드를 제공합니다.
대화 컨텍스트를 사용하면 문자열 ID를 사용하여 대화 상자를 시작하거나 현재 대화 상자(예: 여러 단계가 있는 폭포 대화 상자)를 계속할 수 있습니다. 대화 컨텍스트는 모든 봇의 대화 상자 및 폭포 단계로 전달됩니다.
class DialogHelper:
@staticmethod
async def run_dialog(
dialog: Dialog, turn_context: TurnContext, accessor: StatePropertyAccessor
):
dialog_set = DialogSet(accessor)
dialog_set.add(dialog)
dialog_context = await dialog_set.create_context(turn_context)
results = await dialog_context.continue_dialog()
if results.status == DialogTurnStatus.Empty:
await dialog_context.begin_dialog(dialog.id)
이 봇은 다음 서비스를 사용합니다.
이 봇에서는 두 가지 상태 속성 접근자가 정의됩니다.
이 샘플은 대화 상자 내에서 사용자 프로필 상태를 업데이트합니다. 이 방법은 일부 봇에서 작동할 수 있지만 봇 간에 대화 상자를 다시 사용하려는 경우에는 작동하지 않습니다.
대화 상자 단계와 봇 상태를 분리하는 다양한 옵션이 있습니다. 예를 들어, 대화 상자가 완전한 정보를 수집하면 다음을 수행할 수 있습니다.