빠른 시작: Bicep을 사용하여 AKS(Azure Kubernetes Service) 클러스터 배포
AKS(Azure Kubernetes Service)는 클러스터를 빠르게 배포하고 관리할 수 있는 관리형 Kubernetes 서비스입니다. 이 빠른 시작에서 관련 정보는 다음과 같습니다.
- Bicep을 사용하여 AKS 클러스터 배포
- 소매 시나리오를 시뮬레이션하는 마이크로 서비스 및 웹 프런트 엔드 그룹을 사용하여 샘플 다중 컨테이너 애플리케이션을 실행합니다.
참고 항목
AKS 클러스터 프로비전을 빠르게 시작하기 위해 이 문서에는 평가 목적으로만 기본 설정으로 클러스터를 배포하는 단계가 포함되어 있습니다. 프로덕션에 즉시 사용 가능한 클러스터를 배포하기 전에 기본 참조 아키텍처를 숙지하여 비즈니스 요구 사항에 어떻게 부합하는지 고려하는 것이 좋습니다.
시작하기 전에
- 이 빠른 시작에서는 Kubernetes 기본 개념을 이해하고 있다고 가정합니다. 자세한 내용은 AKS(Azure Kubernetes Service)의 Kubernetes 핵심 개념을 참조하세요.
- 활성 구독이 있는 Azure 계정이 필요합니다. 계정이 없으면 무료 계정을 만듭니다.
- Windows Server 노드 풀을 만드는 방법에 대한 자세한 내용은 Windows Server 컨테이너를 지원하는 AKS 클러스터 만들기를 참조하세요.
- Bicep은 선언적 구문을 사용하여 Azure 리소스를 배포하는 DSL(도메인 특정 언어)입니다. 간결한 구문, 신뢰할 수 있는 형식 안전성 및 코드 다시 사용에 대한 지원을 제공합니다. Bicep은 Azure에서 코드형 인프라 솔루션에 대한 최고의 제작 환경을 제공합니다.
Azure Cloud Shell에서 Bash 환경을 사용합니다. 자세한 내용은 Azure Cloud Shell의 Bash에 대한 빠른 시작을 참조하세요.
CLI 참조 명령을 로컬에서 실행하려면 Azure CLI를 설치합니다. Windows 또는 macOS에서 실행 중인 경우 Docker 컨테이너에서 Azure CLI를 실행하는 것이 좋습니다. 자세한 내용은 Docker 컨테이너에서 Azure CLI를 실행하는 방법을 참조하세요.
로컬 설치를 사용하는 경우 az login 명령을 사용하여 Azure CLI에 로그인합니다. 인증 프로세스를 완료하려면 터미널에 표시되는 단계를 수행합니다. 다른 로그인 옵션은 Azure CLI를 사용하여 로그인을 참조하세요.
메시지가 표시되면 처음 사용할 때 Azure CLI 확장을 설치합니다. 확장에 대한 자세한 내용은 Azure CLI에서 확장 사용을 참조하세요.
az version을 실행하여 설치된 버전과 종속 라이브러리를 찾습니다. 최신 버전으로 업그레이드하려면 az upgrade를 실행합니다.
- 이 문서에는 Azure CLI 버전 2.0.64 이상이 필요합니다. Azure Cloud Shell을 사용하는 경우 최신 버전이 이미 설치되어 있습니다.
- 이 문서에는 기존 Azure 리소스 그룹이 필요합니다. 리소스 그룹을 만들어야 하는 경우 az group create 명령을 사용할 수 있습니다.
- Bicep 파일을 사용하여 AKS 클러스터를 만들려면 SSH 공개 키를 제공합니다. 이 리소스가 필요한 경우 다음 섹션을 참조하세요. 그렇지 않으면 Bicep 파일 검토로 건너뜁니다.
- 클러스터를 만드는 데 사용하는 ID에 적절한 최소 권한이 있어야 합니다. AKS의 액세스 및 ID에 대한 자세한 내용은 AKS(Azure Kubernetes Service)에 대한 액세스 및 ID 옵션을 참조하세요.
- Bicep 파일을 배포하려면 만드는 리소스에 대한 쓰기 액세스 권한과
Microsoft.Resources/deployments리소스 종류의 모든 작업에 대한 액세스 권한이 필요합니다. 예를 들어 가상 머신을 만들려면Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/write및Microsoft.Resources/deployments/*권한이 필요합니다. 역할 및 사용 권한 목록은 Azure 기본 제공 역할을 참조하세요.
SSH 키 쌍 만들기
https://shell.azure.com으로 이동하여 브라우저에서 Cloud Shell을 엽니다.
az sshkey create Azure CLI 명령 또는
ssh-keygen명령을 사용하여 SSH 키 쌍을 만듭니다.# Create an SSH key pair using Azure CLI az sshkey create --name "mySSHKey" --resource-group "myResourceGroup" # Create an SSH key pair using ssh-keygen ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096
SSH 생성에 대한 자세한 내용은 Azure에서 인증용 SSH 키 생성 및 관리를 참조하세요.
Bicep 파일 검토
이 빠른 시작에서 사용되는 Bicep 파일은 Azure 빠른 시작 템플릿에서 나온 것입니다.
@description('The name of the Managed Cluster resource.')
param clusterName string = 'aks101cluster'
@description('The location of the Managed Cluster resource.')
param location string = resourceGroup().location
@description('Optional DNS prefix to use with hosted Kubernetes API server FQDN.')
param dnsPrefix string
@description('Disk size (in GB) to provision for each of the agent pool nodes. This value ranges from 0 to 1023. Specifying 0 will apply the default disk size for that agentVMSize.')
@minValue(0)
@maxValue(1023)
param osDiskSizeGB int = 0
@description('The number of nodes for the cluster.')
@minValue(1)
@maxValue(50)
param agentCount int = 3
@description('The size of the Virtual Machine.')
param agentVMSize string = 'standard_d2s_v3'
@description('User name for the Linux Virtual Machines.')
param linuxAdminUsername string
@description('Configure all linux machines with the SSH RSA public key string. Your key should include three parts, for example \'ssh-rsa AAAAB...snip...UcyupgH azureuser@linuxvm\'')
param sshRSAPublicKey string
resource aks 'Microsoft.ContainerService/managedClusters@2024-02-01' = {
name: clusterName
location: location
identity: {
type: 'SystemAssigned'
}
properties: {
dnsPrefix: dnsPrefix
agentPoolProfiles: [
{
name: 'agentpool'
osDiskSizeGB: osDiskSizeGB
count: agentCount
vmSize: agentVMSize
osType: 'Linux'
mode: 'System'
}
]
linuxProfile: {
adminUsername: linuxAdminUsername
ssh: {
publicKeys: [
{
keyData: sshRSAPublicKey
}
]
}
}
}
}
output controlPlaneFQDN string = aks.properties.fqdn
Bicep 파일에 정의된 리소스는 다음과 같습니다.
AKS 샘플을 더 보려면 AKS 빠른 시작 템플릿 사이트를 참조하세요.
Bicep 파일 배포
- Bicep 파일을 main.bicep으로 로컬 컴퓨터에 저장합니다.
Important
Bicep 파일은 clusterName 매개 변수를 문자열 aks101cluster로 설정합니다. 다른 클러스터 이름을 사용하려면 파일을 컴퓨터에 저장하기 전에 선호하는 클러스터 이름으로 문자열을 업데이트해야 합니다.
Azure CLI 또는 Azure PowerShell을 사용하여 Bicep 파일을 배포합니다.
az deployment group create --resource-group myResourceGroup --template-file main.bicep --parameters dnsPrefix=<dns-prefix> linuxAdminUsername=<linux-admin-username> sshRSAPublicKey='<ssh-key>'다음 값을 명령에 제공합니다.
- DNS 접두사: 클러스터의 고유 DNS 접두사(예: myakscluster)를 입력합니다.
- Linux 관리자 사용자 이름: SSH를 사용하여 연결할 사용자 이름(예: azureuser)을 입력합니다.
- SSH RSA 공개 키: SSH 키 쌍의 public 부분(기본적으로 ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub의 콘텐츠)을 복사하여 붙여넣습니다.
AKS 클러스터를 만드는 데 몇 분이 걸립니다. 다음 단계로 넘어가기 전에 클러스터가 성공적으로 배포될 때까지 기다립니다.
Bicep 배포 유효성 검사
클러스터에 연결
Kubernetes 클러스터를 관리하려면 Kubernetes 명령줄 클라이언트인 kubectl을 사용합니다. Azure Cloud Shell을 사용하는 경우 kubectl이 이미 설치되어 있습니다.
az aks install-cli 명령을 사용하여
kubectl을 로컬로 설치합니다.az aks install-cliaz aks get-credentials 명령을 사용하여 Kubernetes 클러스터에 연결하도록
kubectl을 구성합니다. 이 명령은 자격 증명을 다운로드하고 Kubernetes CLI가 해당 자격 증명을 사용하도록 구성합니다.az aks get-credentials --resource-group myResourceGroup --name myAKSClusterkubectl get 명령을 사용하여 클러스터에 대한 연결을 확인합니다. 이 명령은 클러스터 노드 목록을 반환합니다.
kubectl get nodes다음 예제 출력은 이전 단계에서 만든 단일 노드를 보여줍니다. 노드 상태가 준비인지 확인합니다.
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION aks-agentpool-41324942-0 Ready agent 6m44s v1.12.6 aks-agentpool-41324942-1 Ready agent 6m46s v1.12.6 aks-agentpool-41324942-2 Ready agent 6m45s v1.12.6
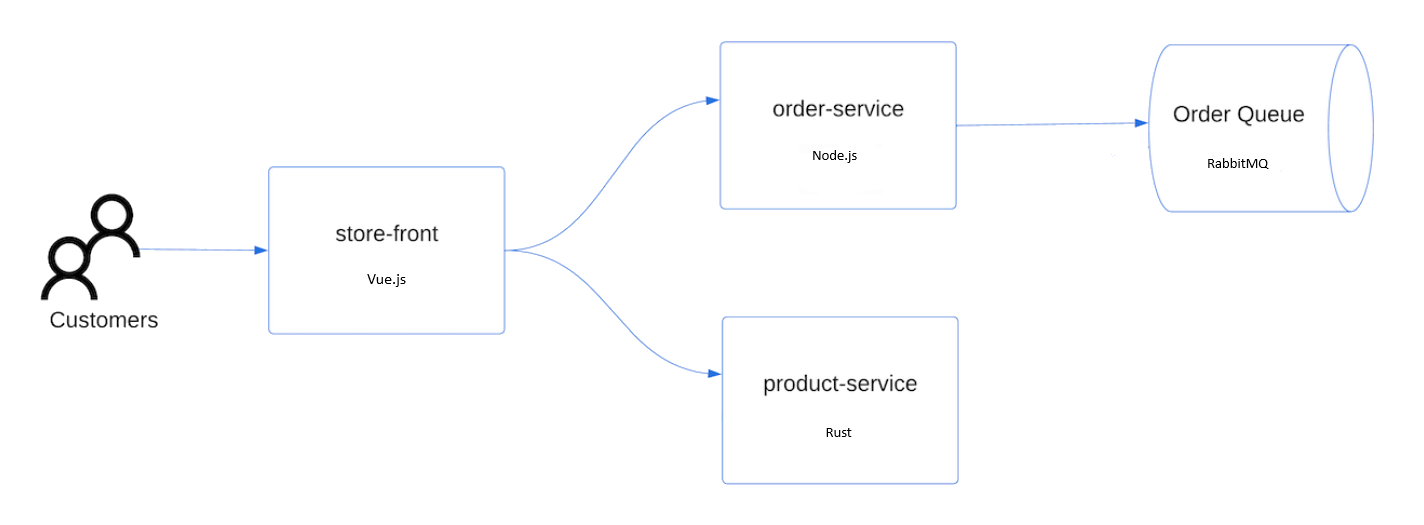
애플리케이션 배포
응용 프로그램을 배포하려면 매니페스트 파일을 사용하여 AKS Store 응용 프로그램을 실행하는 데 필요한 모든 개체를 만듭니다. Kubernetes 매니페스트 파일은 실행할 컨테이너 이미지와 같은 클러스터에 대해 원하는 상태를 정의합니다. 매니페스트에는 다음 Kubernetes 배포 및 서비스가 포함됩니다.
- 스토어 프런트: 고객이 제품을 보고 주문을 할 수 있는 웹 애플리케이션입니다.
- 제품 서비스: 제품 정보를 표시합니다.
- 주문 서비스: 주문을 합니다.
- Rabbit MQ: 주문 큐에 대한 메시지 큐입니다.
참고 항목
프로덕션을 위한 영구 스토리지 없이 Rabbit MQ와 같은 상태 저장 컨테이너를 실행하지 않는 것이 좋습니다. 여기서는 단순화를 위해 사용되었지만 Azure CosmosDB 또는 Azure Service Bus와 같은 관리되는 서비스를 사용하는 것이 좋습니다.
파일
aks-store-quickstart.yaml을 만들고 다음 매니페스트에 복사합니다.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: rabbitmq spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: rabbitmq template: metadata: labels: app: rabbitmq spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: rabbitmq image: mcr.microsoft.com/mirror/docker/library/rabbitmq:3.10-management-alpine ports: - containerPort: 5672 name: rabbitmq-amqp - containerPort: 15672 name: rabbitmq-http env: - name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER value: "username" - name: RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS value: "password" resources: requests: cpu: 10m memory: 128Mi limits: cpu: 250m memory: 256Mi volumeMounts: - name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins mountPath: /etc/rabbitmq/enabled_plugins subPath: enabled_plugins volumes: - name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins configMap: name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins items: - key: rabbitmq_enabled_plugins path: enabled_plugins --- apiVersion: v1 data: rabbitmq_enabled_plugins: | [rabbitmq_management,rabbitmq_prometheus,rabbitmq_amqp1_0]. kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: rabbitmq-enabled-plugins --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: rabbitmq spec: selector: app: rabbitmq ports: - name: rabbitmq-amqp port: 5672 targetPort: 5672 - name: rabbitmq-http port: 15672 targetPort: 15672 type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: order-service spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: order-service template: metadata: labels: app: order-service spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: order-service image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/order-service:latest ports: - containerPort: 3000 env: - name: ORDER_QUEUE_HOSTNAME value: "rabbitmq" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_PORT value: "5672" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_USERNAME value: "username" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_PASSWORD value: "password" - name: ORDER_QUEUE_NAME value: "orders" - name: FASTIFY_ADDRESS value: "0.0.0.0" resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 50Mi limits: cpu: 75m memory: 128Mi initContainers: - name: wait-for-rabbitmq image: busybox command: ['sh', '-c', 'until nc -zv rabbitmq 5672; do echo waiting for rabbitmq; sleep 2; done;'] resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 50Mi limits: cpu: 75m memory: 128Mi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: order-service spec: type: ClusterIP ports: - name: http port: 3000 targetPort: 3000 selector: app: order-service --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: product-service spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: product-service template: metadata: labels: app: product-service spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: product-service image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/product-service:latest ports: - containerPort: 3002 resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 1Mi limits: cpu: 1m memory: 7Mi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: product-service spec: type: ClusterIP ports: - name: http port: 3002 targetPort: 3002 selector: app: product-service --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: store-front spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: store-front template: metadata: labels: app: store-front spec: nodeSelector: "kubernetes.io/os": linux containers: - name: store-front image: ghcr.io/azure-samples/aks-store-demo/store-front:latest ports: - containerPort: 8080 name: store-front env: - name: VUE_APP_ORDER_SERVICE_URL value: "http://order-service:3000/" - name: VUE_APP_PRODUCT_SERVICE_URL value: "http://product-service:3002/" resources: requests: cpu: 1m memory: 200Mi limits: cpu: 1000m memory: 512Mi --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: store-front spec: ports: - port: 80 targetPort: 8080 selector: app: store-front type: LoadBalancerYAML 매니페스트 파일의 분석은 배포 및 YAML 매니페스트를 참조하세요.
YAML 파일을 로컬에서 만들고 저장하는 경우 파일 업로드/다운로드 단추를 선택하고 로컬 파일 시스템에서 파일을 선택하여 매니페스트 파일을 CloudShell의 기본 디렉터리에 업로드할 수 있습니다.
kubectl apply 명령을 사용하여 애플리케이션을 배포하고 YAML 매니페스트의 이름을 지정합니다.
kubectl apply -f aks-store-quickstart.yaml다음 예제 출력은 배포 및 서비스를 보여 줍니다.
deployment.apps/rabbitmq created service/rabbitmq created deployment.apps/order-service created service/order-service created deployment.apps/product-service created service/product-service created deployment.apps/store-front created service/store-front created
애플리케이션 테스트
애플리케이션이 실행되면 애플리케이션 프런트 엔드를 인터넷에 공개하는 Kubernetes 서비스가 만들어집니다. 이 프로세스를 완료하는 데 몇 분이 걸릴 수 있습니다.
배포된 Pod의 상태는 kubectl get pods 명령을 사용하여 확인합니다. 계속하기 전에 모든 Pod를
Running으로 만듭니다.kubectl get podsstore-front 응용 프로그램의 공용 IP 주소를 확인합니다.
--watch인수와 함께 kubectl get service 명령을 사용하여 진행 상황을 모니터링합니다.kubectl get service store-front --watchstore-front서비스에 대한 EXTERNAL-IP 출력은 처음에 보류 중으로 표시됩니다.NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE store-front LoadBalancer 10.0.100.10 <pending> 80:30025/TCP 4h4mEXTERNAL-IP 주소가 보류 중에서 실제 공용 IP 주소로 변경되면
CTRL-C를 사용하여kubectl조사식 프로세스를 중지합니다.다음 예제 출력은 서비스에 할당된 유효한 공용 IP 주소를 보여줍니다.
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE store-front LoadBalancer 10.0.100.10 20.62.159.19 80:30025/TCP 4h5mAzure Store 앱이 작동하는 모습을 보려면 서비스의 외부 IP 주소로 웹 브라우저를 엽니다.
클러스터 삭제
AKS 자습서를 진행할 계획이 없다면 불필요한 리소스를 정리하여 Azure 요금이 청구되지 않도록 합니다.
az group delete 명령을 사용하여 리소스 그룹, 컨테이너 서비스 및 모든 관련 리소스를 제거합니다.
az group delete --name myResourceGroup --yes --no-wait
참고 항목
AKS 클러스터는 이 빠른 시작에서 사용되는 기본 ID 옵션인 시스템이 할당한 관리 ID를 사용하여 만들어졌습니다. 플랫폼이 이 ID를 관리하므로 수동으로 제거할 필요가 없습니다.
다음 단계
이 빠른 시작에서는 Kubernetes 클러스터를 배포한 다음, 해당 클러스터에 간단한 다중 컨테이너 애플리케이션을 배포했습니다. 이 샘플 응용 프로그램은 데모 목적으로만 사용되며 Kubernetes 응용 프로그램에 대한 모든 모범 사례를 나타내지는 않습니다. 프로덕션용 AKS를 사용하여 전체 솔루션을 만드는 방법에 대한 지침은 AKS 솔루션 지침을 참조하세요.
AKS에 대해 자세히 알아보고 배포 예제에 대한 전체 코드를 연습해 보려면 Kubernetes 클러스터 자습서를 계속 진행합니다.
Azure Kubernetes Service