e-Discovery and SharePoint 2013 - An Overview
What is e-discovery
e-discovery (also known as Electronic Discovery) is used to collect, identify and produce relevant information from Electronically Stored Information (ESI) for litigation and legal purposes for investigation.
In the United States, amendments to the US Federal Rules of Civil Procedure in 2006, codified the requirement to provide electronic information and records and these amendments bring the term E-discovery.
ESI can be in form of Email communication, documents, spreadsheets, presentations, social media posts, voice mails and video files.
Electronic Information is different from hard copy documents as it contains metadata information which may play an important role as evidences in legal scenarios. The preservation of metadata is crucial for ESI.
e-Discovery Reference Model
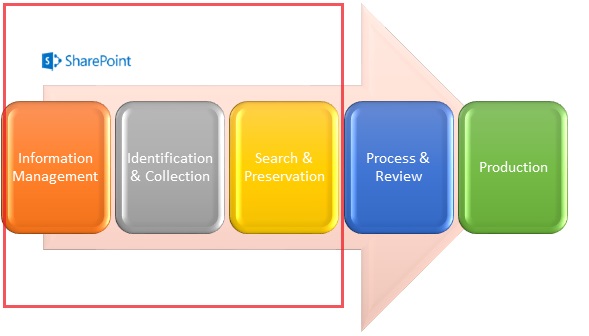
e-discovery process can be well represented by the e-discovery Reference Model (EDRM).
Fig 1: e-Discovery Reference Model (EDRM)
- Information Management
Defines how the organizational data/ documents are managed over the time and what are the policies implemented for retention of important content.
- Identification, Collection of Documents
After the collection and identification of data/ documents for a specific legal case by both the parties.
- Preserve the Identified Documents
The potentially relevant documents are placed on hold i.e. on legal hold, so that they cannot be modified, deleted or destroyed.
- Processing & Review Data
Potentially relevant data is collected and then extracted, indexed and placed into a database. At this point, data is analyzed to segregate the clearly non-relevant documents and e-mails. This data/ documents is stored securely to allow reviewers to access them for legal matters
- Produce documents for legal matters
The reviewed documents/content will be produced as a legal evidence.
Why e-Discovery
e-discovery is essential for any organization’s information management policies. At a grass-root level, the importance of e-discovery stems from the fact that the majority of information these days is electronic and can potentially be sought as evidence in a court of law. Additionally, with the sheer amount of data available and regulatory and legal compliance requirements continuing to evolve, organizations face new challenges when it comes to information retention and governance
- Due to rapidly growing ESI Content, focus on Emails and use of multimedia and social media, E-discovery has become an important tool for organizations to easily collect and identify the potential data from a large pool of information.
- As data is scattered over several networks and mediums, e-discovery can play an important role of aggregate the contents from all the locations and preserve the important document at a central location.
- Timeliness and quick response with relevant information/data become crucial for any organization to impact legal decisions and e-discovery can play an important role in these scenarios.
A Brief history of e-discovery in SharePoint
Microsoft introduced a “hold” feature in SharePoint Server 2007 which can be used for e-discovery but it was scoped to records management site template. Later in SharePoint 2010, e-Discovery capabilities have been greatly enhanced across the SharePoint deployment. The major developments added by Microsoft that supports e-Discovery are:
- Ability to manage holds and search content for e-Discovery on any site collection
- FAST search capabilities are used in SP2010 to search the content for e-Discovery
- Ability to copy identified documents into another/new site collection
Despite of adding the above new features, some major e-discovery features were still missing in SharePoint 2010. SharePoint 2010 cannot
- Search content among all site collections collectively preserving the content for e-discovery. e-Discovery holds can only be done on a single site collection
- On hold documents cannot be edited/ deleted by the users
Overview of e-discovery in SharePoint 2013
SharePoint 2013 introduced a new dimension/ edge to e-Discovery feature eliminating the shortcomings of earlier versions. e-Discovery in SharePoint 2013 includes new way to reduce the cost and complexity of discovery.
- e-Discovery center
A new site collection template “E-Discovery Center” has been introduced
- Enterprise-wide e-Discovery
Facility to search content from SharePoint Online, SharePoint On-premise, Lync 2013 or Exchange 2013 enables to build hybrid approach for E-Discovery
- In Place holds
In place holds applied on the content does not restrict the users to edit or delete the content from the site collection
- Export content from Exchange 2013 and SharePoint 2013 for further analysis & processing
One of the biggest eDiscovery challenges when dealing with SharePoint data stored on cloud or on Exchange servers is getting the data out of the system in a portable offline format. To overcome this challenge, a new feature to export collected/ identified data has been introduced in this new version.
- Query Based Preservation
Allows getting relevant and up to date information/ content more easily and quickly based on the queries and filters specified by the user for a particular case.
- No Impact on Users
Users can seamlessly create, edit or delete the documents without knowing that the content is on hold and is under review for legal purposes.
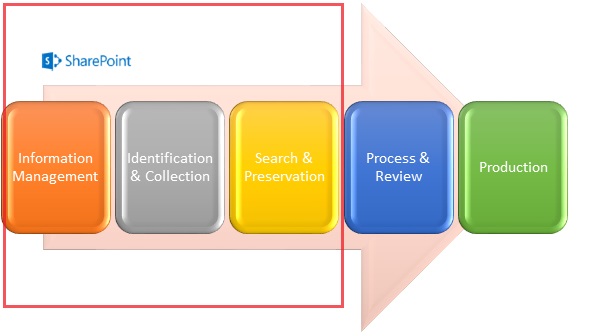
How SharePoint fits with the EDRM
SharePoint 2013 e-Discovery functionality focuses on first three stages of EDRM model. e-Discovery is a very expensive process and reviewing the content is most expensive of all. The better tools help in identifying the most relevant content and thus reduces the content to be reviewed, results in massive cost savings.
Fig 2: SharePoint 2013 & EDRM Mapping
.
SharePoint e-Discovery Architecture
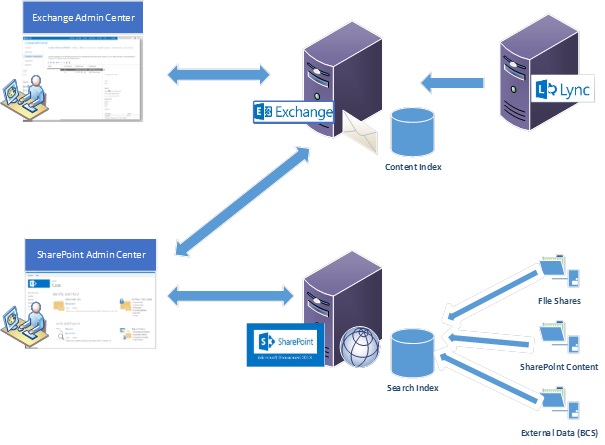
Fig 3: SharePoint 2013 E-Discovery Architecture