3D 参照テーブルの効果
3D 検索テーブルは汎用の効果であり、すべての入力値のサブセットの入力を出力にマップする方法を事前に計算することによって、1 対 1 のイメージング効果をカプセル化するために使用されます。
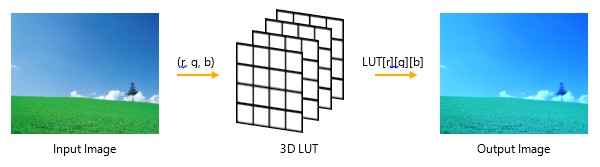
3D 参照テーブル (LUT) 効果は、画像の RGB カラー値を使用して 3D テクスチャのインデックスを作成することで、入力イメージを変更します。テクスチャには、任意の効果パイプラインの事前計算済み出力値が含まれています。
レンダリングするには、3D LUT を GPU テクスチャ リソースに読み込む必要があります。これは、テクスチャのサイズとデバイスの機能によってはコストがかかる場合があります。 アプリケーション開発者は、 ID2D1LookupTable3D D2D リソースを使用して、このコストを支払うタイミングを指定できます。 ID2D1LookupTable3D には、次の属性があります。
- 3D LUT の GPU リソースの抽象化された表現を提供します。
- デバイスの機能に応じて、2D または 3D テクスチャが作成され、指定された LUT データが入力されます。
- レンダリングのために 3D LUT 効果の プロパティに渡すことができます。
この効果の CLSID はCLSID_D2D1LookupTable3D。
画像の例
サンプル コード
//
// 1. Generate the lookup table data and create an ID2D1LookupTable3D.
//
// Create a 16x16x16 LUT of arbitrary data type T.
UINT extents[] = { 16, 16, 16 };
UINT cElements = extents[0] * extents[1] * extents[2] * 4;
UINT cbElements = cElements * formatSize;
// Compute the step size in each direction to vary the RGB
// channels uniformly over the range [0, 1]
float steps[] =
{
1.0f / static_cast<float>(extents[0] - 1),
1.0f / static_cast<float>(extents[1] - 1),
1.0f / static_cast<float>(extents[2] - 1),
};
CArray<BYTE> lutData;
IFR(lutData.Resize(cbElements));
T* pData = reinterpret_cast<T *>(lutData.GetData());
T oneValue = ConvertValue<T>(1.0f);
// Generate the LUT by applying an imaging pipeline to RGB values.
for (UINT iR = 0; iR < extents[2]; iR++)
{
for (UINT iG = 0; iG < extents[1]; iG++)
{
for (UINT iB = 0; iB < extents[0]; iB++)
{
T outputColor[3];
ApplyPipeline(iR * steps[2], iG * steps[1], iB * steps[0], &outputColor);
pData[0] = outColor[0];
pData[1] = outColor[1];
pData[2] = outColor[2];
// Set opaque alpha in the output
pData[3] = oneValue;
// Advance the pointer
pData += sizeof(T) * 4;
}
}
}
// Compute the strides of the LUT data.
UINT strides[2];
IFR(UIntMult(sizeof(T) * 4, extents[0], &strides[0]));
IFR(UIntMult(strides[0], extents[1], &strides[1]));
D2D1_BUFFER_PRECISION precision = GetBufferPrecision<T>();
// Create an ID2D1LookupTable3D from the LUT data.
CComPtr<ID2D1LookupTable3D> sp3dLut;
IFR(_spEffectContext1->CreateLookupTable3D(
precision,
extents,
lutData.GetData(),
lutData.GetCount(),
strides,
&sp3dLut
));
//
// 2. To apply the lookup table to an input image, create a LookupTable3D effect
// and pass the ID2D1LookupTable3D to the effect as a property.
//
// Create a 3D LUT effect to render our LUT.
CComPtr<ID2D1Effect> sp3dLutEffect;
IFR(pEffectContext->CreateEffect(CLSID_D2D1LookupTable3D, &sp3dLutEffect));
// Set the LUT as a property on the effect.
IFR(sp3dLutEffect->SetValue(D2D1_LOOKUPTABLE3D_PROP_LUT, _spLut));
Effect プロパティ
3D 参照テーブル効果のプロパティは、 D2D1_LOOKUPTABLE3D_PROP 列挙によって定義されます。
要件
| 要件 | 値 |
|---|---|
| サポートされている最小のクライアント | Windows 10 [デスクトップ アプリ |Windows ストア アプリ] |
| サポートされている最小のサーバー | Windows 10 [デスクトップ アプリ |Windows ストア アプリ] |
| ヘッダー | d2d1effects_2.h |
| ライブラリ | d2d1.lib、dxguid.lib |