Xamarin.Android GridLayout
GridLayout は、次に示すように、HTML テーブルと同様に 2D グリッドでのビューのレイアウトをサポートする新しい ViewGroup サブクラスです。
GridLayout はフラット ビュー階層で動作します。この階層では、子ビューが存在する行と列を指定することで、グリッド内の位置を設定します。 このように、GridLayout はグリッド内にビューを配置できます。中間ビューが、TableLayout で使用されるテーブル行に表示されるなどの、テーブル構造を指定する必要はありません。 フラット階層を保守することで、GridLayout は子ビューをより迅速にレイアウトできます。 この概念がコードで実際に何を意味するのかを説明する例を見てみましょう。
グリッド レイアウトの作成
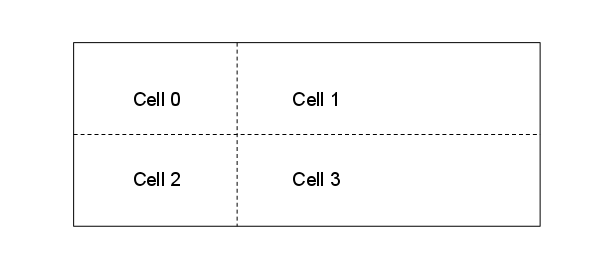
次の XML は、GridLayout にいくつかの TextView コントロールを追加します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="2"
android:columnCount="2">
<TextView
android:text="Cell 0"
android:textSize="14dip" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 1"
android:textSize="14dip" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 2"
android:textSize="14dip" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 3"
android:textSize="14dip" />
</GridLayout>
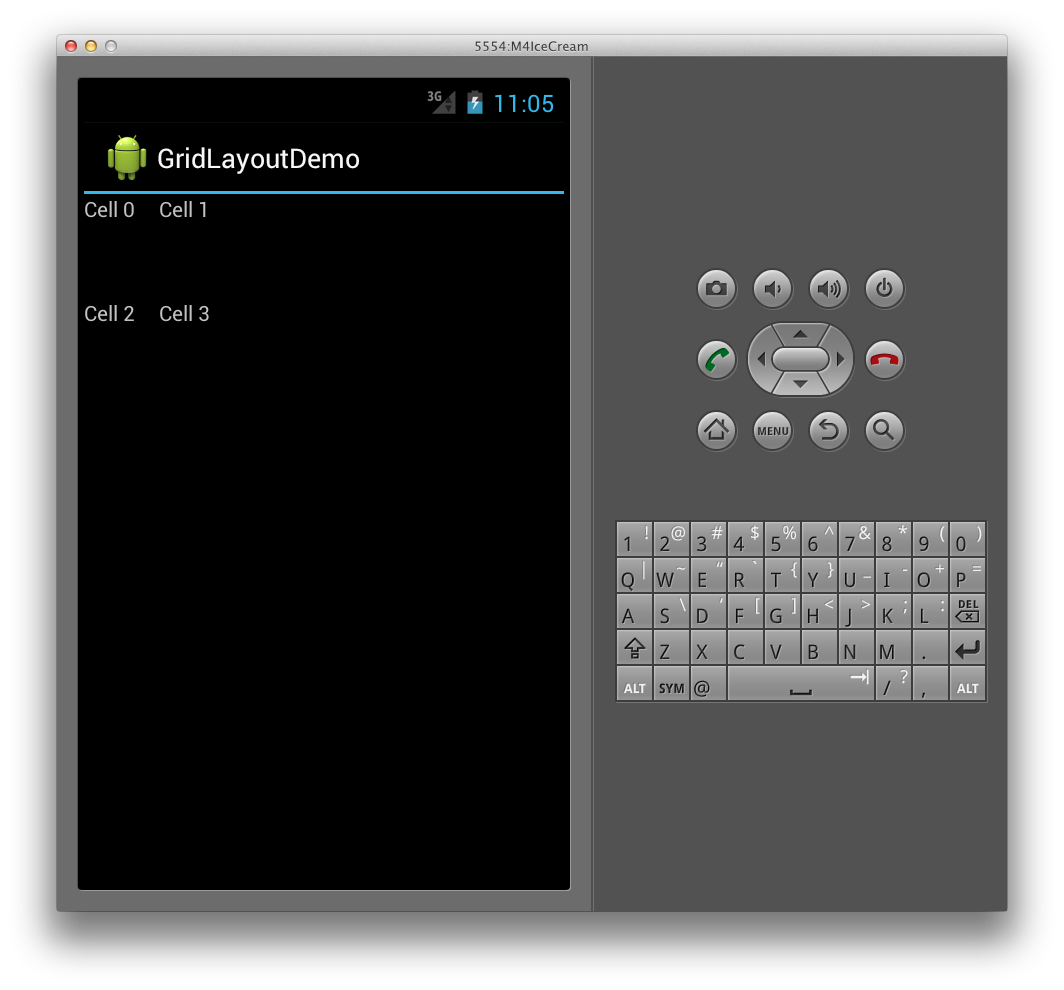
このレイアウトでは、次の図に示すように、セルがコンテンツに合うように行と列のサイズが調整されます。
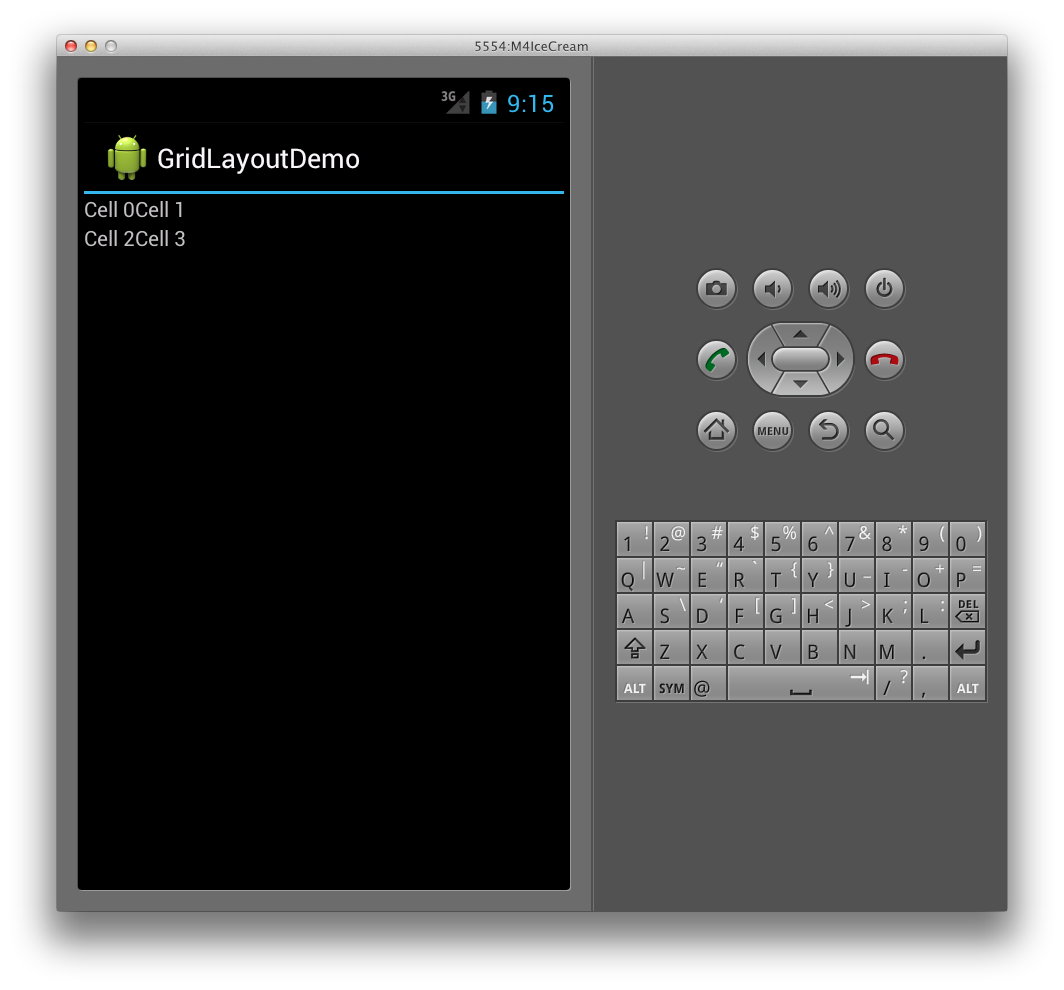
この結果、アプリケーションで実行すると、次のユーザー インターフェイスになります。
向きの指定
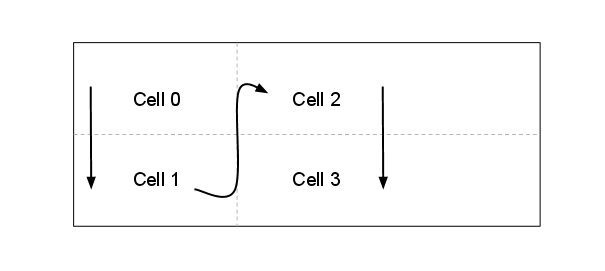
上記の XML では、各 TextView は行も列も指定しないことに注目してください。 これらを指定しない場合、GridLayout は、向きに基づいて各子ビューを順番に割り当てます。 たとえば、GridLayout の向きを次のように既定 (水平) から垂直に変更してみましょう。
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="2"
android:columnCount="2"
android:orientation="vertical">
</GridLayout>
GridLayout は、次に示すように、左から右ではなく、上から下に各列でセルを配置します。
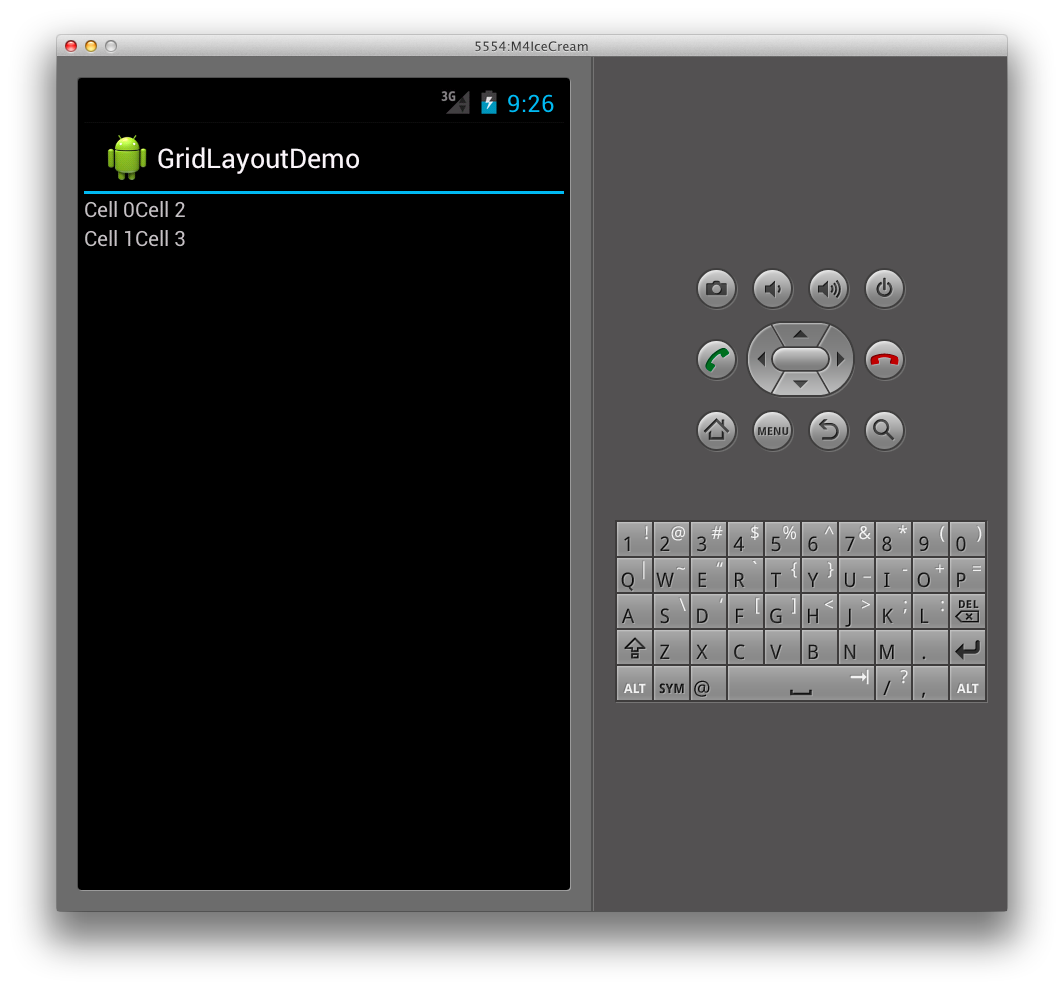
この結果、実行時に次のユーザー インターフェイスになります。
明示的な位置の指定
GridLayout で子ビューの位置を明示的に制御する場合は、layout_row 属性と layout_column 属性を設定できます。 たとえば、次の XML では、向きに関係なく、最初のスクリーンショット (上の図) に示されているレイアウトになります。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="2"
android:columnCount="2">
<TextView
android:text="Cell 0"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 1"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="1" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 2"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 3"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="1" />
</GridLayout>
間隔の指定
GridLayout の子ビュー間の間隔を指定するオプションがいくつかあります。 次に示すように、layout_margin 属性を使用して各子ビューの余白を直接設定できます
<TextView
android:text="Cell 0"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_margin="10dp" />
さらに、Android 4 では、Space と呼ばれる新しい汎用の間隔ビューが使用できるようになりました。 これを使用するには、子ビューとして追加するだけです。
たとえば、次の XML では、rowcount を 3 に設定して GridLayout に追加行を追加し、TextViews の間の間隔を指定する Space ビューを追加します。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="3"
android:columnCount="2"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:text="Cell 0"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 1"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="1" />
<Space
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 2"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 3"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="1" />
</GridLayout>
この XML では、次のように GridLayout で間隔が生じます。
新しい Space ビューを使用する利点は、間隔を確保でき、すべての子ビューに属性を設定する必要がないことです。
列と行のスパニング
また、GridLayout は、複数の列と行にまたがるセルもサポートします。 たとえば、次に示すように、ボタンを含む別の行を GridLayout に追加するとします。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:rowCount="4"
android:columnCount="2"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:text="Cell 0"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 1"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="0"
android:layout_column="1" />
<Space
android:layout_row="1"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_width="50dp"
android:layout_height="50dp" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 2"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="0" />
<TextView
android:text="Cell 3"
android:textSize="14dip"
android:layout_row="2"
android:layout_column="1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/myButton"
android:text="@string/hello"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_column="0" />
</GridLayout>
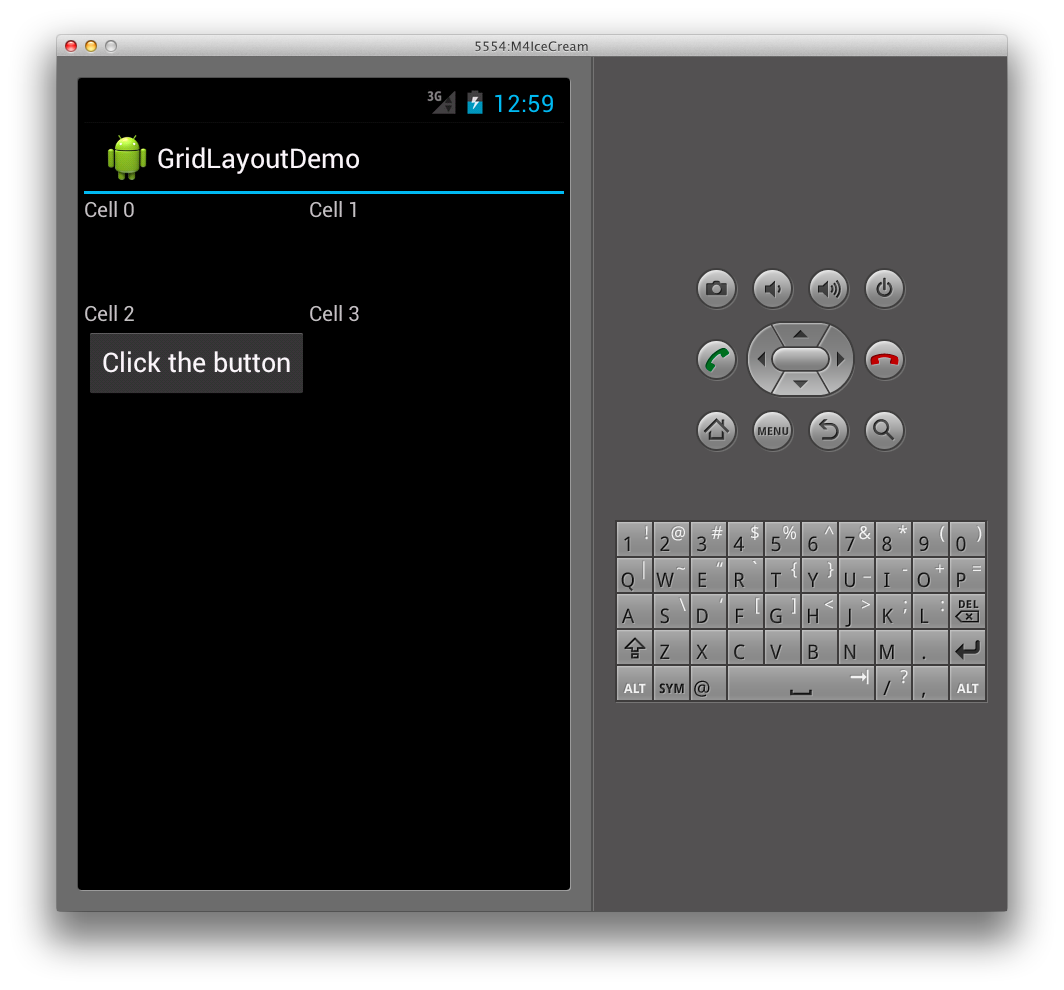
この結果、次に示すように、GridLayout の最初の列がボタンのサイズに合わせて拡張されます。
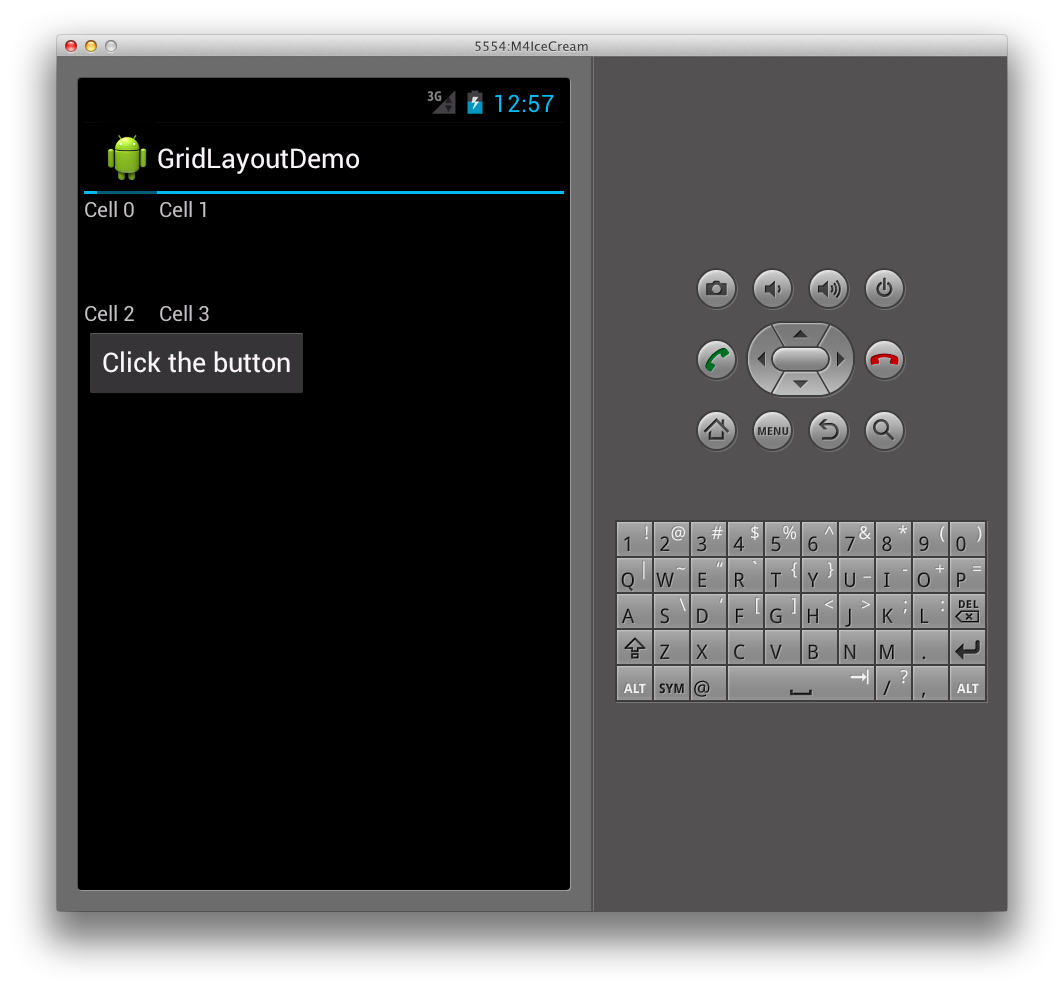
最初の列が拡張されないようにするには、次のように列のスパンを設定して、2 つの列にまたがるようにボタンを設定できます。
<Button
android:id="@+id/myButton"
android:text="@string/hello"
android:layout_row="3"
android:layout_column="0"
android:layout_columnSpan="2" />
これにより、前のレイアウトに似た TextViews のレイアウトになり、次に示すようにボタンが GridLayout の下部に追加されます。