3.7 Negotiation Discovery Details
Using the notation as specified in [RFC2409] section 3.2, the generalized form of an IKE phase 1 (MM) exchange is as shown in the following figure. For more information, see [RFC2409] section 5.
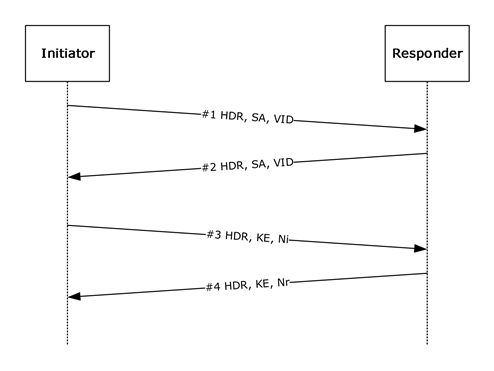
Figure 5: IKE phase 1 (MM) exchange
The description in this section uses the MM message numbers from the protocol sequence diagram.
Using the notation as specified in [RFC2409] section 3.2, the generalized form of an IKE phase 2 (quick mode) exchange is as shown in the following figure. For more information, see [RFC2409] section 5.5.
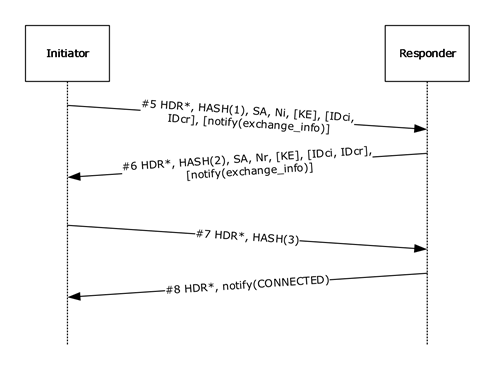
Figure 6: IKE phase 2 (QM) exchange
The description in this section uses the quick mode message numbers from the protocol sequence diagram.
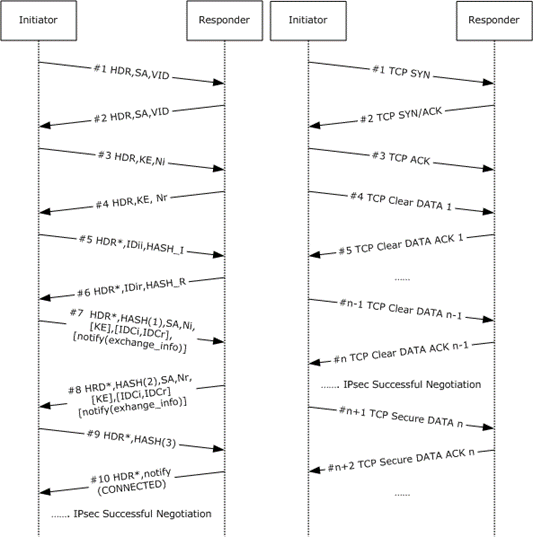
Figure 7: Negotiation discovery of a TCP connection between two IPsec-capable peers
The TCP packet exchanges happen in parallel with the IKE exchanges that are described in the first two figures of this section ("IKE phase 1 (MM) exchange" and "IKE phase 2 (QM) exchange"). The preceding figure illustrates one of many ways in which the packets might interleave. When the IKE exchange completes the successful IPsec negotiation (figure "IKE phase 2 (QM) exchange"), the TCP connection is secured.
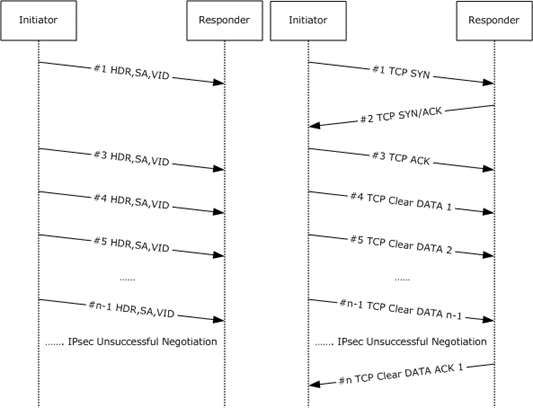
Figure 8: Negotiation discovery of a TCP connection between an IPsec-capable peer and a non-IPsec-capable peer.
The TCP packet exchanges happen in parallel with the IKE exchanges that are described in the first two figures of this section ("IKE phase 1 (MM) exchange" and "IKE phase 2 (QM) exchange"). The preceding figure illustrates one of many ways in which the packets might interleave. The responder (1) does not respond to the IKE negotiation (an unsuccessful IPsec negotiation), and the TCP connection continues in the clear.
If the responder (1) responds to the IKE negotiation, IKE fails because the responder (1) does not have, by definition, a valid credential (it is non-IPsec-capable). However, the IKE failure does not affect the TCP stream, and the TCP connection continues in the clear.