2.1.12.1 Principal
The following example shows the usage of the PrincipalRole element in defining a ReferentialConstraint element.
-
<Principal Role="Employee"> <PropertyRef Name="EmployeeID" /> </Principal>
The following rules apply to the PrincipalRole element:
One PrincipalRole MUST be used to define the Principal end of the ReferentialConstraint.
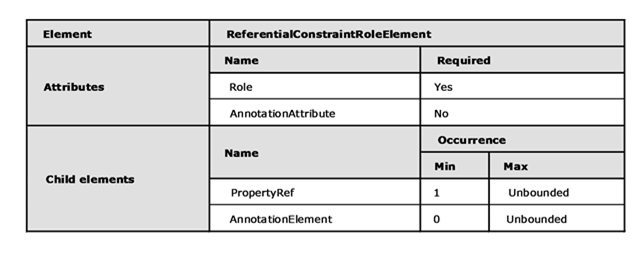
Each PrincipalRole specifies one and only one Role attribute that is of type SimpleIdentifier.
Principal has one or more PropertyRef elements. Each PropertyRef element specifies a name by using the Name attribute.
For each Principal, a PropertyRef definition cannot specify a Name value that is specified for another PropertyRef.
PropertyRef is used to specify the properties that participate in the PrincipalRole of the ReferentialConstraint.
Each PropertyRef element on the Principal corresponds to a PropertyRef on the Dependent. The Principal and the Dependent of the ReferentialConstraint contains the same number of PropertyRef elements. The PropertyRef elements on the Dependent are listed in the same order as the corresponding PropertyRef elements on the Principal.
The Principal of a ReferentialConstraint MUST specify all properties that constitute the Key of the EntityType that forms the Principal of the ReferentialConstraint.
The Multiplicity of the PrincipalRole is 1. For CSDL 2.0 and CSDL 3.0, the Multiplicity of the PrincipalRole can be 1 or 0.1.
The data type of each property that is defined in the PrincipalRole MUST be the same as the data type of the corresponding property that is specified in the DependentRole.
In CSDL 2.0 and CSDL 3.0, Principal can contain any number of AnnotationElement elements.
Child elements of Principal are to appear in this sequence: PropertyRef, AnnotationElement.
 All
child elements are to appear in the order indicated.
All
child elements are to appear in the order indicated.