CloudScript の ES6 機能
CloudScript の実行時環境は、最新の ECMAScript 6 機能のほとんどをサポートしています。 これらの機能の大部分は構文的なトリックですが、これらを使用して CloudScript コードを改善および簡素化できます。
ES6 機能の完全な概要については、こちらのチート シートで確認できます。
このチュートリアルでは、CloudScript で使用できるいくつかのコツを紹介します。
注意
一部の機能では厳格なモードが必要となります。 CloudScript ファイルの最初の行に以下のコードを配置して、このモードを有効にしてください。use strict;
文字列補間
プレイヤーに対するメッセージを作成する際、複数行の補間文字列が必要な場合があります。
バッククォート記号を使用して補間文字列を作成します。 次に、${ variable } 構文を使用して、データを直接文字列に挿入できます。
これによって文字列の連結を避け、コードの読みやすさを改善できます。
注意
バッククォート文字列は逐語的で、複数行の場合があります。 これは、あらゆる余分なスペース/タブが文字列に含まれるため、すべてのインデントに注意する必要があること意味します。
function sendPushNotification(playerName, prizeAmount, newLevel) {
let message = `Congratulations ${playerName}!
You have reached level ${newLevel}.
You get ${prizeAmount} coins for your efforts.`;
// Use message variable and send push notification
// ...
}
新しいメソッドとアロー関数
ES6 ではアロー演算子 => を使用して、新しい文字列で関数を定義できます。 以下のスニペットは、特定の演算子を使用した場合のおおよその変換です。
// The following snippets:
const add = (a,b) => a+b;
const add = (a,b) => {
return a+b;
}
// Both translate into something like
function add(a, b) {
return a+b;
}
この演算子と新しい Array.findIndexメソッドを組み合わせることで、以下の見栄えの良い簡潔なコードで、プリディケートによって検索できます。
const players = [...]; // Suppose this is an array of Player Profiles
// Search by predicate: find item in 'players' that has 'DisplayName' set to 'Bob':
const bobIndex = players.findIndex(p => p.DisplayName === 'Bob');
オブジェクトの割り当て
Object.assign メソッドでは、新しい一連のプロパティとメソッドで、あらゆるオブジェクトを簡単に拡張できます。
幅広い使用方法があるこのメソッドは、ハンドラー オブジェクトを拡張し、ハンドラーのグループを作成する際に特に便利です。
let TestHandlers = {
TestLeaderboards : (args, ctx) => {
// Test leaderboards code
},
TestPrizes : (args, ctx) => {
// Test prizes code
}
// ...
}
let ProductionHandlers = {
CleanUp : (args, ctx) => {
// System clean up code
},
GrantTournamentAccess : (args, ctx) => {
// Another useful production code
}
// ...
}
// Install both handler groups:
Object.assign(handlers, TestHandlers);
Object.assign(handlers, ProductionHandlers);
// Comment out the group to disable it but keep the relevant code
// Object.assign(handlers, SomeOtherHandlers);
これによってハンドラーのグループをすばやく有効化および無効化できるだけでなく、ハンドラーを処理し、例外処理などの役立つコードでラップするためのポイントを提供します。
以下のコードは、前回のスニペットを自動例外ロギングで拡張します。 例としてここでは問題をログ記録しますが (常に役立つとは限りません)、動作は好みに合わせて拡張できます。
// Handlers installer wraps the handler to catch error
function installHandlers(handlersObject) {
for (let property in handlersObject) {
handlersObject[property] = wrapHandler(handlersObject,property)
}
Object.assign(handlers, handlersObject);
}
// Utility
function wrapHandler(obj, key) {
if (obj.hasOwnProperty(key) && typeof obj[key] === 'function') {
let original = obj[key]; // Take the original function
return function() { // return a new function that
try { // Wraps the original invocation with try
return original.apply(null,arguments); // Do not forget to pass arguments
} catch (error) { // If error occurs
log.error(error); // We log it, but you may want to retry / do something else
throw error; // Rethrow to keep the original behaviour
}
}
} else { // If property is not a function, ignore it
return obj[key];
}
}
// Install handler groups:
installHandlers(TestHandlers);
installHandlers(ProductionHandlers);
ゲッター
「ゲッター」を使用して、一般的な API コールをより構文的に適切な形式にカプセル化できます。 以下のタイトル データの状態を検討してください。
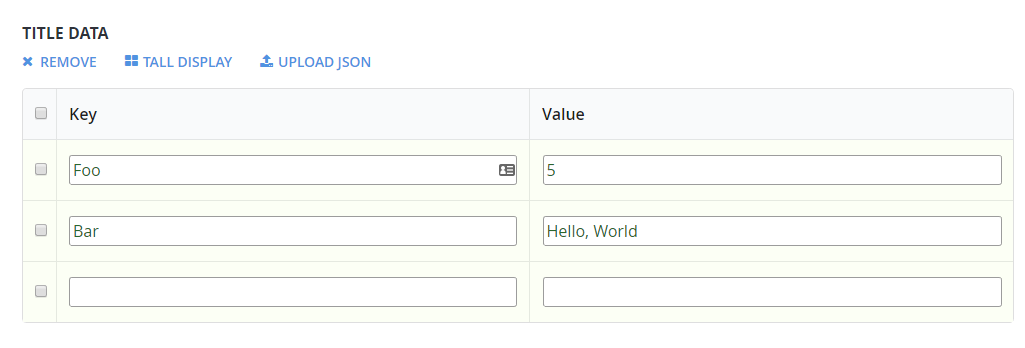
以下のスニペットは、TitleData から Foo と Bar のデータを取得し、それらを非常に簡単に使用する方法を示しています。
'use strict'
// Define
let App = {
get TitleData() {
// Please, consider limiting the query by defining certain keys that you need
return server.GetTitleData({}).Data;
},
}
// Use
handlers.TestFooBar = () => {
// Client code is clean and does not show the fact of calling any functions / making api request
var titleData = App.TitleData; // Note that this implementation makes an API call every time it's accessed
log.debug(titleData.Foo);
log.debug(titleData.Bar);
}