コマンド実行
Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) パターンを使用する .NET Multi-Platform App UI (.NET MAUI) アプリでは、ビューモデル (通常は INotifyPropertyChanged から派生するクラス) のプロパティとビュー (通常は XAML ファイル) のプロパティの間でデータ バインディングが定義されます。 場合によっては、アプリでは、ビューモデルに何らかの影響を及ぼすコマンドの開始をユーザーに求めることで、これらのプロパティ バインディング以上の処理を行う必要があります。 通常、このようなコマンドはボタンのクリックや指のタップによって通知され、従来は、Button の Clicked のイベントまたは TapGestureRecognizer の Tapped イベントに対するハンドラーの分離コード ファイル内で処理されます。
コマンド実行インターフェイスでは、MVVM アーキテクチャにいっそうよく適した代わりのコマンド実装方法が提供されます。 ビューモデル自体にコマンドを含めることができます。その場合のコマンドは、Button クリックのようなビュー内の特定のアクティビティに対応して実行されるメソッドです。 データ バインディングは、これらのコマンドと Button の間で定義されます。
Button とビューモデル間のデータ バインディングを可能にするには、Button で 2 つのプロパティを定義します。
Command(System.Windows.Input.ICommand型)CommandParameter(Object型)
コマンド インターフェイスを使用するには、ビューモデルの ICommand 型のプロパティをソースとし、Button の Command プロパティをターゲットとするデータ バインディングを定義します。 ビューモデルにはその ICommand プロパティに関連付けられたコードが含まれており、ボタンを選択すると実行されます。 複数のボタンがすべてビューモデルの同じ ICommand プロパティにバインドされている場合は、CommandParameter プロパティを任意のデータに設定して、これらのボタンを区別できます。
他の多くのビューにも、Command プロパティと CommandParameter プロパティが定義されています。 これらのコマンドはすべて、ビュー内のユーザー インターフェイス オブジェクトに依存しない方法で、ビューモデル内で処理できます。
ICommand
ICommand インターフェイスは、System.Windows.Input 名前空間に定義されており、2 つのメソッドと 1 つのイベントで構成されます。
public interface ICommand
{
public void Execute (Object parameter);
public bool CanExecute (Object parameter);
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
}
コマンド インターフェイスを使用するには、ビューモデルに ICommand 型のプロパティを含めます。
public ICommand MyCommand { private set; get; }
ビューモデルでは、ICommand インターフェイスを実装するクラスも参照する必要があります。 ビューでは、Button の Command プロパティがそのプロパティにバインドされます。
<Button Text="Execute command"
Command="{Binding MyCommand}" />
ユーザーが Button をクリックすると、Button では、その Command プロパティにバインドされた ICommand オブジェクトの Execute メソッドが呼び出されます。
Button の Command プロパティでバインディングが最初に定義されるとき、およびどこかでデータ バインディングが変更されるときに、Button は ICommand オブジェクトの CanExecute メソッドを呼び出します。 CanExecute から false が返されると、Button はそれ自体を無効にします。 これは、特定のコマンドが現在使用できないか無効であることを示します。
また、Button では、ICommand の CanExecuteChanged イベントでハンドラーがアタッチされます。 このイベントはビューモデル内から発生します。 このイベントが発生すると、Button が CanExecute をもう一度呼び出します。 CanExecute から true が返されると Button は有効になり、CanExecute から false が返されると無効になります。
警告
コマンド インターフェイスを使用している場合は、Button の IsEnabled プロパティを使用しないでください。
ビューモデルで ICommand 型のプロパティを定義する場合は、ICommand インターフェイスを実装するクラスをビューモデルに含めるか、ビューモデルで参照する必要があります。 このクラスでは、Execute および CanExecute メソッドが含まれるか参照されていて、CanExecute メソッドで異なる値が返されたときは常に CanExecuteChanged イベントが生成される必要があります。 .NET MAUI に含まれている Command または Command<T> クラスを使用して、ICommand インターフェイスを実装できます。 これらのクラスを使用すると、クラスのコンストラクターで Execute および CanExecute メソッドの本体を指定できます。
ヒント
CommandParameter プロパティを使用して、同じ ICommand プロパティにバインドされている複数のビューを区別する場合は Command<T> を使用し、その必要がない場合は Command クラスを使用します。
基本的なコマンド実行
次の例では、ビューモデルに実装される基本的なコマンドを示しています。
PersonViewModel クラスには、個人を定義する Name、Age、Skills という名前の 3 つのプロパティが定義されています。
public class PersonViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
string name;
double age;
string skills;
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public string Name
{
set { SetProperty(ref name, value); }
get { return name; }
}
public double Age
{
set { SetProperty(ref age, value); }
get { return age; }
}
public string Skills
{
set { SetProperty(ref skills, value); }
get { return skills; }
}
public override string ToString()
{
return Name + ", age " + Age;
}
bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
if (Object.Equals(storage, value))
return false;
storage = value;
OnPropertyChanged(propertyName);
return true;
}
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
次に示す PersonCollectionViewModel クラスでは、PersonViewModel 型の新しいオブジェクトを作成して、ユーザーがデータを入力できるようにしています。 そのため、このクラスには、bool 型の IsEditing プロパティと、PersonViewModel 型の PersonEdit プロパティが定義されています。 さらに、クラスでは、ICommand 型の 3 つのプロパティと、Persons という名前の IList<PersonViewModel> 型のプロパティが定義されています。
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
PersonViewModel personEdit;
bool isEditing;
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
···
public bool IsEditing
{
private set { SetProperty(ref isEditing, value); }
get { return isEditing; }
}
public PersonViewModel PersonEdit
{
set { SetProperty(ref personEdit, value); }
get { return personEdit; }
}
public ICommand NewCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand SubmitCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand CancelCommand { private set; get; }
public IList<PersonViewModel> Persons { get; } = new ObservableCollection<PersonViewModel>();
bool SetProperty<T>(ref T storage, T value, [CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
if (Object.Equals(storage, value))
return false;
storage = value;
OnPropertyChanged(propertyName);
return true;
}
protected void OnPropertyChanged([CallerMemberName] string propertyName = null)
{
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
}
この例では、3 つの ICommand プロパティと Persons プロパティを変更しても、PropertyChanged イベントは発生しません。 これらのプロパティはすべて、クラスが最初に作成されるときに設定され、その後は変更されません。
次の例は、PersonCollectionViewModel を使用する XAML を示しています。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DataBindingDemos"
x:Class="DataBindingDemos.PersonEntryPage"
Title="Person Entry"
x:DataType="local:PersonCollectionViewModel">
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<local:PersonCollectionViewModel />
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<Grid Margin="10">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<!-- New Button -->
<Button Text="New"
Grid.Row="0"
Command="{Binding NewCommand}"
HorizontalOptions="Start" />
<!-- Entry Form -->
<Grid Grid.Row="1"
IsEnabled="{Binding IsEditing}">
<Grid x:DataType="local:PersonViewModel"
BindingContext="{Binding PersonEdit}">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
<RowDefinition Height="Auto" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="Auto" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Label Text="Name: " Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" />
<Entry Text="{Binding Name}"
Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="1" />
<Label Text="Age: " Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" />
<StackLayout Orientation="Horizontal"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="1">
<Stepper Value="{Binding Age}"
Maximum="100" />
<Label Text="{Binding Age, StringFormat='{0} years old'}"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
</StackLayout>
<Label Text="Skills: " Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0" />
<Entry Text="{Binding Skills}"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1" />
</Grid>
</Grid>
<!-- Submit and Cancel Buttons -->
<Grid Grid.Row="2">
<Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
<ColumnDefinition Width="*" />
</Grid.ColumnDefinitions>
<Button Text="Submit"
Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding SubmitCommand}"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
<Button Text="Cancel"
Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding CancelCommand}"
VerticalOptions="Center" />
</Grid>
<!-- List of Persons -->
<ListView Grid.Row="3"
ItemsSource="{Binding Persons}" />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、ページの BindingContext プロパティは PersonCollectionViewModel に設定されています。 Grid に含まれる Button には、"New" というテキストと、ビューモデルの NewCommand プロパティにバインドされる Command プロパティが設定されています。入力フォームのプロパティは、IsEditing プロパティと PersonViewModel のプロパティにバインドされていて、さらに 2 つのボタンが、ビューモデルの SubmitCommand プロパティと CancelCommand プロパティにバインドされています。 ListView には、既に入力されたユーザーのコレクションが表示されます。
次のスクリーンショットには、年齢を設定した後で有効になった [送信] ボタンが表示されています。
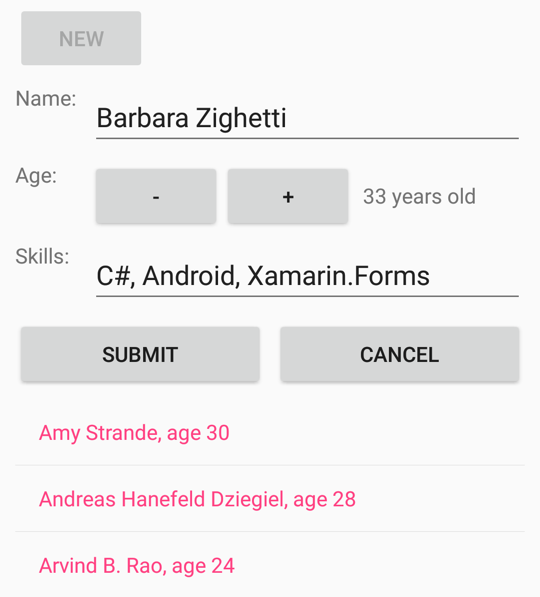
ユーザーが最初に [新規] ボタンを押すと、入力フォームは有効になりますが、[新規] ボタンは無効になります。 その後、ユーザーは名前、年齢、スキルを入力します。 編集中いつでも、ユーザーは [Cancel] ボタンを押して最初からやり直すことができます。 名前と有効な年齢が入力された場合にのみ、[Submit] ボタンが有効になります。 この [Submit] ボタンを押して、ListView に表示されているコレクションにユーザーを転送します。 [Cancel] または [Submit] ボタンを押すと、入力フォームがクリアされ、[New] ボタンが再び有効になります。
[New]、[Submit]、[Cancel] ボタンに対するすべてのロジックは、NewCommand、SubmitCommand、CancelCommand プロパティの定義によって PersonCollectionViewModel で処理されます。 PersonCollectionViewModel のコンストラクターでは、これら 3 つのプロパティに Command 型のオブジェクトが設定されます。
Command クラスのコンストラクターにより、Execute と CanExecute メソッドに対応する Action 型と Func<bool> 型の引数を渡すことができるようになります。 このアクションと関数は、Command コンストラクターでラムダ関数として定義できます。
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
NewCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
PersonEdit = new PersonViewModel();
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged += OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
IsEditing = true;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return !IsEditing;
});
···
}
void OnPersonEditPropertyChanged(object sender, PropertyChangedEventArgs args)
{
(SubmitCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
}
void RefreshCanExecutes()
{
(NewCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
(SubmitCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
(CancelCommand as Command).ChangeCanExecute();
}
···
}
ユーザーが [New] ボタンをクリックすると、Command コンストラクターに渡された execute 関数が実行されます。 これにより、新しい PersonViewModel オブジェクトが作成され、そのオブジェクトの PropertyChanged イベントにハンドラーが設定されて、IsEditing が true に設定された後、コンストラクターの後に定義されている RefreshCanExecutes メソッドが呼び出されます。
ICommand インターフェイスを実装するだけでなく、Command クラスでは ChangeCanExecute という名前のメソッドも定義されています。 ビューモデルでは、CanExecute メソッドの戻り値が変更されるような場合は常に、ICommand プロパティの ChangeCanExecute を呼び出す必要があります。 ChangeCanExecute を呼び出すと、Command クラスで CanExecuteChanged イベントが発生します。 Button では、そのイベントに対してハンドラーがアタッチされており、応答として CanExecute が再び呼び出され、そのメソッドの戻り値に基づいてそれ自体が有効にされます。
NewCommand の execute メソッドで RefreshCanExecutes が呼び出されると、NewCommand プロパティは ChangeCanExecute の呼び出しを取得します。Button では canExecute メソッドが呼び出されて、IsEditing プロパティが true であるためメソッドは false を返します。
新しい PersonViewModel オブジェクトの PropertyChanged ハンドラーは、SubmitCommand の ChangeCanExecute メソッドを呼び出します。
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
···
SubmitCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Persons.Add(PersonEdit);
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged -= OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
PersonEdit = null;
IsEditing = false;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return PersonEdit != null &&
PersonEdit.Name != null &&
PersonEdit.Name.Length > 1 &&
PersonEdit.Age > 0;
});
···
}
···
}
編集されている PersonViewModel オブジェクトでプロパティが変更されるたびに、SubmitCommand の canExecute 関数が呼び出されます。 それは、Name プロパティが 1 文字以上の長さで、Age が 0 より大きい場合にのみ、true を返します。 その時点で、[Submit] ボタンが有効になります。
[送信] ボタンの execute 関数は、PersonViewModel からプロパティ変更ハンドラーを削除し、Persons コレクションにオブジェクトを追加して、すべてを初期状態に戻します。
[Cancel] ボタンの execute 関数で行われることは、コレクションへのオブジェクトの追加を除き、[Submit] ボタンで行われることと同じです。
public class PersonCollectionViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public PersonCollectionViewModel()
{
···
CancelCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
PersonEdit.PropertyChanged -= OnPersonEditPropertyChanged;
PersonEdit = null;
IsEditing = false;
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return IsEditing;
});
}
···
}
canExecute メソッドでは、PersonViewModel が編集されているときは常に true が返されます。
Note
execute および canExecute メソッドをラムダ関数として定義する必要はありません。 ビューモデルでプライベート メソッドとして記述し、Command コンストラクターで参照できます。 ただし、この方法では、ビューモデル内で 1 回だけ参照されるメソッドが多くなる場合があります。
コマンド パラメーターの使用
複数のボタン、または他のユーザー インターフェイス オブジェクトで、ビューモデル内の同じ ICommand プロパティを共有すると便利な場合があります。 この場合、CommandParameter プロパティを使用してボタンを区別します。
これらの共有 ICommand プロパティに対しては、Command クラスを引き続き使用できます。 このクラスでは、Object 型のパラメーターを持つ execute メソッドと canExecute メソッドを受け入れる代替コンストラクターを定義します。 これが、これらのメソッドに CommandParameter を渡す方法です。 ただし、CommandParameter を指定する場合は、汎用の Command<T> クラスを使ってオブジェクトの型を CommandParameter に設定するように指定するのが最も簡単な方法です。 指定した execute および canExecute メソッドは、その型のパラメーターを持つようになります。
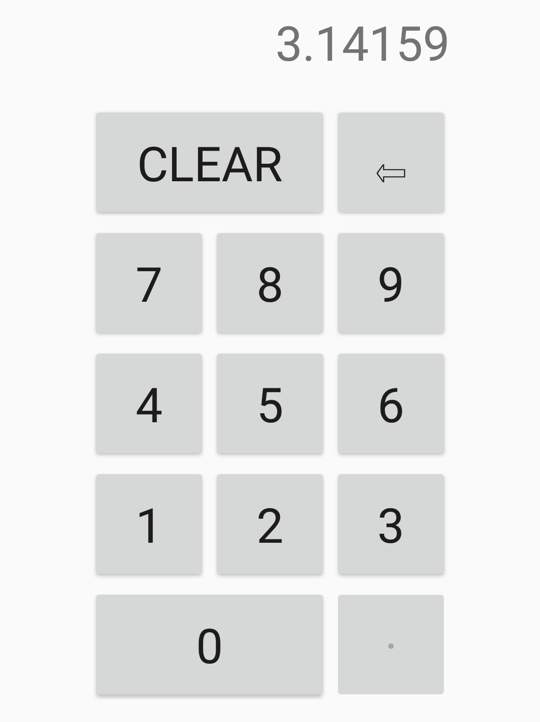
次の例では、10 進数を入力するためのキーボードを示します。
<ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:DataBindingDemos"
x:Class="DataBindingDemos.DecimalKeypadPage"
Title="Decimal Keyboard"
x:DataType="local:DecimalKeypadViewModel">
<ContentPage.BindingContext>
<local:DecimalKeypadViewModel />
</ContentPage.BindingContext>
<ContentPage.Resources>
<Style TargetType="Button">
<Setter Property="FontSize" Value="32" />
<Setter Property="BorderWidth" Value="1" />
<Setter Property="BorderColor" Value="Black" />
</Style>
</ContentPage.Resources>
<Grid WidthRequest="240"
HeightRequest="480"
ColumnDefinitions="80, 80, 80"
RowDefinitions="Auto, Auto, Auto, Auto, Auto, Auto"
ColumnSpacing="2"
RowSpacing="2"
HorizontalOptions="Center"
VerticalOptions="Center">
<Label Text="{Binding Entry}"
Grid.Row="0" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="3"
Margin="0,0,10,0"
FontSize="32"
LineBreakMode="HeadTruncation"
VerticalTextAlignment="Center"
HorizontalTextAlignment="End" />
<Button Text="CLEAR"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Command="{Binding ClearCommand}" />
<Button Text="⇦"
Grid.Row="1" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding BackspaceCommand}" />
<Button Text="7"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="7" />
<Button Text="8"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="8" />
<Button Text="9"
Grid.Row="2" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="9" />
<Button Text="4"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="4" />
<Button Text="5"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="5" />
<Button Text="6"
Grid.Row="3" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="6" />
<Button Text="1"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="0"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="1" />
<Button Text="2"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="1"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="2" />
<Button Text="3"
Grid.Row="4" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="3" />
<Button Text="0"
Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="0" Grid.ColumnSpan="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="0" />
<Button Text="·"
Grid.Row="5" Grid.Column="2"
Command="{Binding DigitCommand}"
CommandParameter="." />
</Grid>
</ContentPage>
この例では、ページの BindingContext は DecimalKeypadViewModel です。 この ViewModel の Entry プロパティは、Label の Text プロパティにバインドされます。 すべての Button オブジェクトは、ViewModel のさまざまなコマンド (ClearCommand、BackspaceCommand、DigitCommand) にバインドされます。 10 桁の数字と小数点を示す 11 個のボタンは、DigitCommand へのバインディングを共有します。 CommandParameter によって、これらのボタンが区別されます。 一般に、CommandParameter に設定される値はボタンによって表示されるテキストと同じですが、小数点だけは例外で、わかりやすくするために中黒の記号で表示されます。
DecimalKeypadViewModel では、string 型の Entry プロパティと、ICommand 型の 3 つのプロパティを定義します。
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
string entry = "0";
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
···
public string Entry
{
private set
{
if (entry != value)
{
entry = value;
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs("Entry"));
}
}
get
{
return entry;
}
}
public ICommand ClearCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand BackspaceCommand { private set; get; }
public ICommand DigitCommand { private set; get; }
}
ClearCommand に対応するボタンは常に有効になっており、単にエントリを「0」に戻します。
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
ClearCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Entry = "0";
RefreshCanExecutes();
});
···
}
void RefreshCanExecutes()
{
((Command)BackspaceCommand).ChangeCanExecute();
((Command)DigitCommand).ChangeCanExecute();
}
···
}
ボタンは常に有効になっているため、Command コンストラクターで canExecute 引数を指定する必要はありません。
バックスペース ボタンは、入力の長さが 1 より大きい場合、または Entry が文字列 "0" と等しくない場合にのみ、有効になります。
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
···
BackspaceCommand = new Command(
execute: () =>
{
Entry = Entry.Substring(0, Entry.Length - 1);
if (Entry == "")
{
Entry = "0";
}
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: () =>
{
return Entry.Length > 1 || Entry != "0";
});
···
}
···
}
バックスペース ボタンの execute 関数のロジックでは、Entry が少なくとも文字列 "0" であることが確認されます。
DigitCommand は 11 個のボタンにバインドされており、それぞれが CommandParameter プロパティで識別されます。 DigitCommand は Command<T> クラスのインスタンスに設定されています。 XAML でコマンド実行インターフェイスを使用する場合、CommandParameter プロパティは通常は文字列であり、汎用引数の型です。 execute 関数と canExecute 関数の引数は string 型です。
public class DecimalKeypadViewModel : INotifyPropertyChanged
{
···
public DecimalKeypadViewModel()
{
···
DigitCommand = new Command<string>(
execute: (string arg) =>
{
Entry += arg;
if (Entry.StartsWith("0") && !Entry.StartsWith("0."))
{
Entry = Entry.Substring(1);
}
RefreshCanExecutes();
},
canExecute: (string arg) =>
{
return !(arg == "." && Entry.Contains("."));
});
}
···
}
execute メソッドは、Entry プロパティに文字列引数を追加します。 ただし、結果が 0 で始まる場合は (ただし、0 でも小数でもない)、Substring 関数を使用して最初の 0 を削除する必要があります。 canExecute メソッドは、引数が小数点であり (小数点が押されたことを示す)、Entry に小数点が既に含まれる場合にのみ、false を返します。 すべての execute メソッドは RefreshCanExecutes を呼び出し、それはさらに DigitCommand と ClearCommand の両方に対して ChangeCanExecute を呼び出します。 これにより、現在入力されている数字のシーケンスに基づいて、小数点ボタンとバックスペース ボタンが有効または無効になります。
.NET MAUI
 サンプルを参照する
サンプルを参照する