チュートリアル: イメージ処理ネットワークの作成
このドキュメントでは、画像処理を実行する非同期メッセージ ブロックのネットワークを作成する方法について説明します。
このネットワークでは、画像の特性に基づいて、画像に対して実行する操作を決定します。 この例では、ネットワークを介して画像をルーティングするために、"データフロー" モデルを使用します。 このデータフロー モデルでは、プログラム内の独立したコンポーネント同士が、メッセージを送信することによって相互に通信します。 コンポーネントは、メッセージを受信すると、なんらかのアクションを実行し、そのアクションの結果を別のコンポーネントに渡すことができます。 これを "制御フロー" モデルと比較してください。制御フロー モデルでは、アプリケーションは制御構造 (条件付きステートメントやループなど) を使用してプログラムでの操作の順序を制御します。
データフローに基づくネットワークでは、タスクの "パイプライン" を作成します。 パイプラインの各ステージでは、タスク全体の一部が同時に実行されます。 これは、自動車製造の組み立てラインに例えることができます。 各車両が組み立てラインを通過するときに、あるステーションではフレームを組み立て、別のステーションではエンジンを取り付けます。 組み立てラインでは、複数の車両を同時に組み立てることができるため、完全な車両を 1 台ずつ組み立てるよりもスループットが向上します。
前提条件
このチュートリアルを開始する前に、次のドキュメントを参照してください。
また、このチュートリアルを開始する前に、GDI+ の基本を理解しておくことをお勧めします。
セクション
このチュートリアルは、次のセクションで構成されています。
画像処理機能の定義
このセクションでは、画像処理ネットワークがディスクから読み取られた画像を処理するために使用するサポート関数を示します。
次の GetRGB 関数と MakeColor 関数は、それぞれ、指定された色の個々の成分を抽出し、結合します。
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
次の ProcessImage 関数は、指定された std::function オブジェクトを呼び出して、GDI+ Bitmap オブジェクト内の各ピクセルのカラー値を変換します。 ProcessImage 関数は、concurrency::parallel_for アルゴリズムを使用して、ビットマップの各行を並列処理します。
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
次の Grayscale、Sepiatone、ColorMask、Darken の各関数は、ProcessImage 関数を呼び出して、Bitmap オブジェクト内の各ピクセルのカラー値を変換します。 これらの各関数では、ラムダ式を使用して 1 つのピクセルの色変換を定義します。
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
次の GetColorDominance 関数も ProcessImage 関数を呼び出します。 ただし、この関数は各色の値を変更するのではなく、concurrency::combinable オブジェクトを使用して、赤、緑、青のどの色成分が画像の主調色となっているかを計算します。
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
次の GetEncoderClsid 関数は、指定された MIME の種類のエンコーダーのクラス識別子を取得します。 アプリケーションは、この関数を使用してビットマップのエンコーダーを取得します。
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
[トップ]
画像処理ネットワークの作成
このセクションでは、指定されたディレクトリ内の各 JPEG (.jpg) イメージに対して画像処理を実行する非同期メッセージ ブロックのネットワークを作成する方法について説明します。 このネットワークでは、次の画像処理操作を実行します。
Tom によって作成された画像の場合、グレースケールに変換します。
赤を主調色とする画像の場合、緑と青の成分を除去して暗くします。
その他の画像にはセピア調を適用します。
ネットワークは、これらの条件のいずれかに一致する最初の画像処理操作のみを適用します。 たとえば、画像が Tom によって作成され、主調色が赤の場合、その画像ではグレースケールへの変換のみが行われます。
ネットワークは、各画像処理操作を実行した後、画像をビットマップ (.bmp) ファイルとしてディスクに保存します。
次の手順では、この画像処理ネットワークを実装し、そのネットワークを指定されたディレクトリ内のすべての JPEG イメージに適用する関数を作成する方法を示します。
画像処理ネットワークを作成するには
ディスク上のディレクトリの名前を受け取る
ProcessImages関数を作成します。void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory) { }ProcessImages関数で、countdown_event変数を作成します。countdown_eventクラスについては、このチュートリアルで後述します。// Holds the number of active image processing operations and // signals to the main thread that processing is complete. countdown_event active(0);Bitmapオブジェクトを元のファイル名に関連付ける std::map オブジェクトを作成します。// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names. map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;次のコードを追加して、画像処理ネットワークのメンバーを定義します。
// // Create the nodes of the network. // // Loads Bitmap objects from disk. transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap( [&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* { Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str()); if (bmp != nullptr) bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name)); return bmp; } ); // Holds loaded Bitmap objects. unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps; // Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Grayscale(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; // Retrieve the artist name from metadata. UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist); if (size == 0) // Image does not have the Artist property. return false; PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size); bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty); string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value)); free(artistProperty); return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0); } ); // Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as // their dominant color. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { if (bmp == nullptr) return false; return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000); } ); // Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) { return Darken(bmp, 50); }); // Applies sepia toning to the remaining images. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone( [](Bitmap* bmp) { return Sepiatone(bmp); }, nullptr, [](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; } ); // Saves Bitmap objects to disk. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { // Replace the file extension with .bmp. wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp]; file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp"); // Save the processed image. CLSID bmpClsid; GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid); bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid); return bmp; }); // Deletes Bitmap objects. transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* { delete bmp; return nullptr; }); // Decrements the event counter. call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) { active.signal(); });次のコードを追加して、ネットワークに接続します。
// // Connect the network. // load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask); colormask.link_target(&darken); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone); loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement); grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap); darken.link_target(&save_bitmap); sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap); save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap); delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);次のコードを追加して、ディレクトリ内の各 JPEG ファイルの完全なパスをネットワークのヘッドに送信します。
// Traverse all files in the directory. wstring searchPattern = directory; searchPattern.append(L"\\*"); WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData; HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData); if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE) return; do { if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY)) { wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName; // Process only JPEG files. if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4) { // Form the full path to the file. wstring full_path(directory); full_path.append(L"\\"); full_path.append(file); // Increment the count of work items. active.add_count(); // Send the path name to the network. send(load_bitmap, full_path); } } } while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0); FindClose(hFind);countdown_event変数が 0 になるまで待ちます。// Wait for all operations to finish. active.wait();
ネットワークのメンバーを次の表に示します。
| メンバー | 説明 |
|---|---|
load_bitmap |
ディスクから Bitmap オブジェクトを読み込み、map オブジェクトにエントリを追加して、画像を元のファイル名に関連付ける concurrency::transformer オブジェクト。 |
loaded_bitmaps |
読み込まれた画像を画像処理フィルターに送信する concurrency::unbounded_buffer オブジェクト。 |
grayscale |
Tom によって作成された画像をグレースケールに変換する transformer オブジェクト。 作成者は画像のメタデータを使用して判断されます。 |
colormask |
赤を主調色とする画像から緑と青の色成分を除去する transformer オブジェクト。 |
darken |
赤を主調色とする画像を暗くする transformer オブジェクト。 |
sepiatone |
Tom によって作成されておらず、主調色が赤ではない画像にセピア調を適用する transformer オブジェクト。 |
save_bitmap |
処理された image をビットマップとしてディスクに保存する transformer オブジェクト。 save_bitmap は、map オブジェクトから元のファイル名を取得し、そのファイル名拡張子を .bmp に変更します。 |
delete_bitmap |
画像のメモリを解放する transformer オブジェクト。 |
decrement |
ネットワークのターミナル ノードとして機能する concurrency::call オブジェクト。 countdown_event オブジェクトをデクリメントして、画像が処理されたことをメイン アプリケーションに通知します。 |
loaded_bitmaps メッセージ バッファーは、unbounded_buffer オブジェクトとして、Bitmap オブジェクトを複数の受信者に提供するので重要です。 1 つのターゲット ブロックが Bitmap オブジェクトを受け入れると、unbounded_buffer オブジェクトはその Bitmap オブジェクトを他のターゲットには提供しません。 そのため、オブジェクトを unbounded_buffer オブジェクトにリンクする順序が重要となります。 grayscale、colormask、sepiatone の各メッセージ ブロックは、フィルターを使用して特定の Bitmap オブジェクトだけを受け入れます。 decrement メッセージ バッファーは、他のメッセージ バッファーによって拒否されたすべての Bitmap オブジェクトを受け入れるため、loaded_bitmaps メッセージ バッファーの重要なターゲットです。 unbounded_buffer オブジェクトには、メッセージを順番に伝達することが求められます。 そのため、unbounded_buffer オブジェクトは、新しいターゲット ブロックがリンクされるまでブロックし、現在のターゲット ブロックがメッセージを受け入れない場合にそのメッセージを受け入れます。
アプリケーションで、最初にメッセージを受け入れたメッセージ ブロックだけがそのメッセージを処理するのではなく、複数のメッセージ ブロックがメッセージを処理することが必要な場合は、メッセージ ブロックの別の型 (overwrite_buffer など) を使用できます。 overwrite_buffer クラスは、保持するメッセージは一度に 1 つですが、そのメッセージを各ターゲットに伝達します。
次の図は、イメージ処理ネットワークを示しています。
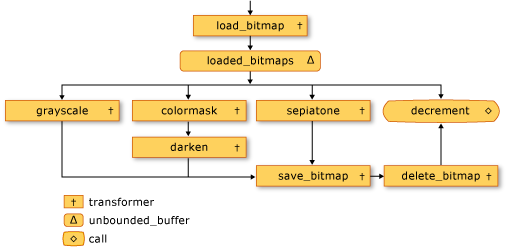
この例の countdown_event オブジェクトを使用すると、画像処理ネットワークは、すべての画像が処理されたときにメイン アプリケーションに通知できます。 countdown_event クラスは、concurrency::event オブジェクトを使用して、カウンター値が 0 になったことを通知します。 メイン アプリケーションは、ファイル名をネットワークに送信するたびにカウンターをインクリメントします。 ネットワークのターミナル ノードは、各画像が処理されたらカウンターをデクリメントします。 メイン アプリケーションは、指定されたディレクトリを走査した後、countdown_event オブジェクトからカウンターが 0 になったことが通知されるのを待ちます。
次の例は、countdown_event クラスを示しています。
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
[トップ]
完全な例
コード例全体を次に示します。 wmain 関数は GDI+ ライブラリを管理し、ProcessImages 関数を呼び出して、Sample Pictures ディレクトリ内の JPEG ファイルを処理します。
// image-processing-network.cpp
// compile with: /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib
#include <windows.h>
#include <gdiplus.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <map>
#include <agents.h>
#include <ppl.h>
using namespace concurrency;
using namespace Gdiplus;
using namespace std;
// Retrieves the red, green, and blue components from the given
// color value.
void GetRGB(DWORD color, BYTE& r, BYTE& g, BYTE& b)
{
r = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x00ff0000) >> 16);
g = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x0000ff00) >> 8);
b = static_cast<BYTE>((color & 0x000000ff));
}
// Creates a single color value from the provided red, green,
// and blue components.
DWORD MakeColor(BYTE r, BYTE g, BYTE b)
{
return (r<<16) | (g<<8) | (b);
}
// Calls the provided function for each pixel in a Bitmap object.
void ProcessImage(Bitmap* bmp, const function<void (DWORD&)>& f)
{
int width = bmp->GetWidth();
int height = bmp->GetHeight();
// Lock the bitmap.
BitmapData bitmapData;
Rect rect(0, 0, bmp->GetWidth(), bmp->GetHeight());
bmp->LockBits(&rect, ImageLockModeWrite, PixelFormat32bppRGB, &bitmapData);
// Get a pointer to the bitmap data.
DWORD* image_bits = (DWORD*)bitmapData.Scan0;
// Call the function for each pixel in the image.
parallel_for (0, height, [&, width](int y)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; ++x)
{
// Get the current pixel value.
DWORD* curr_pixel = image_bits + (y * width) + x;
// Call the function.
f(*curr_pixel);
}
});
// Unlock the bitmap.
bmp->UnlockBits(&bitmapData);
}
// Converts the given image to grayscale.
Bitmap* Grayscale(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
// Set each color component to the average of
// the original components.
BYTE c = (static_cast<WORD>(r) + g + b) / 3;
color = MakeColor(c, c, c);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies sepia toning to the provided image.
Bitmap* Sepiatone(Bitmap* bmp)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r0, g0, b0;
GetRGB(color, r0, g0, b0);
WORD r1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .393) + (g0 *.769) + (b0 * .189));
WORD g1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .349) + (g0 *.686) + (b0 * .168));
WORD b1 = static_cast<WORD>((r0 * .272) + (g0 *.534) + (b0 * .131));
color = MakeColor(min(0xff, r1), min(0xff, g1), min(0xff, b1));
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Applies the given color mask to each pixel in the provided image.
Bitmap* ColorMask(Bitmap* bmp, DWORD mask)
{
ProcessImage(bmp,
[mask](DWORD& color) {
color = color & mask;
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Darkens the provided image by the given amount.
Bitmap* Darken(Bitmap* bmp, unsigned int percent)
{
if (percent > 100)
throw invalid_argument("Darken: percent must less than 100.");
double factor = percent / 100.0;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[factor](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
r = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*r);
g = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*g);
b = static_cast<BYTE>(factor*b);
color = MakeColor(r, g, b);
}
);
return bmp;
}
// Determines which color component (red, green, or blue) is most dominant
// in the given image and returns a corresponding color mask.
DWORD GetColorDominance(Bitmap* bmp)
{
// The ProcessImage function processes the image in parallel.
// The following combinable objects enable the callback function
// to increment the color counts without using a lock.
combinable<unsigned int> reds;
combinable<unsigned int> greens;
combinable<unsigned int> blues;
ProcessImage(bmp,
[&](DWORD& color) {
BYTE r, g, b;
GetRGB(color, r, g, b);
if (r >= g && r >= b)
reds.local()++;
else if (g >= r && g >= b)
greens.local()++;
else
blues.local()++;
}
);
// Determine which color is dominant and return the corresponding
// color mask.
unsigned int r = reds.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int g = greens.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
unsigned int b = blues.combine(plus<unsigned int>());
if (r + r >= g + b)
return 0x00ff0000;
else if (g + g >= r + b)
return 0x0000ff00;
else
return 0x000000ff;
}
// Retrieves the class identifier for the given MIME type of an encoder.
int GetEncoderClsid(const WCHAR* format, CLSID* pClsid)
{
UINT num = 0; // number of image encoders
UINT size = 0; // size of the image encoder array in bytes
ImageCodecInfo* pImageCodecInfo = nullptr;
GetImageEncodersSize(&num, &size);
if(size == 0)
return -1; // Failure
pImageCodecInfo = (ImageCodecInfo*)(malloc(size));
if(pImageCodecInfo == nullptr)
return -1; // Failure
GetImageEncoders(num, size, pImageCodecInfo);
for(UINT j = 0; j < num; ++j)
{
if( wcscmp(pImageCodecInfo[j].MimeType, format) == 0 )
{
*pClsid = pImageCodecInfo[j].Clsid;
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return j; // Success
}
}
free(pImageCodecInfo);
return -1; // Failure
}
// A synchronization primitive that is signaled when its
// count reaches zero.
class countdown_event
{
public:
countdown_event(unsigned int count = 0)
: _current(static_cast<long>(count))
{
// Set the event if the initial count is zero.
if (_current == 0L)
_event.set();
}
// Decrements the event counter.
void signal() {
if(InterlockedDecrement(&_current) == 0L) {
_event.set();
}
}
// Increments the event counter.
void add_count() {
if(InterlockedIncrement(&_current) == 1L) {
_event.reset();
}
}
// Blocks the current context until the event is set.
void wait() {
_event.wait();
}
private:
// The current count.
volatile long _current;
// The event that is set when the counter reaches zero.
event _event;
// Disable copy constructor.
countdown_event(const countdown_event&);
// Disable assignment.
countdown_event const & operator=(countdown_event const&);
};
// Demonstrates how to set up a message network that performs a series of
// image processing operations on each JPEG image in the given directory and
// saves each altered image as a Windows bitmap.
void ProcessImages(const wstring& directory)
{
// Holds the number of active image processing operations and
// signals to the main thread that processing is complete.
countdown_event active(0);
// Maps Bitmap objects to their original file names.
map<Bitmap*, wstring> bitmap_file_names;
//
// Create the nodes of the network.
//
// Loads Bitmap objects from disk.
transformer<wstring, Bitmap*> load_bitmap(
[&](wstring file_name) -> Bitmap* {
Bitmap* bmp = new Bitmap(file_name.c_str());
if (bmp != nullptr)
bitmap_file_names.insert(make_pair(bmp, file_name));
return bmp;
}
);
// Holds loaded Bitmap objects.
unbounded_buffer<Bitmap*> loaded_bitmaps;
// Converts images that are authored by Tom to grayscale.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> grayscale(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Grayscale(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
// Retrieve the artist name from metadata.
UINT size = bmp->GetPropertyItemSize(PropertyTagArtist);
if (size == 0)
// Image does not have the Artist property.
return false;
PropertyItem* artistProperty = (PropertyItem*) malloc(size);
bmp->GetPropertyItem(PropertyTagArtist, size, artistProperty);
string artist(reinterpret_cast<char*>(artistProperty->value));
free(artistProperty);
return (artist.find("Tom ") == 0);
}
);
// Removes the green and blue color components from images that have red as
// their dominant color.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> colormask(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return ColorMask(bmp, 0x00ff0000);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool {
if (bmp == nullptr)
return false;
return (GetColorDominance(bmp) == 0x00ff0000);
}
);
// Darkens the color of the provided Bitmap object.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> darken([](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Darken(bmp, 50);
});
// Applies sepia toning to the remaining images.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> sepiatone(
[](Bitmap* bmp) {
return Sepiatone(bmp);
},
nullptr,
[](Bitmap* bmp) -> bool { return bmp != nullptr; }
);
// Saves Bitmap objects to disk.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> save_bitmap([&](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
// Replace the file extension with .bmp.
wstring file_name = bitmap_file_names[bmp];
file_name.replace(file_name.rfind(L'.') + 1, 3, L"bmp");
// Save the processed image.
CLSID bmpClsid;
GetEncoderClsid(L"image/bmp", &bmpClsid);
bmp->Save(file_name.c_str(), &bmpClsid);
return bmp;
});
// Deletes Bitmap objects.
transformer<Bitmap*, Bitmap*> delete_bitmap([](Bitmap* bmp) -> Bitmap* {
delete bmp;
return nullptr;
});
// Decrements the event counter.
call<Bitmap*> decrement([&](Bitmap* _) {
active.signal();
});
//
// Connect the network.
//
load_bitmap.link_target(&loaded_bitmaps);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&grayscale);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&colormask);
colormask.link_target(&darken);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&sepiatone);
loaded_bitmaps.link_target(&decrement);
grayscale.link_target(&save_bitmap);
darken.link_target(&save_bitmap);
sepiatone.link_target(&save_bitmap);
save_bitmap.link_target(&delete_bitmap);
delete_bitmap.link_target(&decrement);
// Traverse all files in the directory.
wstring searchPattern = directory;
searchPattern.append(L"\\*");
WIN32_FIND_DATA fileFindData;
HANDLE hFind = FindFirstFile(searchPattern.c_str(), &fileFindData);
if (hFind == INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE)
return;
do
{
if (!(fileFindData.dwFileAttributes & FILE_ATTRIBUTE_DIRECTORY))
{
wstring file = fileFindData.cFileName;
// Process only JPEG files.
if (file.rfind(L".jpg") == file.length() - 4)
{
// Form the full path to the file.
wstring full_path(directory);
full_path.append(L"\\");
full_path.append(file);
// Increment the count of work items.
active.add_count();
// Send the path name to the network.
send(load_bitmap, full_path);
}
}
}
while (FindNextFile(hFind, &fileFindData) != 0);
FindClose(hFind);
// Wait for all operations to finish.
active.wait();
}
int wmain()
{
GdiplusStartupInput gdiplusStartupInput;
ULONG_PTR gdiplusToken;
// Initialize GDI+.
GdiplusStartup(&gdiplusToken, &gdiplusStartupInput, nullptr);
// Perform image processing.
// TODO: Change this path if necessary.
ProcessImages(L"C:\\Users\\Public\\Pictures\\Sample Pictures");
// Shutdown GDI+.
GdiplusShutdown(gdiplusToken);
}
次の画像は出力例を示しています。 各ソース画像は、対応する変更後の画像の上にあります。

Lighthouse は Tom Alphin によって作成されているため、グレースケールに変換されています。 Chrysanthemum、Desert、Koala、Tulips は赤を主調色とするため、青と緑の色成分が除去され、暗くなっています。 Hydrangeas、Jellyfish、Penguins は既定の基準に一致するため、セピア調になっています。
[トップ]
コードのコンパイル
コード例をコピーし、Visual Studio プロジェクトに貼り付けるか、image-processing-network.cpp という名前のファイルに貼り付けてから、Visual Studio のコマンド プロンプト ウィンドウで次のコマンドを実行します。
cl.exe /DUNICODE /EHsc image-processing-network.cpp /link gdiplus.lib