チュートリアル: REST を使用して Azure Storage から入れ子になった Markdown BLOB のインデックスを作成する
Note
現在、この機能はパブリック プレビュー段階にあります。 このプレビュー版はサービス レベル アグリーメントなしで提供されています。運用環境のワークロードに使用することはお勧めできません。 特定の機能はサポート対象ではなく、機能が制限されることがあります。 詳しくは、Microsoft Azure プレビューの追加使用条件に関するページをご覧ください。
Azure AI 検索では、Markdown データの読み方を理解しているインデクサーを使って、Azure Blob Storage 内の Markdown のドキュメントや配列のインデックスを作成できます。
このチュートリアルでは、oneToMany Markdown 解析モードを使ってインデックス付けされた Markdown ファイルのインデックスを作成する方法について説明します。 REST クライアントと Search REST API を使用して次のタスクを実行します。
- サンプル データを設定し、
azureblobデータ ソースを構成する - 検索可能なコンテンツを格納する Azure AI Search インデックスを作成する
- インデクサーを作成して実行してコンテナーを読み取り、検索可能なコンテンツを抽出する
- 作成したインデックスを検索する
Azure サブスクリプションをお持ちでない場合は、開始する前に 無料アカウント を作成してください。
前提条件
Azure AI 検索. 現在のサブスクリプションで、既存の Azure AI 検索サービスを見つけるか、または作成します。
Note
このチュートリアルには無料のサービスを使用できます。 無料の検索サービスでは、3 つのインデックス、3 つのインデクサー、3 つのデータ ソースという制限があります。 このチュートリアルでは、それぞれ 1 つずつ作成します。 開始する前に、ご利用のサービスに新しいリソースを受け入れる余地があることを確認してください。
Markdown ドキュメントを作成する
次の Markdown をコピーし、sample_markdown.md という名前のファイルに貼り付けます。 サンプル データは、さまざまな Markdown 要素を含む 1 つの Markdown ファイルです。 Free レベルのストレージ制限に収まるよう、1 つの Markdown ファイルにしました。
# Project Documentation
## Introduction
This document provides a complete overview of the **Markdown Features** used within this project. The following sections demonstrate the richness of Markdown formatting, with examples of lists, tables, links, images, blockquotes, inline styles, and more.
---
## Table of Contents
1. [Headers](#headers)
2. [Introduction](#introduction)
3. [Basic Text Formatting](#basic-text-formatting)
4. [Lists](#lists)
5. [Blockquotes](#blockquotes)
6. [Images](#images)
7. [Links](#links)
8. [Tables](#tables)
9. [Code Blocks and Inline Code](#code-blocks-and-inline-code)
10. [Horizontal Rules](#horizontal-rules)
11. [Inline Elements](#inline-elements)
12. [Escaping Characters](#escaping-characters)
13. [HTML Elements](#html-elements)
14. [Emojis](#emojis)
15. [Footnotes](#footnotes)
16. [Task Lists](#task-lists)
17. [Conclusion](#conclusion)
---
## Headers
Markdown supports six levels of headers. Use `#` to create headers:
"# Project Documentation" at the top of the document is an example of an h1 header.
"## Headers" above is an example of an h2 header.
### h3 example
#### h4 example
##### h5 example
###### h6 example
This is an example of content underneath a header.
## Basic Text Formatting
You can apply various styles to your text:
- **Bold**: Use double asterisks or underscores: `**bold**` or `__bold__`.
- *Italic*: Use single asterisks or underscores: `*italic*` or `_italic_`.
- ~~Strikethrough~~: Use double tildes: `~~strikethrough~~`.
## Lists
### Ordered List
1. First item
2. Second item
3. Third item
### Unordered List
- Item A
- Item B
- Item C
### Nested List
1. Parent item
- Child item
- Child item
## Blockquotes
> This is a blockquote.
> Blockquotes are great for emphasizing important information.
>> Nested blockquotes are also possible!
## Images

## Links
[Visit Markdown Guide](https://www.markdownguide.org)
## Tables
| Syntax | Description | Example |
|-------------|-------------|---------------|
| Header | Title | Header Cell |
| Paragraph | Text block | Row Content |
## Code Blocks and Inline Code
### Inline Code
Use backticks to create `inline code`.
### Code Block
```javascript
// JavaScript example
function greet(name) {
console.log(`Hello, ${name}!`);
}
greet('World');
```
## Horizontal Rules
Use three or more dashes or underscores to create a horizontal rule.
---
___
## Inline Elements
Sometimes, it’s useful to include `inline code` to highlight code-like content.
You can also emphasize text like *this* or make it **bold**.
## Escaping Characters
To render special Markdown characters, use backslashes:
- \*Asterisks\*
- \#Hashes\#
- \[Brackets\]
## HTML Elements
You can mix HTML tags with Markdown:
<table>
<tr>
<th>HTML Table</th>
<th>With Markdown</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Row 1</td>
<td>Data 1</td>
</tr>
</table>
## Emojis
Markdown supports some basic emojis:
- :smile: 😄
- :rocket: 🚀
- :checkered_flag: 🏁
## Footnotes
This is an example of a footnote[^1]. Footnotes allow you to add notes without cluttering the main text.
[^1]: This is the content of the footnote.
## Task Lists
- [x] Complete the introduction
- [ ] Add more examples
- [ ] Review the document
## Conclusion
Markdown is a lightweight yet powerful tool for writing documentation. It supports a variety of formatting options while maintaining simplicity and readability.
Thank you for reviewing this example!
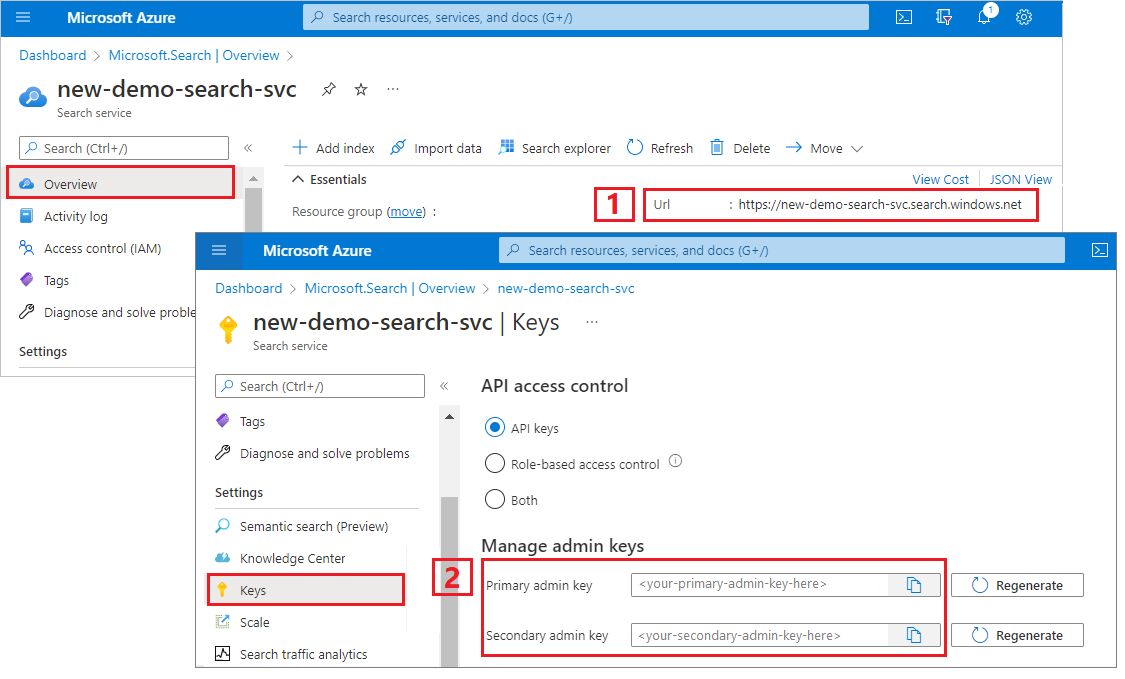
検索サービスの URL と API キーをコピーする
このチュートリアルでは、Azure AI 検索への接続にエンドポイントと API キーが必要です。 これらの値は Azure portal から取得できます。 別の接続方法については、マネージド ID に関する記事をご覧ください。
Azure portal にサインインし、検索サービスの [概要] ページに移動して URL をコピーします。 たとえば、エンドポイントは
https://mydemo.search.windows.netのようになります。[設定]>[キー] で管理者キーをコピーします。 管理者キーは、オブジェクトの追加、変更、削除で使用します。 2 つの交換可能な管理者キーがあります。 どちらかをコピーします。
REST ファイルを設定する
Visual Studio Code を起動して、新しいファイルを作成します。
要求で使用される変数の値を指定します。
@baseUrl = PUT-YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-ENDPOINT-HERE @apiKey = PUT-YOUR-ADMIN-API-KEY-HERE @storageConnectionString = PUT-YOUR-STORAGE-CONNECTION-STRING-HERE @blobContainer = PUT-YOUR-CONTAINER-NAME-HEREファイル拡張子
.restまたは.httpを使用してファイルを保存します。
REST クライアントに関するヘルプが必要な場合は、「クイック スタート: REST を使用したテキスト検索」を参照してください。
データ ソースを作成する
データ ソースの作成 (REST) では、インデックスを付けるデータを指定するデータ ソース接続を作成します。
### Create a data source
POST {{baseUrl}}/datasources?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name" : "sample-markdown-ds",
"description": null,
"type": "azureblob",
"subtype": null,
"credentials": {
"connectionString": "{{storageConnectionString}}"
},
"container": {
"name": "{{blobContainer}}",
"query": null
},
"dataChangeDetectionPolicy": null,
"dataDeletionDetectionPolicy": null
}
要求を送信します。 応答は次のようになります。
HTTP/1.1 201 Created
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
ETag: "0x8DCF52E926A3C76"
Location: https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net:443/datasources('sample-markdown-ds')?api-version=2024-11-01-preview
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: 0714c187-217e-4d35-928a-5069251e5cba
elapsed-time: 204
Date: Fri, 25 Oct 2024 19:52:35 GMT
Connection: close
{
"@odata.context": "https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net/$metadata#datasources/$entity",
"@odata.etag": "\"0x8DCF52E926A3C76\"",
"name": "sample-markdown-ds",
"description": null,
"type": "azureblob",
"subtype": null,
"credentials": {
"connectionString": null
},
"container": {
"name": "markdown-container",
"query": null
},
"dataChangeDetectionPolicy": null,
"dataDeletionDetectionPolicy": null,
"encryptionKey": null,
"identity": null
}
インデックスを作成する
インデックスの作成 (REST) では、検索サービスに検索インデックスを作成します。 インデックスでは、すべてのフィールドとその属性が指定されています。
一対多の解析では、検索ドキュメントでリレーションシップの '多' の側が定義されます。 ユーザーがインデックスで指定するフィールドによって、検索ドキュメントの構造が決まります。
パーサーがサポートする Markdown 要素のフィールドのみが必要です。 これらのフィールドを次に示します。
content: 特定の場所で見つかった未処理の Markdown が含まれている文字列。ドキュメント内のその時点のヘッダー メタデータに基づいています。sections: 目的のヘッダー レベルにまでヘッダー メタデータのサブフィールドが含まれているオブジェクト。 たとえば、markdownHeaderDepthがh3に設定されている場合は、文字列フィールドh1、h2、h3が含まれます。 これらのフィールドには、インデックス内でこの構造をミラーリングするか、/sections/h1、sections/h2などの形式でフィールド マッピングを行うことでインデックスが作成されます。コンテキスト内の例については、次のサンプルのインデックスとインデクサーの構成を確認してください。 含まれているサブフィールドは次のとおりです。-
h1: h1 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。 - (省略可能)
h2: h2 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。 - (省略可能)
h3: h3 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。 - (省略可能)
h4: h4 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。 - (省略可能)
h5: h5 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。 - (省略可能)
h6: h6 ヘッダー値を含む文字列。 ドキュメントのこの時点に設定されていない場合は、空の文字列。
-
ordinal_position: ドキュメントの階層内でのセクションの位置を示す整数値。 このフィールドは、ドキュメント内で出現する元の順序でセクションを並べるために使われます。序数位置 1 から始まり、コンテンツ ブロックごとに順番にインクリメントします。
この実装では、インデクサーのフィールド マッピングを利用して、エンリッチされたコンテンツからインデックスにマップします。 解析された一対多のドキュメント構造について詳しくは、マークダウン BLOB のインデックス作成に関する記事をご覧ください。
この例では、フィールド マッピングがある場合とない場合の両方について、データのインデックスを作成する方法のサンプルを示します。 この場合、h1 にはドキュメントのタイトルが含まれることがわかっているため、それを title という名前のフィールドにマップできます。 また、h2 と h3 フィールドを、それぞれ h2_subheader と h3_subheader にマッピングします。
content と ordinal_position フィールドについては、それらはその名前を使って Markdown からフィールドに直接抽出されるため、マッピングは必要ありません。 フィールド マッピングを必要としない完全なインデックス スキーマの例については、このセクションの最後を参照してください。
### Create an index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name": "sample-markdown-index",
"fields": [
{"name": "id", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "content", "type": "Edm.String", "key": false, "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "title", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "h2_subheader", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "h3_subheader", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "ordinal_position", "type": "Edm.Int32", "searchable": false, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true}
]
}
フィールド マッピングのない構成のインデックス スキーマ
フィールド マッピングを使って、エンリッチされたコンテンツを操作し、目的のインデックスの形状に収まるようにフィルター処理できますが、エンリッチされたコンテンツを単に直接取得したいこともあります。 その場合、スキーマは次のようになります。
{
"name": "sample-markdown-index",
"fields": [
{"name": "id", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "content", "type": "Edm.String", "key": false, "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "sections",
"type": "Edm.ComplexType",
"fields": [
{"name": "h1", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "h2", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true},
{"name": "h3", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true}
]
},
{"name": "ordinal_position", "type": "Edm.Int32", "searchable": false, "retrievable": true, "filterable": true, "facetable": true, "sortable": true}
]
}
繰り返しますが、markdownHeaderDepth が h3 に設定されているため、セクション オブジェクト内のサブフィールドは h3 までです。
このスキーマを使う場合は、それに応じて後の要求を調整してください。 そのためには、インデクサーの構成からフィールド マッピングを削除し、対応するフィールド名を使うように検索クエリを更新する必要があります。
インデクサーの作成と実行
インデクサーの作成では、検索サービスにインデクサーを作成します。 インデクサーではデータ ソースに接続し、インデックス データを読み込み、データ更新を自動化するスケジュールを必要に応じて提供します。
### Create and run an indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"name": "sample-markdown-indexer",
"dataSourceName": "sample-markdown-ds",
"targetIndexName": "sample-markdown-index",
"parameters" : {
"configuration": {
"parsingMode": "markdown",
"markdownParsingSubmode": "oneToMany",
"markdownHeaderDepth": "h3"
}
},
"fieldMappings" : [
{
"sourceFieldName": "/sections/h1",
"targetFieldName": "title",
"mappingFunction": null
}
]
}
重要なポイント:
インデクサーは、ヘッダーを
h3までしか解析しません。 下位レベルのヘッダー (h4、h5、h6) はプレーンテキストとして扱われ、contentフィールドに表示されます。 インデックスとフィールドのマッピングがh3の深さまでしかないのはこのためです。contentとordinal_positionフィールドは、エンリッチされたコンテンツ内にそれらの名前で存在するため、フィールド マッピングは必要ありません。
クエリを実行する
最初のドキュメントが読み込まれたらすぐに、検索を始めることができます。
### Query the index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/sample-markdown-index/docs/search?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "*",
"count": true
}
要求を送信します。 これは、指定のないフルテキスト検索クエリです。インデックスで取得可能としてマークされたすべてのフィールドがドキュメント数と共に返されます。 応答は次のようになります。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
Content-Encoding: gzip
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: 6b94e605-55e8-47a5-ae15-834f926ddd14
elapsed-time: 77
Date: Fri, 25 Oct 2024 20:22:58 GMT
Connection: close
{
"@odata.context": "https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net/indexes('sample-markdown-index')/$metadata#docs(*)",
"@odata.count": 22,
"value": [
<22 search documents here>
]
}
文字列で検索する search パラメーターを追加します。
### Query the index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/sample-markdown-index/docs/search?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "h4",
"count": true,
}
要求を送信します。 応答は次のようになります。
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
Content-Encoding: gzip
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: ec5d03f1-e3e7-472f-9396-7ff8e3782105
elapsed-time: 52
Date: Fri, 25 Oct 2024 20:26:29 GMT
Connection: close
{
"@odata.context": "https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net/indexes('sample-markdown-index')/$metadata#docs(*)",
"@odata.count": 1,
"value": [
{
"@search.score": 0.8744742,
"section_id": "aHR0cHM6Ly9hcmphZ2Fubmpma2ZpbGVzLmJsb2IuY29yZS53aW5kb3dzLm5ldC9tYXJrZG93bi10dXRvcmlhbC9zYW1wbGVfbWFya2Rvd24ubWQ7NA2",
"content": "#### h4 example\r\n##### h5 example\r\n###### h6 example\r\nThis is an example of content underneath a header.\r\n",
"title": "Project Documentation",
"h2_subheader": "Headers",
"h3_subheader": "h3 example",
"ordinal_position": 4
}
]
}
重要なポイント:
markdownHeaderDepthがh3に設定されているため、h4、h5、h6ヘッダーはプレーンテキストとして扱われ、contentフィールドに表示されます。ここでの序数位置は
4です。 このコンテンツは、合計 22 個のコンテンツ セクションのうち 4 番目に表示されます。
結果を数フィールドに限定するため、select パラメーターを追加します。 検索をさらに絞り込むには、filter を追加してください。
### Query the index
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexes/sample-markdown-index/docs/search?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
Content-Type: application/json
api-key: {{apiKey}}
{
"search": "Markdown",
"count": true,
"select": "title, content, h2_subheader",
"filter": "h2_subheader eq 'Conclusion'"
}
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal; odata.streaming=true; charset=utf-8
Content-Encoding: gzip
Vary: Accept-Encoding
Server: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
Strict-Transport-Security: max-age=2592000, max-age=15724800; includeSubDomains
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
OData-Version: 4.0
request-id: a6f9bd46-a064-4e28-818f-ea077618014b
elapsed-time: 35
Date: Fri, 25 Oct 2024 20:36:10 GMT
Connection: close
{
"@odata.context": "https://<YOUR-SEARCH-SERVICE-NAME>.search.windows.net/indexes('sample-markdown-index')/$metadata#docs(*)",
"@odata.count": 1,
"value": [
{
"@search.score": 1.1029507,
"content": "Markdown is a lightweight yet powerful tool for writing documentation. It supports a variety of formatting options while maintaining simplicity and readability.\r\n\r\nThank you for reviewing this example!",
"title": "Project Documentation",
"h2_subheader": "Conclusion"
}
]
}
フィルター処理のため、論理演算子 (and、or、not) と比較演算子 (eq、ne、gt、lt、ge、le) を使用することもできます。 文字列比較では大文字と小文字が区別されます。 詳細と例については、クエリを作成する方法に関するページを参照してください。
Note
$filter パラメーターは、インデックスの作成時にフィルター可能としてマークされたフィールドでのみ使用できます。
リセットして再実行する
インデクサーをリセットして実行履歴をクリアすると、完全な再実行が可能になります。 次の GET 要求はリセット用であり、その後に再実行されます。
### Reset the indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers/sample-markdown-indexer/reset?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
### Run the indexer
POST {{baseUrl}}/indexers/sample-markdown-indexer/run?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
### Check indexer status
GET {{baseUrl}}/indexers/sample-markdown-indexer/status?api-version=2024-11-01-preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: {{apiKey}}
リソースをクリーンアップする
所有するサブスクリプションを使用している場合は、プロジェクトの終了時に、不要になったリソースを削除することをお勧めします。 リソースを実行したままにすると、お金がかかる場合があります。 リソースを個別に削除するか、リソース グループを削除してリソースのセット全体を削除することができます。
Azure portal を使って、インデックス、インデクサー、データ ソースを削除できます。
次のステップ
Azure Blob のインデックス作成の基礎を理解したので、Azure Storage での Markdown BLOB のインデクサー構成について詳しく見てみましょう。