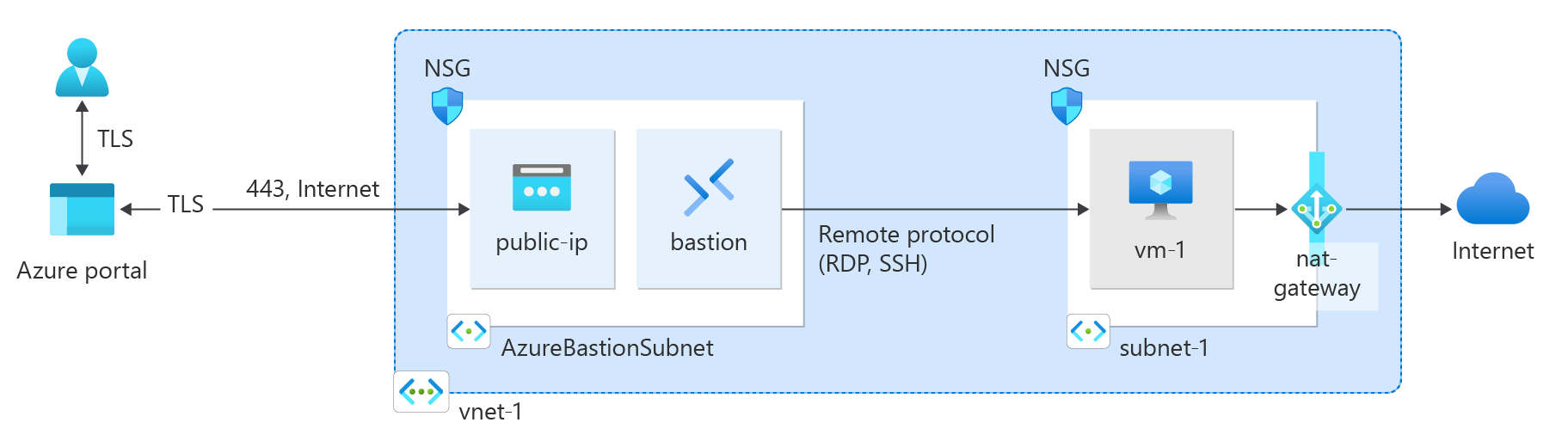
クイック スタート: Terraform を使用して Azure NAT Gateway を作成する
Terraform を使用して Azure NAT Gateway の使用を開始します。 この Terraform ファイルを使用すると、仮想ネットワーク、NAT ゲートウェイ リソース、Ubuntu 仮想マシンをデプロイできます。 Ubuntu 仮想マシンは、NAT ゲートウェイ リソースに関連付けられているサブネットにデプロイされます。
また、スクリプトは、ランダムな SSH 公開キーを生成し、安全なアクセスのために仮想マシンに関連付けます。 公開キーはスクリプト実行の最後に出力されます。
このスクリプトは、AzureRM プロバイダーに加えて、Random プロバイダーと AzAPI プロバイダーを使用します。 Random プロバイダーは、リソース グループと SSH キーの一意の名前を生成するために使用されます。 AzAPI プロバイダーは、SSH 公開キーを生成するために使用されます。
公開キーと同様に、作成されたリソース グループ、仮想ネットワーク、サブネット、NAT ゲートウェイの名前は、スクリプトの実行時に出力されます。
Terraform を使用すると、クラウド インフラストラクチャの定義、プレビュー、およびデプロイを行うことができます。 Terraform を使用する際は、HCL 構文を使って構成ファイルを作成します。 HCL 構文では、Azure などのクラウド プロバイダーと、クラウド インフラストラクチャを構成する要素を指定できます。 構成ファイルを作成したら、"実行プラン" を作成します。これにより、インフラストラクチャの変更をデプロイ前にプレビューすることができます。 変更を確認したら、実行プランを適用してインフラストラクチャをデプロイします。
前提条件
アクティブなサブスクリプションが含まれる Azure アカウント。 無料でアカウントを作成できます。
Terraform をインストールおよび構成します。
Terraform コードを実装する
注意
この記事のサンプル コードは、Azure Terraform GitHub リポジトリにあります。
Terraform を使用して Azure リソースを管理する方法を示すその他の記事とサンプル コードを参照してください
サンプル Terraform コードをテストして実行するディレクトリを作成し、それを現在のディレクトリにします。
main.tfという名前のファイルを作成し、次のコードを挿入します。# Resource Group resource "azurerm_resource_group" "rg" { location = var.resource_group_location name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-rg" } # Virtual Network resource "azurerm_virtual_network" "my_terraform_network" { name = "${random_pet.prefix.id}-vnet" address_space = ["10.0.0.0/16"] location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } # Subnet 1 resource "azurerm_subnet" "my_terraform_subnet_1" { name = "subnet-1" resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name virtual_network_name = azurerm_virtual_network.my_terraform_network.name address_prefixes = ["10.0.0.0/24"] } # Public IP address for NAT gateway resource "azurerm_public_ip" "my_public_ip" { name = "public-ip-nat" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name allocation_method = "Static" sku = "Standard" } # NAT Gateway resource "azurerm_nat_gateway" "my_nat_gateway" { name = "nat-gateway" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } # Associate NAT Gateway with Public IP resource "azurerm_nat_gateway_public_ip_association" "example" { nat_gateway_id = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.my_public_ip.id } # Associate NAT Gateway with Subnet resource "azurerm_subnet_nat_gateway_association" "example" { subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.id nat_gateway_id = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id } # Create public IP for virtual machine resource "azurerm_public_ip" "my_public_ip_vm" { name = "public-ip-vm" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name allocation_method = "Static" sku = "Standard" } # Create Network Security Group and rule resource "azurerm_network_security_group" "my_terraform_nsg" { name = "nsg-1" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name security_rule { name = "SSH" priority = 1001 direction = "Inbound" access = "Allow" protocol = "Tcp" source_port_range = "*" destination_port_range = "22" source_address_prefix = "*" destination_address_prefix = "*" } } # Create network interface resource "azurerm_network_interface" "my_terraform_nic" { name = "nic-1" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name ip_configuration { name = "my_nic_configuration" subnet_id = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.id private_ip_address_allocation = "Dynamic" public_ip_address_id = azurerm_public_ip.my_public_ip_vm.id } } # Connect the security group to the network interface resource "azurerm_network_interface_security_group_association" "example" { network_interface_id = azurerm_network_interface.my_terraform_nic.id network_security_group_id = azurerm_network_security_group.my_terraform_nsg.id } # Generate random text for a unique storage account name resource "random_id" "random_id" { keepers = { # Generate a new ID only when a new resource group is defined resource_group = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } byte_length = 8 } # Create storage account for boot diagnostics resource "azurerm_storage_account" "my_storage_account" { name = "diag${random_id.random_id.hex}" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name account_tier = "Standard" account_replication_type = "LRS" } # Create virtual machine resource "azurerm_linux_virtual_machine" "my_terraform_vm" { name = "vm-1" location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location resource_group_name = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name network_interface_ids = [azurerm_network_interface.my_terraform_nic.id] size = "Standard_DS1_v2" os_disk { name = "myOsDisk" caching = "ReadWrite" storage_account_type = "Premium_LRS" } source_image_reference { publisher = "Canonical" offer = "0001-com-ubuntu-server-jammy" sku = "22_04-lts-gen2" version = "latest" } computer_name = "hostname" admin_username = var.username admin_ssh_key { username = var.username public_key = azapi_resource_action.ssh_public_key_gen.output.publicKey } boot_diagnostics { storage_account_uri = azurerm_storage_account.my_storage_account.primary_blob_endpoint } } resource "random_pet" "prefix" { prefix = var.resource_group_name_prefix length = 1 }outputs.tfという名前のファイルを作成し、次のコードを挿入します。output "resource_group_name" { description = "The name of the created resource group." value = azurerm_resource_group.rg.name } output "virtual_network_name" { description = "The name of the created virtual network." value = azurerm_virtual_network.my_terraform_network.name } output "subnet_name_1" { description = "The name of the created subnet 1." value = azurerm_subnet.my_terraform_subnet_1.name } output "nat_gateway"{ description = "The name of the created NAT gateway." value = azurerm_nat_gateway.my_nat_gateway.id }providers.tfという名前のファイルを作成し、次のコードを挿入します。terraform { required_providers { azapi = { source = "azure/azapi" version = "~>1.5" } azurerm = { source = "hashicorp/azurerm" version = "~>3.0" } random = { source = "hashicorp/random" version = "~>3.0" } } } provider "azurerm" { features {} }ssh.tfという名前のファイルを作成し、次のコードを挿入します。resource "random_pet" "ssh_key_name" { prefix = "ssh" separator = "" } resource "azapi_resource_action" "ssh_public_key_gen" { type = "Microsoft.Compute/sshPublicKeys@2022-11-01" resource_id = azapi_resource.ssh_public_key.id action = "generateKeyPair" method = "POST" response_export_values = ["publicKey", "privateKey"] } resource "azapi_resource" "ssh_public_key" { type = "Microsoft.Compute/sshPublicKeys@2022-11-01" name = random_pet.ssh_key_name.id location = azurerm_resource_group.rg.location parent_id = azurerm_resource_group.rg.id } output "key_data" { value = azapi_resource_action.ssh_public_key_gen.output.publicKey }variables.tfという名前のファイルを作成し、次のコードを挿入します。variable "resource_group_location" { type = string default = "eastus" description = "Location of the resource group." } variable "resource_group_name_prefix" { type = string default = "rg" description = "Prefix of the resource group name that's combined with a random ID so name is unique in your Azure subscription." } variable "username" { type = string description = "The username for the local account that will be created on the new VM." default = "azureuser" }
Terraform を初期化する
terraform init を実行して、Terraform のデプロイを初期化します。 このコマンドによって、Azure リソースを管理するために必要な Azure プロバイダーがダウンロードされます。
terraform init -upgrade
重要なポイント:
-upgradeパラメーターは、必要なプロバイダー プラグインを、構成のバージョン制約に準拠する最新バージョンにアップグレードします。
Terraform 実行プランを作成する
terraform plan を実行して、実行プランを作成します。
terraform plan -out main.tfplan
重要なポイント:
terraform planコマンドは、実行プランを作成しますが、実行はしません。 代わりに、構成ファイルに指定された構成を作成するために必要なアクションを決定します。 このパターンを使用すると、実際のリソースに変更を加える前に、実行プランが自分の想定と一致しているかどうかを確認できます。- 省略可能な
-outパラメーターを使用すると、プランの出力ファイルを指定できます。-outパラメーターを使用すると、レビューしたプランが適用内容とまったく同じであることが確実になります。
Terraform 実行プランを適用する
terraform apply を実行して、クラウド インフラストラクチャに実行プランを適用します。
terraform apply main.tfplan
重要なポイント:
terraform applyコマンドの例は、以前にterraform plan -out main.tfplanが実行されたことを前提としています。-outパラメーターに別のファイル名を指定した場合は、terraform applyの呼び出しで同じファイル名を使用します。-outパラメーターを使用しなかった場合は、パラメーターを指定せずにterraform applyを呼び出します。
結果を確認する
- Azure リソース グループ名を取得します。
resource_group_name=$(terraform output -raw resource_group_name)
- NAT ゲートウェイ ID を取得します。
nat_gateway=$(terraform output -raw nat_gateway)
- az network nat gateway show を実行して、NAT ゲートウェイの詳細を表示します。
az network nat gateway show \
--resource-group $resource_group_name \
--ids $nat_gateway
リソースをクリーンアップする
Terraform を使用して作成したリソースが不要になった場合は、次の手順を実行します。
terraform plan を実行して、
destroyフラグを指定します。terraform plan -destroy -out main.destroy.tfplan重要なポイント:
terraform planコマンドは、実行プランを作成しますが、実行はしません。 代わりに、構成ファイルに指定された構成を作成するために必要なアクションを決定します。 このパターンを使用すると、実際のリソースに変更を加える前に、実行プランが自分の想定と一致しているかどうかを確認できます。- 省略可能な
-outパラメーターを使用すると、プランの出力ファイルを指定できます。-outパラメーターを使用すると、レビューしたプランが適用内容とまったく同じであることが確実になります。
terraform apply を実行して、実行プランを適用します。
terraform apply main.destroy.tfplan
Azure での Terraform のトラブルシューティング
Azure で Terraform を使用する場合の一般的な問題のトラブルシューティング。