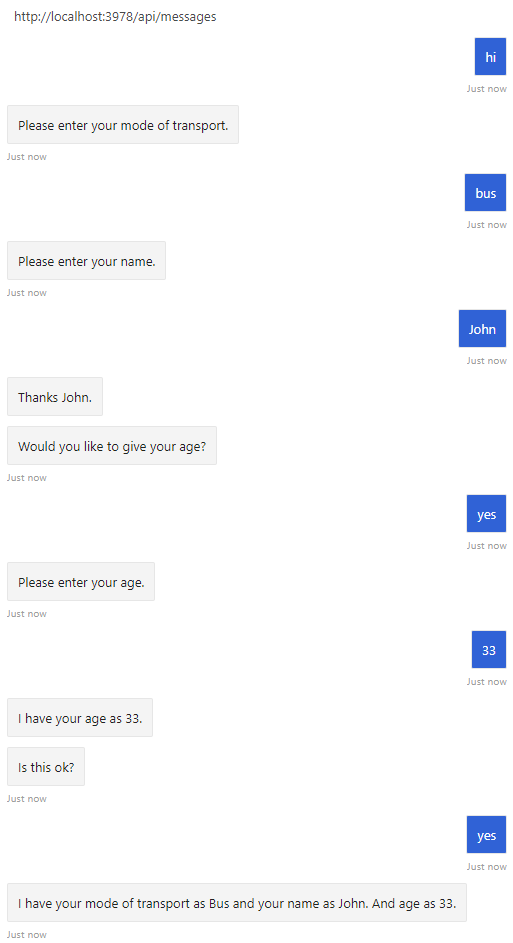
質問を投稿して情報を収集することは、ボットがユーザーとやり取りする主な手段の 1 つです。 ダイアログ ライブラリでは、質問を行いやすくなるだけでなく、応答が検証され、確実に特定のデータ型と一致するように、またはカスタム検証ルールを満たすように、prompt クラスなどの便利な組み込み機能が提供されます。
ダイアログ ライブラリを使用して、線形型の会話フローとより複雑な会話フローを管理できます。 線形型のインタラクションでは、ボットは決まった一連のステップを順番に実行していき、最後に会話が終了します。 ダイアログは、ボットがユーザーから情報を収集する必要がある場合に役立ちます。
この記事では、プロンプトを作成してウォーターフォール ダイアログから呼び出すことで、線形型の会話フローを実装する方法について説明します。
ダイアログ ライブラリを使用することなく、独自のプロンプトを作成する方法の例については、「ユーザー入力を収集するために独自のプロンプトを作成する」の記事を参照してください。
マルチターン プロンプト サンプルでは、ウォーターフォール ダイアログ、いくつかのプロンプト、コンポーネント ダイアログを使用して、ユーザーに一連の質問を行う線形型の対話を作成します。 コードはダイアログを使用して、これらの手順を順番に切り替えます。
ダイアログを使用するには、Microsoft.Bot.Builder.Dialogs NuGet パッケージをインストールします。
ボットは UserProfileDialog を介してユーザーと対話します。 ボットの DialogBot クラスを作成するときに、UserProfileDialog がメイン ダイアログとして設定されます。 その後、ボットは Run ヘルパー メソッドを使用して、ダイアログにアクセスします。
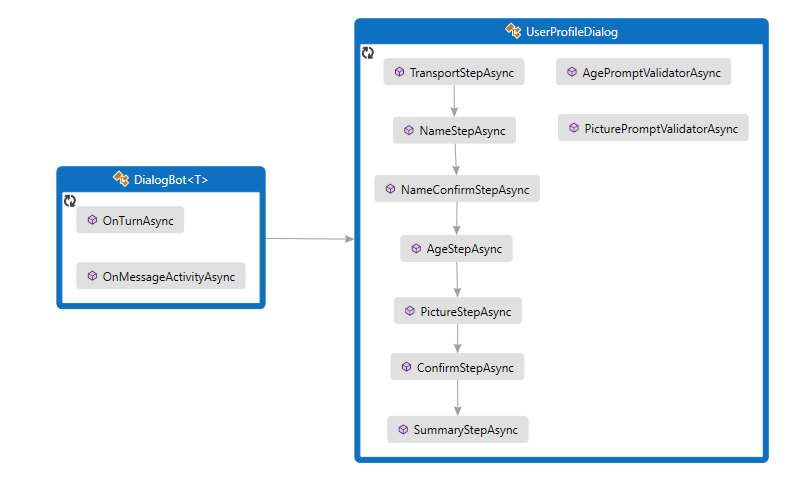
Dialogs\UserProfileDialog.cs
最初に、ComponentDialog クラスから派生し、7 つのステップがある UserProfileDialog を作成します。
UserProfileDialog コンストラクターで、ウォーターフォール ステップ、プロンプト、およびウォーターフォール ダイアログを作成し、ダイアログ セットに追加します。 プロンプトは、それが使用されるダイアログ セットに追加する必要があります。
public UserProfileDialog(UserState userState)
: base(nameof(UserProfileDialog))
{
_userProfileAccessor = userState.CreateProperty<UserProfile>("UserProfile");
// This array defines how the Waterfall will execute.
var waterfallSteps = new WaterfallStep[]
{
TransportStepAsync,
NameStepAsync,
NameConfirmStepAsync,
AgeStepAsync,
PictureStepAsync,
SummaryStepAsync,
ConfirmStepAsync,
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
AddDialog(new WaterfallDialog(nameof(WaterfallDialog), waterfallSteps));
AddDialog(new TextPrompt(nameof(TextPrompt)));
AddDialog(new NumberPrompt<int>(nameof(NumberPrompt<int>), AgePromptValidatorAsync));
AddDialog(new ChoicePrompt(nameof(ChoicePrompt)));
AddDialog(new ConfirmPrompt(nameof(ConfirmPrompt)));
AddDialog(new AttachmentPrompt(nameof(AttachmentPrompt), PicturePromptValidatorAsync));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
InitialDialogId = nameof(WaterfallDialog);
}
次に、ダイアログが入力を求めるために使用する手順を追加します。 プロンプトを使用するには、そのプロンプトをご自身のダイアログのステップから呼び出し、stepContext.Result を使用して、次のステップでプロンプトの結果を取得します。 バックグラウンドでは、プロンプトは 2 つのステップから成るダイアログです。 最初に、プロンプトで入力が求められます。 その後、有効な値を返すします。それ以外の場合は最初からやり直し、有効な入力を受信するまでユーザーに再入力を要求します。
ウォーターフォール ステップからは常に null 以外の DialogTurnResult を返す必要があります。 そうしないと、ダイアログは設計どおりに機能しません。 以下に、ウォーターフォール ダイアログの NameStepAsync に対する実装を示します。
private static async Task<DialogTurnResult> NameStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
stepContext.Values["transport"] = ((FoundChoice)stepContext.Result).Value;
return await stepContext.PromptAsync(nameof(TextPrompt), new PromptOptions { Prompt = MessageFactory.Text("Please enter your name.") }, cancellationToken);
}
AgeStepAsync で、ユーザー入力を検証できず、その理由が入力を検証できない原因は、その入力がプロンプトで解析できない形式であるか、検証基準を満たしていないかのいずれかである場合の、再試行プロンプトを指定します。 この場合、再試行プロンプトが指定されていないと、プロンプトは最初のプロンプト テキストを使用して、再びユーザーに入力を求めます。
private async Task<DialogTurnResult> AgeStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
if ((bool)stepContext.Result)
{
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
var promptOptions = new PromptOptions
{
Prompt = MessageFactory.Text("Please enter your age."),
RetryPrompt = MessageFactory.Text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."),
};
return await stepContext.PromptAsync(nameof(NumberPrompt<int>), promptOptions, cancellationToken);
}
else
{
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await stepContext.NextAsync(-1, cancellationToken);
}
}
UserProfile.cs
ユーザーの移動手段、名前、および年齢は UserProfile クラスのインスタンスに保存されています。
public class UserProfile
{
public string Transport { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int Age { get; set; }
public Attachment Picture { get; set; }
}
Dialogs\UserProfileDialog.cs
最後のステップで、前のウォーターフォール ステップで呼び出されたダイアログによって返された stepContext.Result を確認します。 戻り値が true の場合は、ユーザー プロファイル アクセサーを使用して、ユーザー プロファイルを取得し、更新します。 ユーザー プロファイルを取得するには、GetAsync を呼び出した後に、userProfile.Transport、userProfile.Name、userProfile.Age、userProfile.Picture の各プロパティの値を設定します。 最後に、ダイアログを終了する EndDialogAsync を呼び出す前に、ユーザーの情報をまとめます。 ダイアログを終了すると、そのダイアログはダイアログ スタックから取り出され、ダイアログの親に省略可能な結果が返されます。 この親は、終了したばかりのダイアログを開始したダイアログまたはメソッドです。
else
{
msg += $" Your profile will not be kept.";
}
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text(msg), cancellationToken);
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is the end.
return await stepContext.EndDialogAsync(cancellationToken: cancellationToken);
}
private async Task<DialogTurnResult> SummaryStepAsync(WaterfallStepContext stepContext, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
stepContext.Values["picture"] = ((IList<Attachment>)stepContext.Result)?.FirstOrDefault();
// Get the current profile object from user state.
var userProfile = await _userProfileAccessor.GetAsync(stepContext.Context, () => new UserProfile(), cancellationToken);
userProfile.Transport = (string)stepContext.Values["transport"];
userProfile.Name = (string)stepContext.Values["name"];
userProfile.Age = (int)stepContext.Values["age"];
userProfile.Picture = (Attachment)stepContext.Values["picture"];
var msg = $"I have your mode of transport as {userProfile.Transport} and your name as {userProfile.Name}";
if (userProfile.Age != -1)
{
msg += $" and your age as {userProfile.Age}";
}
msg += ".";
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text(msg), cancellationToken);
if (userProfile.Picture != null)
{
try
{
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Attachment(userProfile.Picture, "This is your profile picture."), cancellationToken);
}
catch
{
await stepContext.Context.SendActivityAsync(MessageFactory.Text("A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."), cancellationToken);
ダイアログを使用するには、ご自身のプロジェクトで botbuilder-dialogs npm パッケージをインストールする必要があります。
ボットは UserProfileDialog を介してユーザーと対話します。 ボットの DialogBot を作成するときに、UserProfileDialog がメイン ダイアログとして設定されます。 その後、ボットは run ヘルパー メソッドを使用して、ダイアログにアクセスします。
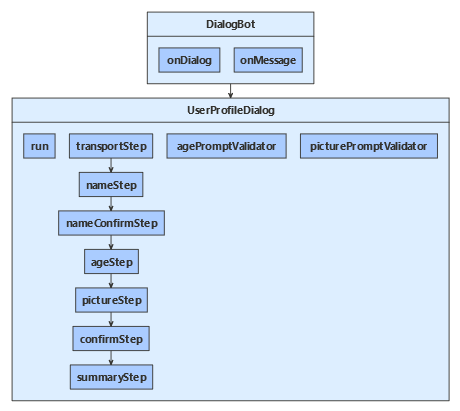
dialogs/userProfileDialog.js
最初に、ComponentDialog クラスから派生し、7 つのステップがある UserProfileDialog を作成します。
UserProfileDialog コンストラクターで、ウォーターフォール ステップ、プロンプト、およびウォーターフォール ダイアログを作成し、ダイアログ セットに追加します。 プロンプトは、それが使用されるダイアログ セットに追加する必要があります。
constructor(userState) {
super('userProfileDialog');
this.userProfile = userState.createProperty(USER_PROFILE);
this.addDialog(new TextPrompt(NAME_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new ChoicePrompt(CHOICE_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt(CONFIRM_PROMPT));
this.addDialog(new NumberPrompt(NUMBER_PROMPT, this.agePromptValidator));
this.addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt(ATTACHMENT_PROMPT, this.picturePromptValidator));
this.addDialog(new WaterfallDialog(WATERFALL_DIALOG, [
this.transportStep.bind(this),
this.nameStep.bind(this),
this.nameConfirmStep.bind(this),
this.ageStep.bind(this),
this.pictureStep.bind(this),
this.summaryStep.bind(this),
this.confirmStep.bind(this)
]));
this.initialDialogId = WATERFALL_DIALOG;
}
次に、ダイアログが入力を求めるために使用する手順を追加します。 プロンプトを使用するには、そのプロンプトをご自身のダイアログのステップから呼び出し、この場合は step.result を使用して、ステップ コンテキストの次のステップでプロンプトの結果を取得します。 バックグラウンドでは、プロンプトは 2 つのステップから成るダイアログです。 最初に、プロンプトで入力が求められます。 その後、有効な値を返すします。それ以外の場合は最初からやり直し、有効な入力を受信するまでユーザーに再入力を要求します。
ウォーターフォール ステップからは常に null 以外の DialogTurnResult を返す必要があります。 そうしないと、ダイアログは設計どおりに機能しません。 以下に、ウォーターフォール ダイアログの nameStep に対する実装を示します。
async nameStep(step) {
step.values.transport = step.result.value;
return await step.prompt(NAME_PROMPT, 'Please enter your name.');
}
ageStep で、ユーザー入力を検証できず、その理由が入力を検証できない原因は、その入力がプロンプトで解析できない形式であるか、上記のコンストラクターにおける検証基準を満たしていないかのいずれかである場合の、再試行プロンプトを指定します。 この場合、再試行プロンプトが指定されていないと、プロンプトは最初のプロンプト テキストを使用して、再びユーザーに入力を求めます。
async ageStep(step) {
if (step.result) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
const promptOptions = { prompt: 'Please enter your age.', retryPrompt: 'The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150.' };
return await step.prompt(NUMBER_PROMPT, promptOptions);
} else {
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await step.next(-1);
}
}
userProfile.js
ユーザーの移動手段、名前、および年齢は UserProfile クラスのインスタンスに保存されています。
class UserProfile {
constructor(transport, name, age, picture) {
this.transport = transport;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.picture = picture;
}
}
dialogs/userProfileDialog.js
最後のステップで、前のウォーターフォール ステップで呼び出されたダイアログによって返された step.result を確認します。 戻り値が true の場合は、ユーザー プロファイル アクセサーを使用して、ユーザー プロファイルを取得し、更新します。 ユーザー プロファイルを取得するには、get を呼び出した後に、userProfile.transport、userProfile.name、userProfile.age、userProfile.picture の各プロパティの値を設定します。 最後に、ダイアログを終了する endDialog を呼び出す前に、ユーザーの情報をまとめます。 ダイアログを終了すると、そのダイアログはダイアログ スタックから取り出され、ダイアログの親に省略可能な結果が返されます。 この親は、終了したばかりのダイアログを開始したダイアログまたはメソッドです。
await step.context.sendActivity(msg);
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
return await step.endDialog();
}
async summaryStep(step) {
step.values.picture = step.result && step.result[0];
// Get the current profile object from user state.
const userProfile = await this.userProfile.get(step.context, new UserProfile());
userProfile.transport = step.values.transport;
userProfile.name = step.values.name;
userProfile.age = step.values.age;
userProfile.picture = step.values.picture;
let msg = `I have your mode of transport as ${ userProfile.transport } and your name as ${ userProfile.name }`;
if (userProfile.age !== -1) {
msg += ` and your age as ${ userProfile.age }`;
}
msg += '.';
await step.context.sendActivity(msg);
if (userProfile.picture) {
try {
await step.context.sendActivity(MessageFactory.attachment(userProfile.picture, 'This is your profile picture.'));
} catch {
await step.context.sendActivity('A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here.');
}
拡張メソッドを作成してウォーターフォール ダイアログを実行する
userProfileDialog で定義される run ヘルパー メソッドメソッドは、ダイアログ コンテキストの作成およびアクセスに使用されます。 ここでは accessor はダイアログ状態プロパティの状態プロパティ アクセサーで、this はユーザー プロファイルのコンポーネント ダイアログです。 コンポーネント ダイアログによって内部ダイアログ セットが定義されているため、メッセージ ハンドラー コードに表示され、ダイアログ コンテキストの作成に使用するための外部ダイアログ セットを作成する必要があります。
ダイアログ コンテキストは、createContext メソッドを呼び出すことで作成され、ボットのターン ハンドラー内からダイアログ セットと対話するために使用されます。 ダイアログ コンテキストには、現在のターン コンテキスト、親ダイアログ、およびダイアログの状態が含まれています。ダイアログの状態が、ダイアログ内の情報を保持する方法を指定します。
ダイアログ コンテキストでは、文字列 ID を使用してダイアログを開始したり、現在のダイアログ (複数のステップが含まれるウォーターフォール ダイアログなど) を続行したりすることができます。 ダイアログ コンテキストは、ボットのすべてのダイアログおよびウォーターフォール ステップに渡されます。
async run(turnContext, accessor) {
const dialogSet = new DialogSet(accessor);
dialogSet.add(this);
const dialogContext = await dialogSet.createContext(turnContext);
const results = await dialogContext.continueDialog();
if (results.status === DialogTurnStatus.empty) {
await dialogContext.beginDialog(this.id);
}
}
ボットは UserProfileDialog を介してユーザーと対話します。 ボットの DialogBot クラスを作成するときに、UserProfileDialog がメイン ダイアログとして設定されます。 その後、ボットは Run ヘルパー メソッドを使用して、ダイアログにアクセスします。
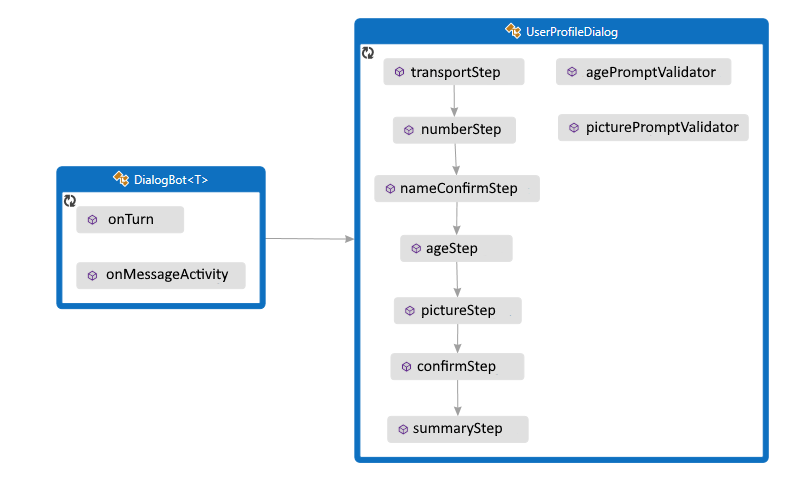
UserProfileDialog.java
最初に、ComponentDialog クラスから派生し、7 つのステップがある UserProfileDialog を作成します。
UserProfileDialog コンストラクターで、ウォーターフォール ステップ、プロンプト、およびウォーターフォール ダイアログを作成し、ダイアログ セットに追加します。 プロンプトは、それが使用されるダイアログ セットに追加する必要があります。
public UserProfileDialog(UserState withUserState) {
super("UserProfileDialog");
userProfileAccessor = withUserState.createProperty("UserProfile");
WaterfallStep[] waterfallSteps = {
UserProfileDialog::transportStep,
UserProfileDialog::nameStep,
this::nameConfirmStep,
this::ageStep,
UserProfileDialog::pictureStep,
this::confirmStep,
this::summaryStep
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
addDialog(new WaterfallDialog("WaterfallDialog", Arrays.asList(waterfallSteps)));
addDialog(new TextPrompt("TextPrompt"));
addDialog(new NumberPrompt<Integer>("NumberPrompt", UserProfileDialog::agePromptValidator, Integer.class));
addDialog(new ChoicePrompt("ChoicePrompt"));
addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt("ConfirmPrompt"));
addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt("AttachmentPrompt", UserProfileDialog::picturePromptValidator));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
setInitialDialogId("WaterfallDialog");
}
次に、ダイアログが入力を求めるために使用する手順を追加します。 プロンプトを使用するには、そのプロンプトをご自身のダイアログのステップから呼び出し、stepContext.getResult() を使用して、次のステップでプロンプトの結果を取得します。 バックグラウンドでは、プロンプトは 2 つのステップから成るダイアログです。 最初に、プロンプトで入力が求められます。 その後、有効な値を返すします。それ以外の場合は最初からやり直し、有効な入力を受信するまでユーザーに再入力を要求します。
ウォーターフォール ステップからは常に null 以外の DialogTurnResult を返す必要があります。 そうしないと、ダイアログは設計どおりに機能しません。 以下に、ウォーターフォール ダイアログの nameStep に対する実装を示します。
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("transport", ((FoundChoice) stepContext.getResult()).getValue());
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name."));
return stepContext.prompt("TextPrompt", promptOptions);
}
ageStep で、ユーザー入力を検証できず、その理由が入力を検証できない原因は、その入力がプロンプトで解析できない形式であるか、検証基準を満たしていないかのいずれかである場合の、再試行プロンプトを指定します。 この場合、再試行プロンプトが指定されていないと、プロンプトは最初のプロンプト テキストを使用して、再びユーザーに入力を求めます。
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> ageStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."));
return stepContext.prompt("NumberPrompt", promptOptions);
}
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return stepContext.next(-1);
}
UserProfile.java
ユーザーの移動手段、名前、および年齢は UserProfile クラスのインスタンスに保存されています。
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.microsoft.bot.sample.multiturnprompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.schema.Attachment;
/**
* This is our application state.
*/
public class UserProfile {
public String transport;
public String name;
public Integer age;
public Attachment picture;
}
UserProfileDialog.java
最後のステップで、前のウォーターフォール ステップで呼び出されたダイアログによって返された stepContext.Result を確認します。 戻り値が true の場合は、ユーザー プロファイル アクセサーを使用して、ユーザー プロファイルを取得し、更新します。 ユーザー プロファイルを取得するには、get を呼び出した後に、userProfile.Transport、userProfile.Name、userProfile.Age、userProfile.Picture の各プロパティの値を設定します。 最後に、ダイアログを終了する endDialog を呼び出す前に、ユーザーの情報をまとめます。 ダイアログを終了すると、そのダイアログはダイアログ スタックから取り出され、ダイアログの親に省略可能な結果が返されます。 この親は、終了したばかりのダイアログを開始したダイアログまたはメソッドです。
// Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation. All rights reserved.
// Licensed under the MIT License.
package com.microsoft.bot.sample.multiturnprompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.MessageFactory;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.StatePropertyAccessor;
import com.microsoft.bot.builder.UserState;
import com.microsoft.bot.connector.Channels;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.ComponentDialog;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.DialogTurnResult;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallDialog;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallStep;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.WaterfallStepContext;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.choices.ChoiceFactory;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.choices.FoundChoice;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.AttachmentPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.ChoicePrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.ConfirmPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.NumberPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.PromptOptions;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.PromptValidatorContext;
import com.microsoft.bot.dialogs.prompts.TextPrompt;
import com.microsoft.bot.schema.Attachment;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
public class UserProfileDialog extends ComponentDialog {
private final StatePropertyAccessor<UserProfile> userProfileAccessor;
public UserProfileDialog(UserState withUserState) {
super("UserProfileDialog");
userProfileAccessor = withUserState.createProperty("UserProfile");
WaterfallStep[] waterfallSteps = {
UserProfileDialog::transportStep,
UserProfileDialog::nameStep,
this::nameConfirmStep,
this::ageStep,
UserProfileDialog::pictureStep,
this::confirmStep,
this::summaryStep
};
// Add named dialogs to the DialogSet. These names are saved in the dialog state.
addDialog(new WaterfallDialog("WaterfallDialog", Arrays.asList(waterfallSteps)));
addDialog(new TextPrompt("TextPrompt"));
addDialog(new NumberPrompt<Integer>("NumberPrompt", UserProfileDialog::agePromptValidator, Integer.class));
addDialog(new ChoicePrompt("ChoicePrompt"));
addDialog(new ConfirmPrompt("ConfirmPrompt"));
addDialog(new AttachmentPrompt("AttachmentPrompt", UserProfileDialog::picturePromptValidator));
// The initial child Dialog to run.
setInitialDialogId("WaterfallDialog");
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> transportStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
// Running a prompt here means the next WaterfallStep will be run when the user's response is received.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your mode of transport."));
promptOptions.setChoices(ChoiceFactory.toChoices("Car", "Bus", "Bicycle"));
return stepContext.prompt("ChoicePrompt", promptOptions);
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("transport", ((FoundChoice) stepContext.getResult()).getValue());
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name."));
return stepContext.prompt("TextPrompt", promptOptions);
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> nameConfirmStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("name", stepContext.getResult());
// We can send messages to the user at any point in the WaterfallStep.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(String.format("Thanks %s.", stepContext.getResult())))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> {
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Would you like to give your age?"));
return stepContext.prompt("ConfirmPrompt", promptOptions);
});
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> ageStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."));
return stepContext.prompt("NumberPrompt", promptOptions);
}
// User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return stepContext.next(-1);
}
private static CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> pictureStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
stepContext.getValues().put("age", (Integer) stepContext.getResult());
String msg = (Integer)stepContext.getValues().get("age") == -1
? "No age given."
: String.format("I have your age as %d.", (Integer)stepContext.getValues().get("age"));
// We can send messages to the user at any point in the WaterfallStep.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> {
if (StringUtils.equals(stepContext.getContext().getActivity().getChannelId(), Channels.MSTEAMS)) {
// This attachment prompt example is not designed to work for Teams attachments, so skip it in this case
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text("Skipping attachment prompt in Teams channel..."))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse1 -> stepContext.next(null));
}
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Please attach a profile picture (or type any message to skip)."));
promptOptions.setRetryPrompt(MessageFactory.text("The attachment must be a jpeg/png image file."));
return stepContext.prompt("AttachmentPrompt", promptOptions);
});
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> confirmStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
List<Attachment> attachments = (List<Attachment>)stepContext.getResult();
stepContext.getValues().put("picture", attachments == null ? null : attachments.get(0));
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is a Prompt Dialog.
PromptOptions promptOptions = new PromptOptions();
promptOptions.setPrompt(MessageFactory.text("Is this ok?"));
return stepContext.prompt("ConfirmPrompt", promptOptions);
}
private CompletableFuture<DialogTurnResult> summaryStep(WaterfallStepContext stepContext) {
if ((Boolean)stepContext.getResult()) {
// Get the current profile object from user state.
return userProfileAccessor.get(stepContext.getContext(), () -> new UserProfile())
.thenCompose(userProfile -> {
userProfile.transport = (String) stepContext.getValues().get("transport");
userProfile.name = (String) stepContext.getValues().get("name");
userProfile.age = (Integer) stepContext.getValues().get("age");
userProfile.picture = (Attachment) stepContext.getValues().get("picture");
String msg = String.format(
"I have your mode of transport as %s and your name as %s",
userProfile.transport, userProfile.name
);
if (userProfile.age != -1) {
msg += String.format(" and your age as %s", userProfile.age);
}
msg += ".";
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
.thenApply(resourceResponse -> userProfile);
})
.thenCompose(userProfile -> {
if (userProfile.picture != null) {
try {
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.attachment(userProfile.picture,
"This is your profile picture."
));
} catch(Exception ex) {
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.text(
"A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."
));
}
}
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(
MessageFactory.text("A profile picture wasn't attached.")
);
})
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> stepContext.endDialog());
}
// WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog; here it is the end.
return stepContext.getContext().sendActivity(MessageFactory.text("Thanks. Your profile will not be kept."))
.thenCompose(resourceResponse -> stepContext.endDialog());
}
private static CompletableFuture<Boolean> agePromptValidator(
PromptValidatorContext<Integer> promptContext
) {
// This condition is our validation rule. You can also change the value at this point.
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(
promptContext.getRecognized().getSucceeded()
&& promptContext.getRecognized().getValue() > 0
&& promptContext.getRecognized().getValue() < 150);
}
private static CompletableFuture<Boolean> picturePromptValidator(
PromptValidatorContext<List<Attachment>> promptContext
) {
if (promptContext.getRecognized().getSucceeded()) {
List<Attachment> attachments = promptContext.getRecognized().getValue();
List<Attachment> validImages = new ArrayList<>();
for (Attachment attachment : attachments) {
if (StringUtils.equals(
attachment.getContentType(), "image/jpeg") || StringUtils.equals(attachment.getContentType(), "image/png")
) {
validImages.add(attachment);
}
}
promptContext.getRecognized().setValue(validImages);
// If none of the attachments are valid images, the retry prompt should be sent.
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(!validImages.isEmpty());
}
else {
// We can return true from a validator function even if Recognized.Succeeded is false.
return promptContext.getContext().sendActivity("No attachments received. Proceeding without a profile picture...")
.thenApply(resourceResponse -> true);
}
}
}
ダイアログを使用するには、ターミナルから pip install botbuilder-dialogs と pip install botbuilder-ai を実行して botbuilder-dialogs および botbuilder-ai PyPI パッケージをインストールします。
ボットは UserProfileDialog を介してユーザーと対話します。 ボットの DialogBot クラスが作成されるときに、UserProfileDialog がメイン ダイアログとして設定されます。 その後、ボットは run_dialog ヘルパー メソッドを使用して、ダイアログにアクセスします。
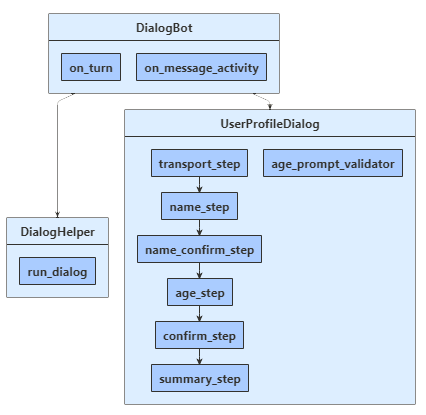
dialogs\user_profile_dialog.py
最初に、ComponentDialog クラスから派生し、7 つのステップがある UserProfileDialog を作成します。
UserProfileDialog コンストラクターで、ウォーターフォール ステップ、プロンプト、およびウォーターフォール ダイアログを作成し、ダイアログ セットに追加します。 プロンプトは、それが使用されるダイアログ セットに追加する必要があります。
def __init__(self, user_state: UserState):
super(UserProfileDialog, self).__init__(UserProfileDialog.__name__)
self.user_profile_accessor = user_state.create_property("UserProfile")
self.add_dialog(
WaterfallDialog(
WaterfallDialog.__name__,
[
self.transport_step,
self.name_step,
self.name_confirm_step,
self.age_step,
self.picture_step,
self.summary_step,
self.confirm_step,
],
)
)
self.add_dialog(TextPrompt(TextPrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(
NumberPrompt(NumberPrompt.__name__, UserProfileDialog.age_prompt_validator)
)
self.add_dialog(ChoicePrompt(ChoicePrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(ConfirmPrompt(ConfirmPrompt.__name__))
self.add_dialog(
AttachmentPrompt(
AttachmentPrompt.__name__, UserProfileDialog.picture_prompt_validator
)
)
self.initial_dialog_id = WaterfallDialog.__name__
次に、ダイアログが入力を求めるために使用する手順を追加します。 プロンプトを使用するには、そのプロンプトをご自身のダイアログのステップから呼び出し、step_context.result を使用して、次のステップでプロンプトの結果を取得します。 バックグラウンドでは、プロンプトは 2 つのステップから成るダイアログです。 最初に、プロンプトで入力が求められます。 その後、有効な値を返すします。それ以外の場合は最初からやり直し、有効な入力を受信するまでユーザーに再入力を要求します。
ウォーターフォール ステップからは常に null 以外の DialogTurnResult を返す必要があります。 そうしないと、ダイアログは設計どおりに機能しません。 ここでは、ウォーターフォール ダイアログの name_step に対する実装を示します。
async def name_step(self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext) -> DialogTurnResult:
step_context.values["transport"] = step_context.result.value
return await step_context.prompt(
TextPrompt.__name__,
PromptOptions(prompt=MessageFactory.text("Please enter your name.")),
)
age_step で、ユーザー入力を検証できず、その理由が入力を検証できない原因は、その入力がプロンプトで解析できない形式であるか、上記のコンストラクターにおける検証基準を満たしていないかのいずれかである場合の、再試行プロンプトを指定します。 この場合、再試行プロンプトが指定されていないと、プロンプトは最初のプロンプト テキストを使用して、再びユーザーに入力を求めます。
async def age_step(self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext) -> DialogTurnResult:
if step_context.result:
# User said "yes" so we will be prompting for the age.
# WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another dialog,
# here it is a Prompt Dialog.
return await step_context.prompt(
NumberPrompt.__name__,
PromptOptions(
prompt=MessageFactory.text("Please enter your age."),
retry_prompt=MessageFactory.text(
"The value entered must be greater than 0 and less than 150."
),
),
)
# User said "no" so we will skip the next step. Give -1 as the age.
return await step_context.next(-1)
data_models\user_profile.py
ユーザーの移動手段、名前、および年齢は UserProfile クラスのインスタンスに保存されています。
class UserProfile:
"""
This is our application state. Just a regular serializable Python class.
"""
def __init__(self, name: str = None, transport: str = None, age: int = 0, picture: Attachment = None):
self.name = name
self.transport = transport
self.age = age
self.picture = picture
dialogs\user_profile_dialog.py
最後のステップで、前のウォーターフォール ステップで呼び出されたダイアログによって返された step_context.result を確認します。 戻り値が true の場合は、ユーザー プロファイル アクセサーを使用して、ユーザー プロファイルを取得し、更新します。 ユーザー プロファイルを取得するには、get を呼び出した後に、user_profile.transport、user_profile.name、user_profile.age の各プロパティの値を設定します。 最後に、ダイアログを終了する end_dialog を呼び出す前に、ユーザーの情報をまとめます。 ダイアログを終了すると、そのダイアログはダイアログ スタックから取り出され、ダイアログの親に省略可能な結果が返されます。 この親は、終了したばかりのダイアログを開始したダイアログまたはメソッドです。
async def summary_step(
self, step_context: WaterfallStepContext
) -> DialogTurnResult:
step_context.values["picture"] = (
None if not step_context.result else step_context.result[0]
)
# Get the current profile object from user state. Changes to it
# will saved during Bot.on_turn.
user_profile = await self.user_profile_accessor.get(
step_context.context, UserProfile
)
user_profile.transport = step_context.values["transport"]
user_profile.name = step_context.values["name"]
user_profile.age = step_context.values["age"]
user_profile.picture = step_context.values["picture"]
msg = f"I have your mode of transport as {user_profile.transport} and your name as {user_profile.name}."
if user_profile.age != -1:
msg += f" And age as {user_profile.age}."
await step_context.context.send_activity(MessageFactory.text(msg))
if user_profile.picture:
await step_context.context.send_activity(
MessageFactory.attachment(
user_profile.picture, "This is your profile picture."
)
)
else:
await step_context.context.send_activity(
"A profile picture was saved but could not be displayed here."
)
# WaterfallStep always finishes with the end of the Waterfall or with another
# dialog, here it is the end.
return await step_context.prompt(
ConfirmPrompt.__name__,
拡張メソッドを作成してウォーターフォール ダイアログを実行する
ダイアログ コンテキストの作成とアクセスに使用する run_dialog() ヘルパー メソッドが helpers\dialog_helper.py 内に定義されています。 ここでは accessor はダイアログ状態プロパティの状態プロパティ アクセサーで、dialog はユーザー プロファイルのコンポーネント ダイアログです。 コンポーネント ダイアログによって内部ダイアログ セットが定義されているため、メッセージ ハンドラー コードに表示される外部ダイアログ セットを作成し、それを使用してダイアログ コンテキストを作成する必要があります。
create_context を呼び出すことで、ボットのターン ハンドラー内からダイアログ セットと対話するために使用されるダイアログ コンテキストを作成します。 ダイアログ コンテキストには、現在のターン コンテキスト、親ダイアログ、およびダイアログの状態が含まれています。ダイアログの状態が、ダイアログ内の情報を保持する方法を指定します。
ダイアログ コンテキストを使用すると、文字列 ID を使用してダイアログを開始したり、現在のダイアログ (複数のステップが含まれるウォーターフォール ダイアログなど) を続行したりすることができます。 ダイアログ コンテキストは、ボットのすべてのダイアログおよびウォーターフォール ステップに渡されます。
class DialogHelper:
@staticmethod
async def run_dialog(
dialog: Dialog, turn_context: TurnContext, accessor: StatePropertyAccessor
):
dialog_set = DialogSet(accessor)
dialog_set.add(dialog)
dialog_context = await dialog_set.create_context(turn_context)
results = await dialog_context.continue_dialog()
if results.status == DialogTurnStatus.Empty:
await dialog_context.begin_dialog(dialog.id)
このサンプルでは、ダイアログ内からユーザー プロファイルの状態が更新されます。 この方法は一部のボットには有効ですが、複数ボットにわたりダイアログを再利用する場合は機能しません。
ダイアログ ステップとボットの状態を別々に維持するオプションには、さまざまな種類があります。 たとえば、お使いのダイアログで完全な情報を収集すると、以下を行うことができます。