How to Add Translated Strings By Importing and Exporting Multilanguage Files in Dynamics NAV
To add string translations for UI elements in a standard country/region-specific version of Microsoft Dynamics NAV 2018, you install a language module so that end users can view the UI elements in a different language. If you have customized objects in the application, then you must also add translations for those objects. You can translate strings in the following ways:
By importing and exporting text files that contain translated strings for multiple objects in the Microsoft Dynamics NAV Development Environment.
By using the Multilanguage Editor and editing the CaptionML property of individual objects.
By running Windows PowerShell cmdlets to update CaptionML properties.
This topic describes how to import and export multilanguage files. For more information about how to use the Multilanguage Editor, see How to: Add Translated Strings By Using the Multilanguage Editor. For more information about how to run Windows PowerShell cmdlets to export and import languages, see Working with Application Objects as Text Files.
Exporting Multilanguage Files
To translate strings for multiple objects, you must first export all text strings.
To export a multilanguage file
In the development environment, in Object Designer, select the objects that you want to export strings for.
On the Tools menu, point to Translate, and then choose Export.
In the Translate Export window, select the location where you want to export the file.
In the File name field, enter an appropriate name for the file.
In the Save as Type field, select the format type, and then choose the Save button.
Translating Multilanguage Files
You can add translated strings directly to the exported file, or you can use a translation tool. If you add translated strings directly to the exported file, then use the following procedure.
To translate strings in a multilanguage file
Open the multilanguage file for editing. For example, open the file with a text editor or in Microsoft Office Excel.
For each string that you want to translate, create a new line in the file.
Copy and paste the source ID of the item to be translated into the new line.
Modify the four-character language code to the language to which you are translating.
Add the translated string to the new line.
The following illustration uses #### to represent the language code of the language to which you translate the string.
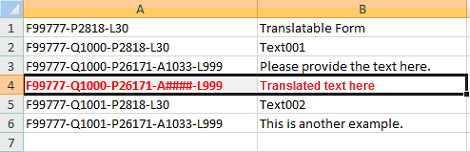
Importing Multilanguage Files
After you add translated strings to the multilanguage file in .txt format, there are three ways to ensure that translations are used.
- Import the multilanguage file using Object Designer. This is described in the To import a multilanguage file section below.
- Place the translated files on the server, or on each service instance in a
/Translationsfolder. For more information, see this guidance. - If you have added extensions to your solution, you must take the .txt file, and place the file in the extension root folder. When the extension is compiled, the .txt file is packaged with the extension. We recommend that you use only one .txt file per language. There is no enforced naming on the file, but a suggested good practice is to name it
<extensionname>.<language>.txt.
For more information about translations using .xlf files only, see Working With Translation Files.
To import a multilanguage file
In the development environment, in Object Designer, select the objects that you want to import strings for.
If you do not know which objects are included in the multilanguage file, select all objects.
On the Tools menu, point to Translate, and then choose Import.
In the TranslateImport window, navigate to the file that you want to import.
Select the file, and then choose Open.
See Also
Multilanguage Development
Working with Application Objects as Text Files